Abstract
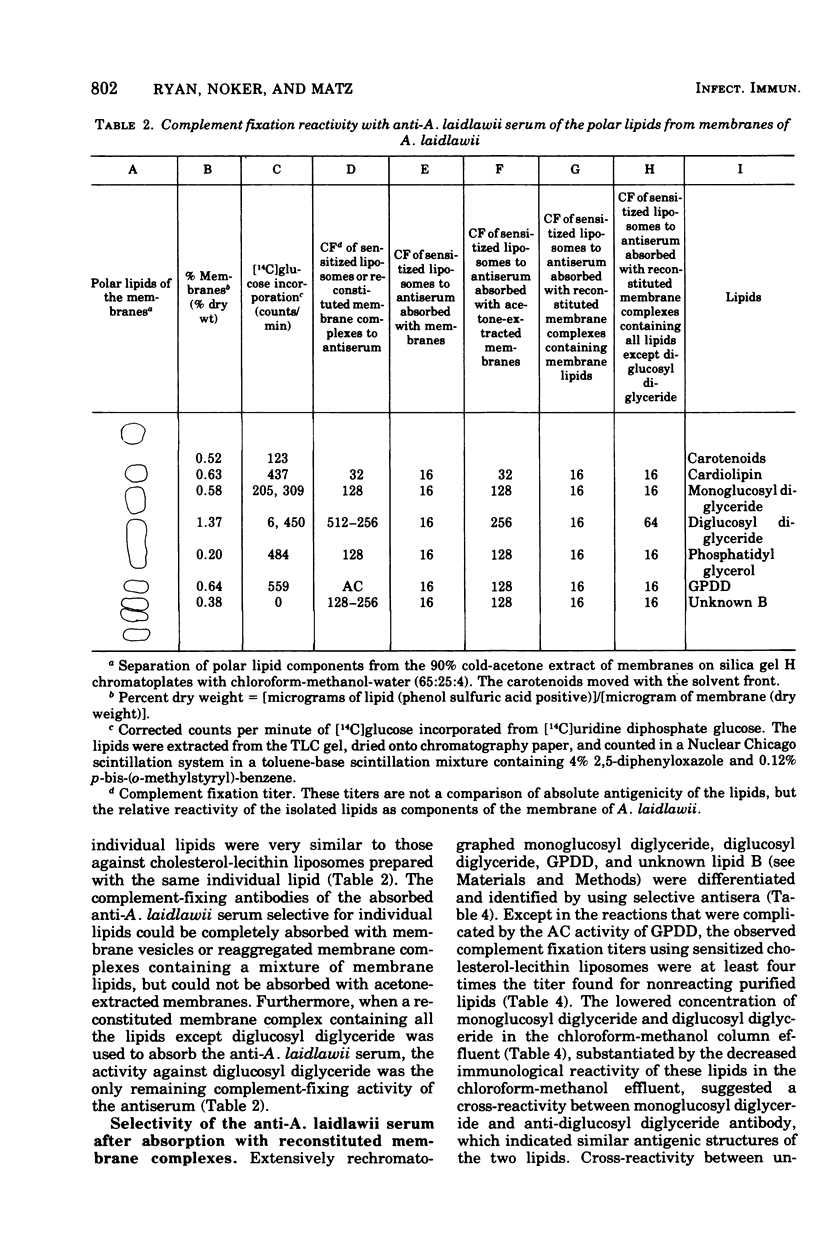
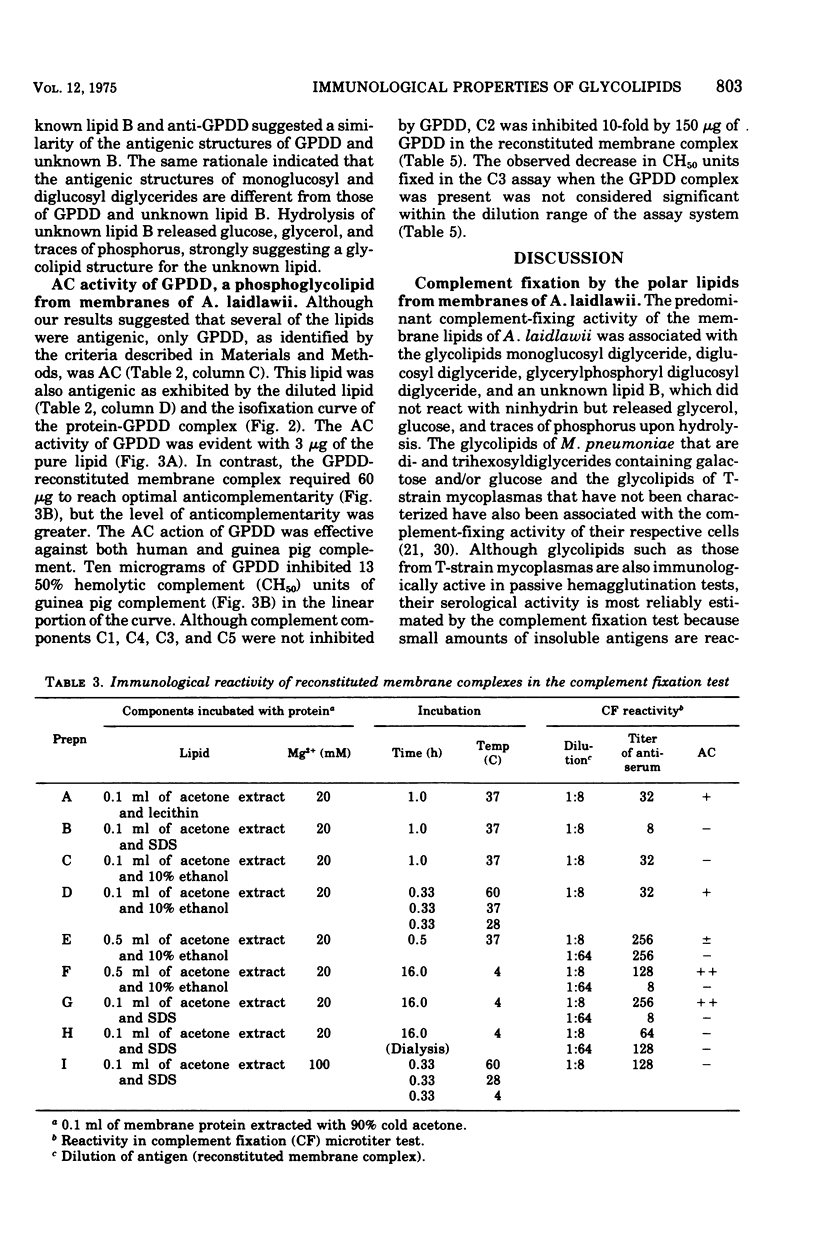
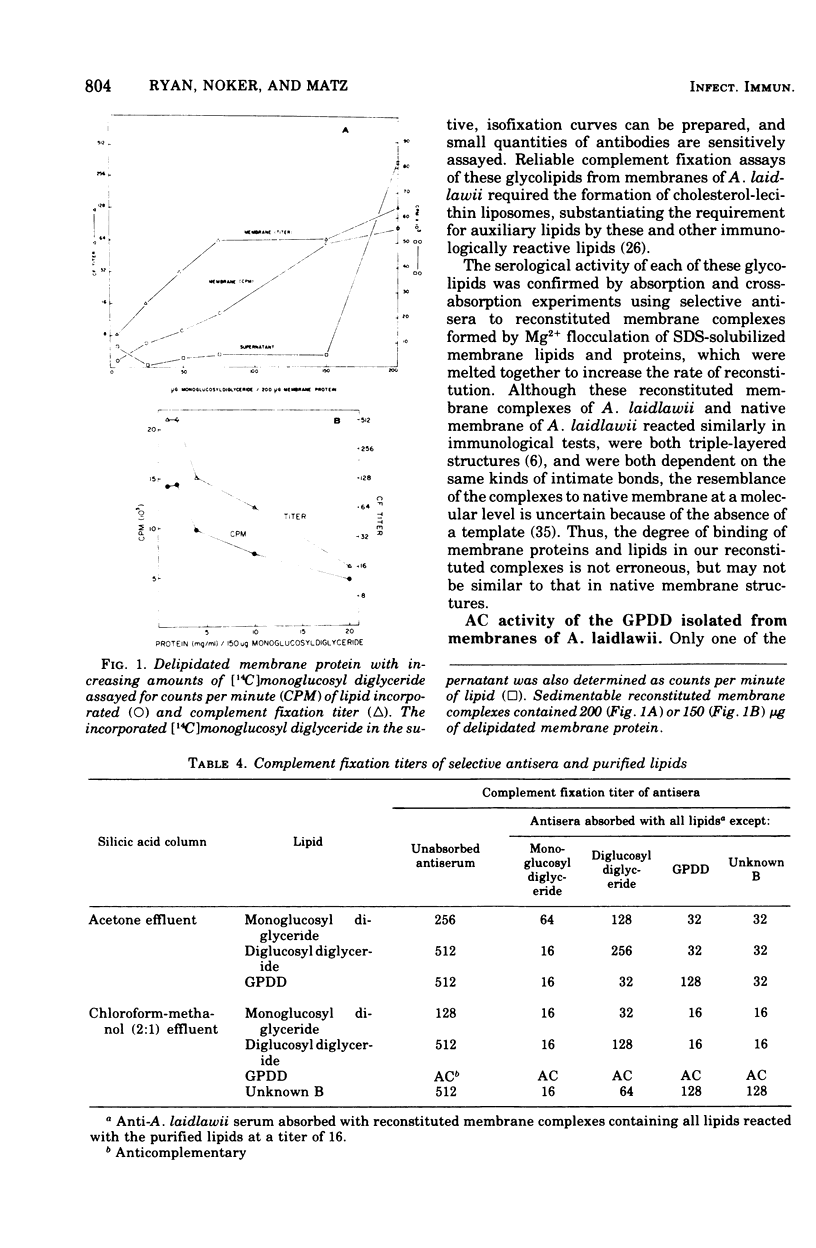
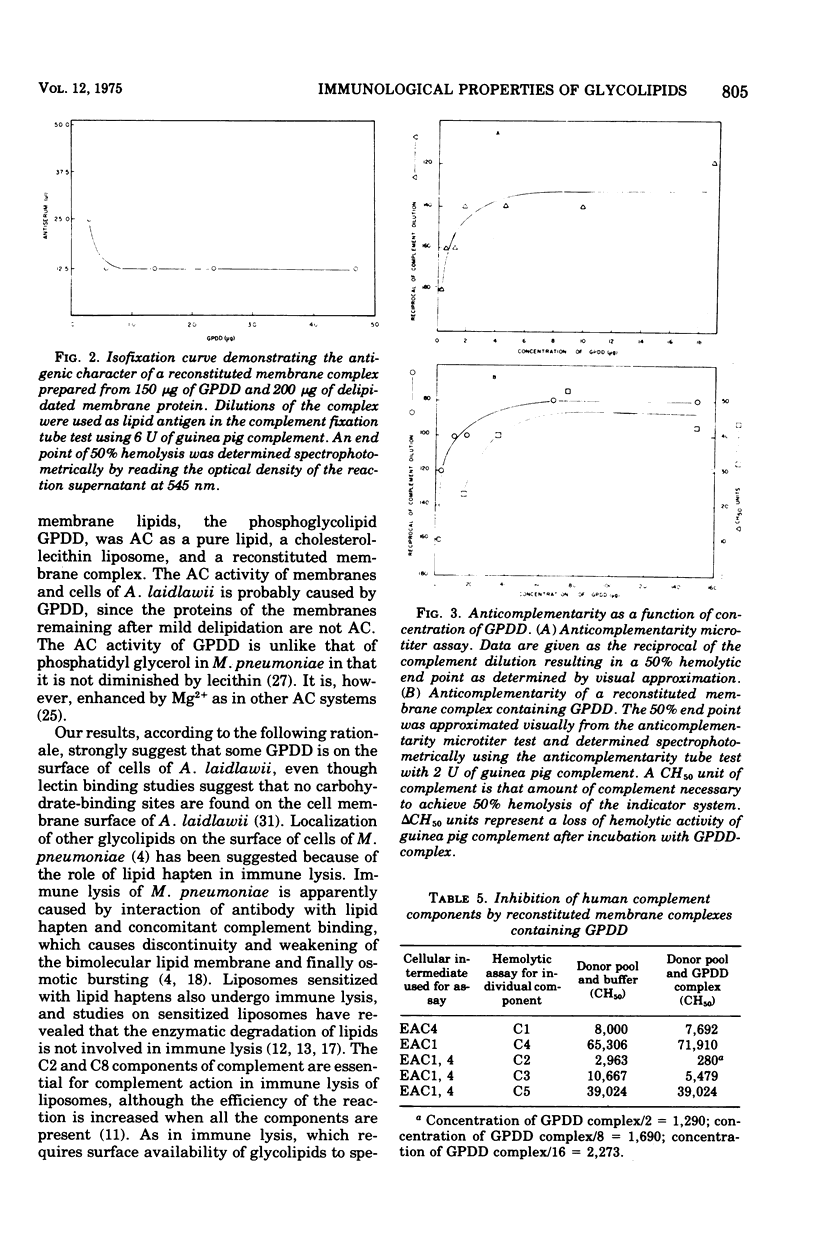
Glycolipids, the predominant class of lipids in the membranes of Acholeplasma laidlawii, are the haptenic determinants that react with anti-A. Laidlawii serum to fix complement. The predominant complement-fixing activity of the membrane glycolipids was associated with the monoglucoysyl diglyceride, diglucosyl diglyceride, glycerlphosphoryl diglucosyl diglyceride (GPDD), and an unknown lipid B, which did not react with ninhydrin but release glucose and glycerol and traces of phosphorus upon hydrolysis. The glycolipids monoglucosyl diglyceride and diglucosyl diglyceride or GPDD and unknown lipid B were paired as a result of their cross-reactions with selective antisera prepared with the aid of reconstituted membrane complexes containing membrane lipids. Reconstituted membrane complexes assembled from [14C]monoglucosyl diglyceride and delipidated membrane proteins gave optimal complement fixation titers before saturation of the complexes with the ]14C]monoglucosyl diglyceride. The phosphoglycolipid of the membrane, GPDD, was anticomplementary as a pure lipid, a cholesterol liposome, and a reconstituted membrane complex. This anticomplementary activity, which was caused by 3 mug of pure GPDD, affected both human and guinea pig complement. Although human C1, C4, C3, and C5 were not inhibited by GPDD, C2 was inhibited 10-fold by reconstituted membrane complexes containing 150 mug of GPDD. A role for this phosphoglycolipid is discussed in the hypothetical mechanism of inhibition of C2 attachment to SAC1, 4 sites.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMENTA J. S. A RAPID CHEMICAL METHOD FOR QUANTIFICATION OF LIPIDS SEPARATED BY THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY. J Lipid Res. 1964 Apr;5:270–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambron R. T., Pieringer R. A. The metabolism of glyceride glycolipids. V. Identification of the membrane lipid formed from diglucosyl diglyceride in Streptococcus faecalis ATCC 9790 as an acylated derivative of glyceryl phosphoryl diglucosyl glycerol. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4216–4225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman B. L., Kenny G. E. Immunochemical analysis of serologically active lipids of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1171–1180. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1171-1180.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H., Razin S., Kalica A. R., Chanock R. M. Lysis and death of Mycoplasma pneumoniae by antibody and complement. J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):907–916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYDE W. A., Jr MYCOPLASMA SPECIES IDENTIFICATION BASED UPON GROWTH INHIBITION BY SPECIFIC ANTISERA. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:958–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. M., Popkin T. J., Prescott B., Chanock R. M., Razin S. Electron microscopy of solubilized Acholeplasma laidlawii membrane proteins reaggregated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae glycolipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 9;233(1):76–83. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSiervo A. J. Anti-cardiolipin and anti-phosphatidylglycerol antibodies prepared against bacterial phospholipids. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):835–838. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.835-838.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W. A new phosphoglycolipid from Streptococcus lactis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Nov 9;41(3):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haxby J. A., Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Kinsky S. C. Release of trapped marker from liposomes by the action of purified complement components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):290–295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Kataoka T., Kinsky S. C. Comparative responses of liposomes prepared with different ceramide antigens to antibody and complement. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2574–2581. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Kinsky S. C. Fate of phospholipids in liposomal model membranes damaged by antibody and complement. Biochemistry. 1970 Nov 24;9(24):4767–4776. doi: 10.1021/bi00826a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka I., Yamakawa T. Further characterization of the two glycosyl glycerides from Streptococcus hemolyticus strain D-58. Jpn J Exp Med. 1969 Jun;39(3):321–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENT J. F., FIFE E. H., Jr Precise standardization of reagents for complement fixation. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1963 Jan;12:103–116. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1963.12.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiszkiss D. F., Downey R. J. Physical aggregation and functional reconstitution of solubilized membranes of Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):811–819. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.811-819.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Munn E. A., Weissmanng Complement-mediated lysis of liposomes produced by the reactive lysis procedure. Immunology. 1970 Dec;19(6):983–986. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. M. Highlights of complement research during the past twenty-five years. Immunochemistry. 1970 May;7(5):485–496. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90231-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. A., Jr, Jensen J., Gigli I., Tamura N. Methods for the separation, purification and measurement of nine components of hemolytic complement in guinea-pig serum. Immunochemistry. 1966 Mar;3(2):111–135. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(66)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plackett P., Marmion B. P., Shaw E. J., Lemcke R. M. Immunochemical analysis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. 3. Separation and chemical identification of serologically active lipids. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1969 Apr;47(2):171–195. doi: 10.1038/icb.1969.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plackett P., Shaw E. J. Glucolipids from Mycoplasma laidlawii and Streptococcus MG. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):61C–62C. doi: 10.1042/bj1040061c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. D., Razin S., Cleverdon R. C. Localization of Enzymes in Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1965 Sep;90(3):617–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.3.617-622.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polley M. J., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Enharncement of the hemolytic activity of the second component of human complement by oxidation. J Exp Med. 1967 Dec 1;126(6):1013–1025. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.6.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPPORT M. M., GRAF L. Immunochemical analysis based on complement fixation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Dec 16;69(4):608–632. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb49700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S. OSMOTIC LYSIS OF MYCOPLASMA. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:471–475. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapport M. M., Graf L. Immunochemical reactions of lipids. Prog Allergy. 1969;13:273–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Prescott B., Caldes G., James W. D., Chanock R. M. Role of Glycolipids and Phosphatidylglycerol in the Serological Activity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1970 Apr;1(4):408–416. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.4.408-416.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Prescott B., Chanock R. M. Immunogenicity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae glycolipids: a novel approach to the production of antisera to membrane lipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):590–597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano N., Scarlata G. Serological activity of lipids of a T strain of Mycoplasma. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1062–1065. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1062-1065.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiefer H. G., Gerhardt U., Brunner H., Krüpe M. Studies with lectins on the surface carbohydrate structures of mycoplasma membranes. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):81–88. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.81-88.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw N. Bacterial glycolipids. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Dec;34(4):365–377. doi: 10.1128/br.34.4.365-377.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw N., Smith P. F., Koostra W. L. The lipid composition of Mycoplasma laidlawii strain B. Biochem J. 1968 Apr;107(3):329–333. doi: 10.1042/bj1070329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw N., Smith P. F., Verheij H. M. The structure of a glycerylphosphoryldiglucosyl diglyceride from the lipids of Acholeplasma laidlawii strain B. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;129(1):167–173. doi: 10.1042/bj1290167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw N. The detection of lipids on thin-layer chromatograms with the periodate-Schiff reagents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 22;164(2):435–436. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90171-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F. Biosynthesis of glucosyl diglycerides by Mycoplasma laidlawii strain B. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):480–486. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.480-486.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Smith P. F., Langworthy T. A., Mayberry W. R. Immunological analysis of glycolipids and lipopolysaccharides derived from various mycoplasmas. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1273–1279. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1273-1279.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toon P., Brown P. E., Baddiley J. The lipid-teichoic acid complex in the cytoplasmic membrane of Streptococcus faecalis N.C.I.B. 8191. Biochem J. 1972 Apr;127(2):399–409. doi: 10.1042/bj1270399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Studies on the group F antigen of lactobacilli: isolation of a teichoic acid-lipid complex from Lactobacillus fermenti NCTC 6991. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):293–301. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos Mota J. M., den Kamp J. A., Verheij H. M., van Deenen L. L. Phospholipids of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):611–619. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.611-619.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


