Abstract
The cell wall O antigen is known to affect mouse virulence of Salmonella. We have shown earlier that S. typhimurium expressing somatic antigen 9,12 is less virulent than its 4,12 sister transductants in mice after intraperitoneal inoculation, suggesting that the 4,12-type O antigen is connected with high virulence in mice. In this report we show, in accord with this suggestion, that when the naturally occurring O-9,12 S. enteritidis is made O-4,12 by transduction, its virulence is increased. The difference between O-9,12 and O-4,12 sister transductants is highly significant, with P less than 0.001.
Full text
PDF
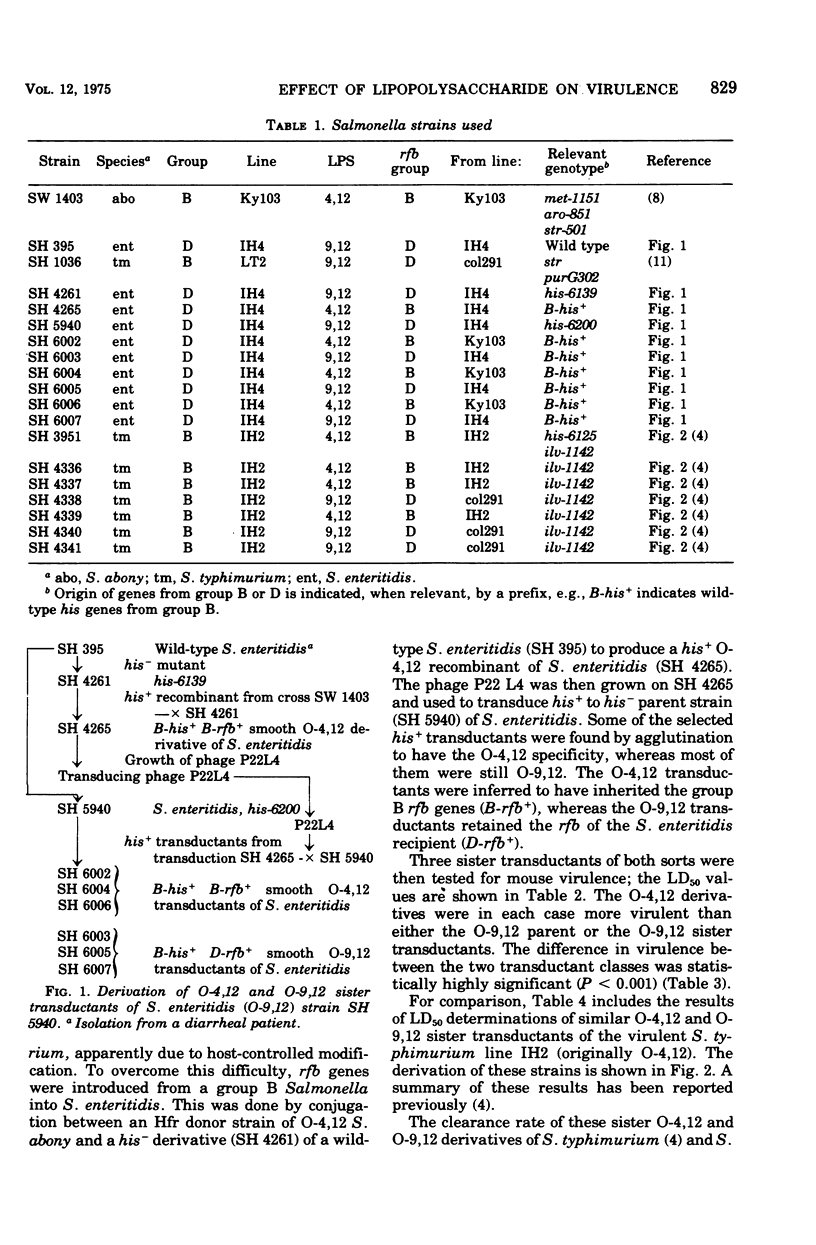
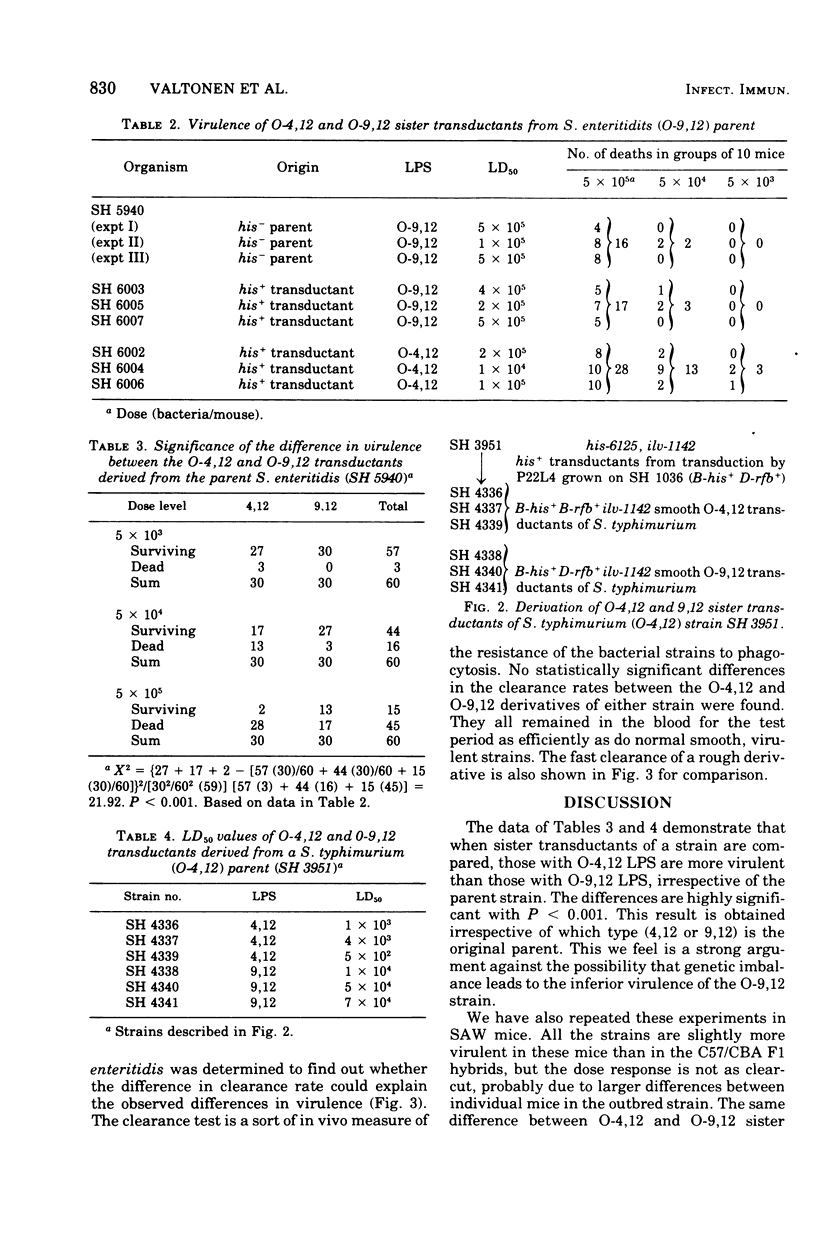
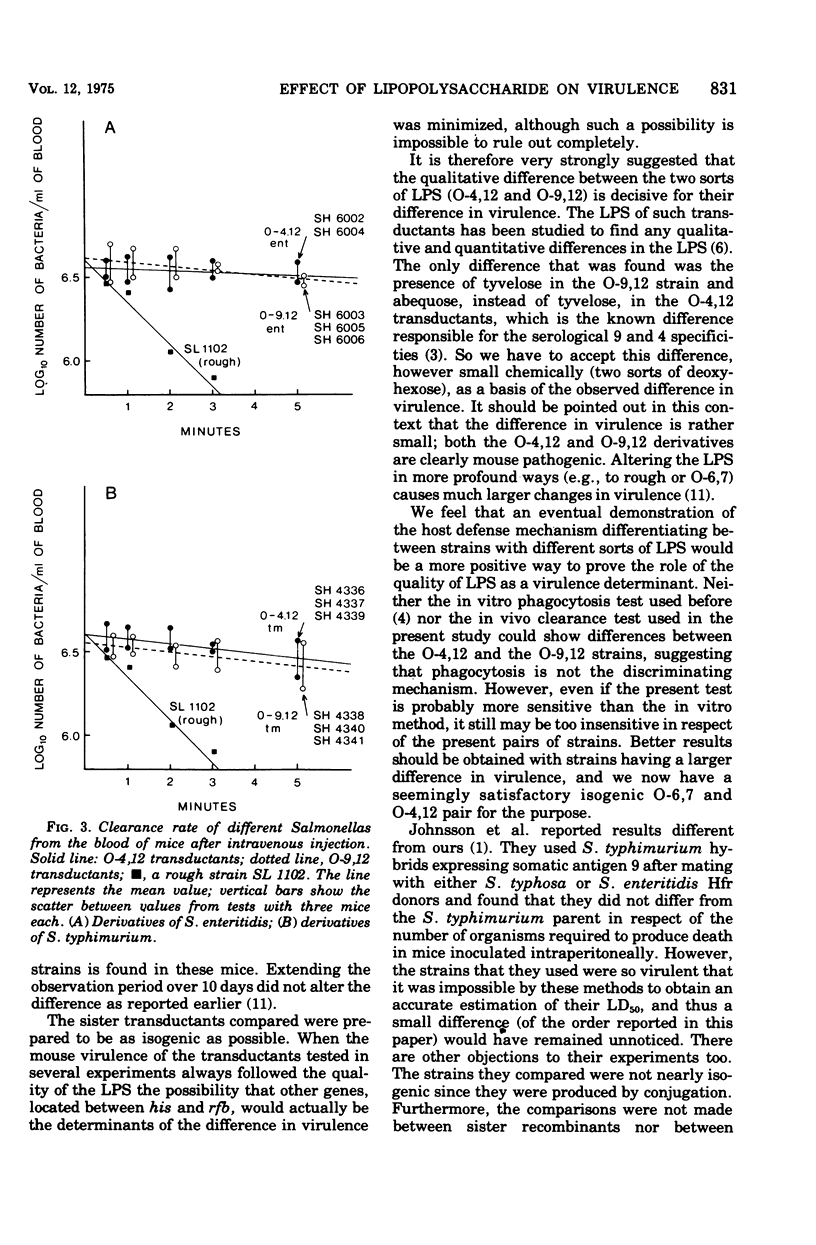

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Johnson E. M., Snellings N. J., Life C. A., Baron L. S. Intraperitoneal mouse virulence of Salmonella typhimurium hybrids expressing somatic antigen 9. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):669–671. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.669-671.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnapillai V., Karthigasu K. Salmonella abony-Salmonella typhimurium recombinant nonvirulent for the mouse. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1343–1351. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1343-1351.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä P. H., Valtonen V. V., Valtonen M. Role of O-antigen (lipopolysaccharide) factors in the virulence of Salmonella. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(Suppl):81–85. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_1.s81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M., Saito K. Chemical components in the cell wall of Salmonella typhimurium affecting its virulence and immunogenicity in mice. Nature. 1969 Jun 14;222(5198):1085–1086. doi: 10.1038/2221085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurminen M., Hellerqvist C. G., Valtonen V. V., Mäkelä P. H. The smooth lipopolysaccharide character of 1,4,(5),12 and 1,9,12 transductants formed as hybrids between groups B and D of salmonella. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Oct 26;22(4):500–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01569.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Ross H., Ziegler L., Mäkelä P. H. F + , Hfr, and F' strains of Salmonella typhimurium and Salmonella abony. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):608–637. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.608-637.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Levine M. A phage P22 gene controlling integration of prophage. Virology. 1967 Feb;31(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90164-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Parsell Z. The effect of virulence of converting the O antigen of Salmonella cholerae-suis from 627 to 617 by phage. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Mar;81(1):217–224. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-1-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtonen V. V. Mouse virulence of Salmonella strains: the effect of different smooth-type O side-chains. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(3):255–268. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-3-255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



