Abstract
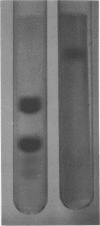
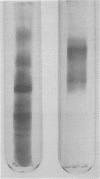
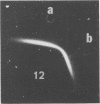
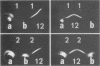
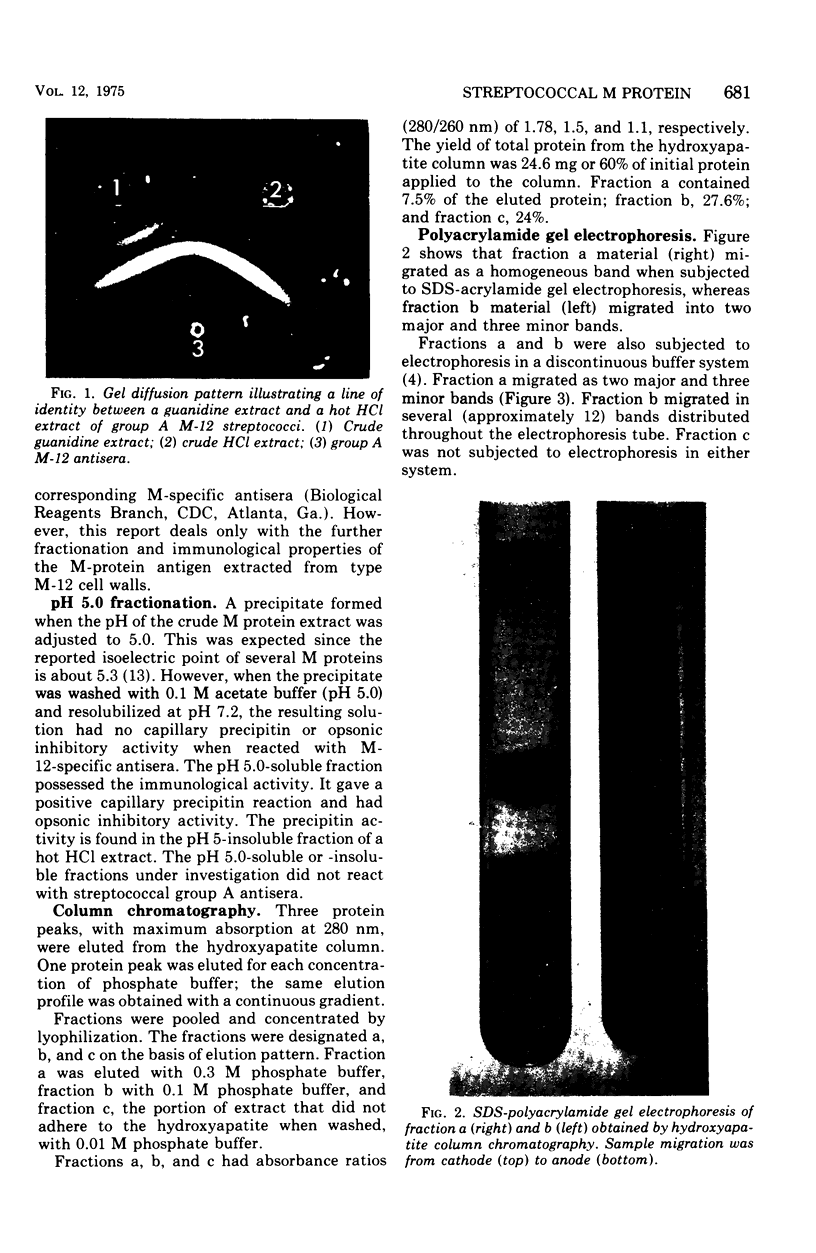
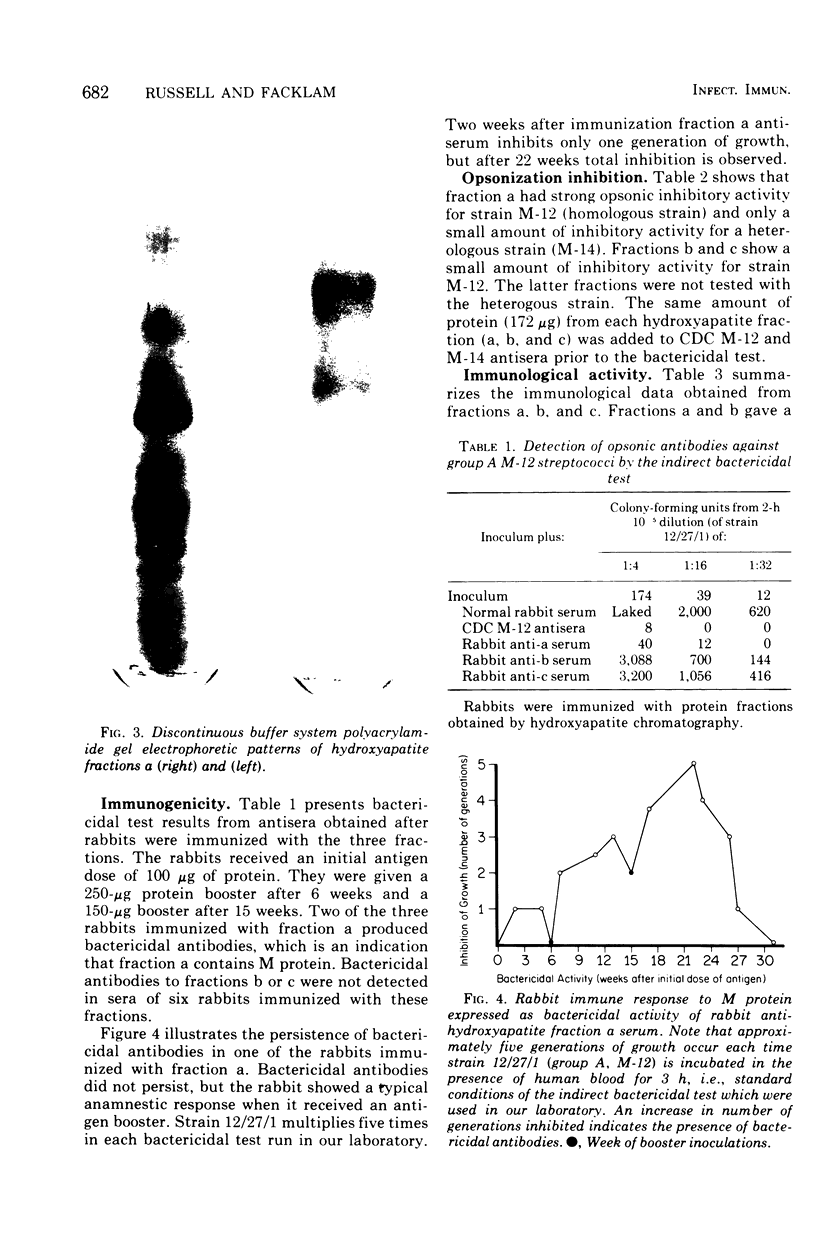
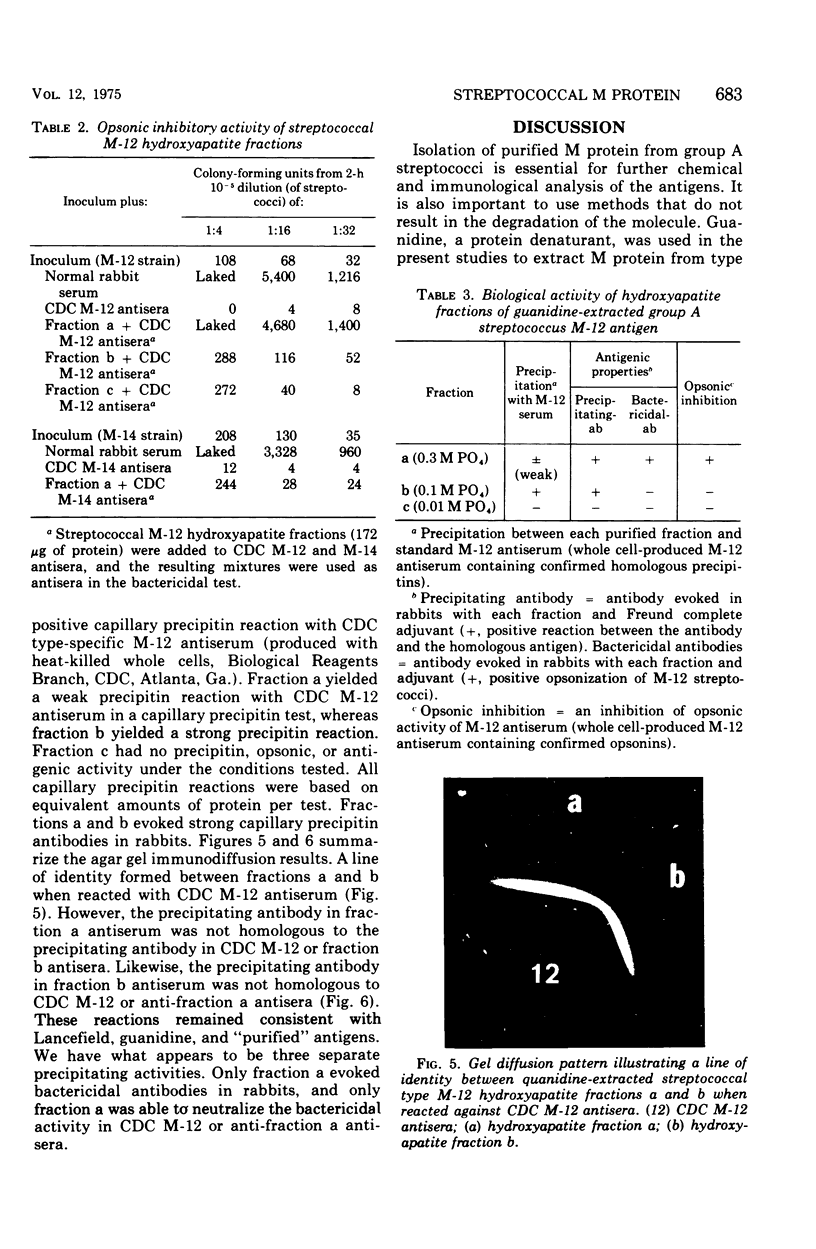
A new method of extracting M protein from streptococcal cell walls has been presented. The extracting agent was guanidine-hydrochloride, a protein denaturant. The crude guanidine extract was further purified by ammonium sulfate and pH 5 fractionation and by hydroxyapatite column chromatography. Three major protein peaks were eluted from the hydroxyapatite column with 0.01, 0.1 and 0.3 M phosphate buffer, respectively. Protein fractions eluted at 0.1 and 0.3 M phosphate concentractions contained antigens that precipitated with homologous M-protein specific antisera, whereas the 0.01 M phosphate fraction had no immunological activity. The fraction eluted with 0.3 M phosphate was electrophoretically homogeneous in sodium dodecyl sulfate-acrylamide gels and elicited the production of bactericidal antibodies in rabbits. The 0.1 M phosphate buffer eluant was electrophoretically heterogeneous and did not elicit the production of bactericidal antibodies in rabbits.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECKER C. G. SELECTION OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI RICH IN M-PROTEIN FROM POPULATIONS POOR IN M-PROTEIN. Am J Pathol. 1964 Jan;44:51–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLEIWEIS A. S., KARAKAWA W. W., KRAUSE R. M. IMPROVED TECHNIQUE FOR THE PREPARATION OF STREPTOCOCCAL CELL WALLS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1198–1200. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1198-1200.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Cunningham M. Type-specific inhibition of preopsonization versus immunoprecipitation by Streptococcal M proteins. Infect Immun. 1973 Jul;8(1):19–24. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.1.19-24.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX E. N. ANTIGENICITY OF THE M PROTEINS OF GROUP A HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCI. J Immunol. 1964 Nov;93:826–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N. M proteins of group A streptococci. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):57–86. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.57-86.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Wittner M. K. Antigenicity of the M proteins of group A hemolytic streptococci. IV. Cross-reactivity between serotypes. J Immunol. 1968 Jan;100(1):39–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg I. Mechanisms of cell and tissue injury induced by group A streptococci: relation to poststreptococcal sequelae. J Infect Dis. 1972 Oct;126(4):419–456. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. H., Vosti K. L. Purification of two fragments of M protein from a strain of group A, type 12 streptococcus. J Immunol. 1968 Sep;101(3):381–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Current knowledge of type-specific M antigens of group A streptococci. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Differentiation of group A streptococci with a common R antigen into three serological types, with special reference to the bactericidal test. J Exp Med. 1957 Oct 1;106(4):525–544. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.4.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C., PERLMANN G. E. Preparation and properties of type-specific M antigen isolated from a group A, type 1 hemolytic streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1952 Jul;96(1):71–82. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Bergner-Rabinowitz S., Davies A. M. Opsonic capacity of type specific streptococcal antibodies. Isr J Med Sci. 1969 May-Jun;5(3):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosti K. L., Johnson R. H., Dillon M. F. Further characterization of purified fractions of M protein from a strain of group A, type 12 Streptococcus. J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):104–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADSWORTH C. A slide microtechnique for the analysis of immune precipitates in gel. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1957;10(6):355–360. doi: 10.1159/000228394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE F. H., Jr Regeneration of native secondary and tertiary structures by air oxidation of reduced ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1353–1360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]