Abstract
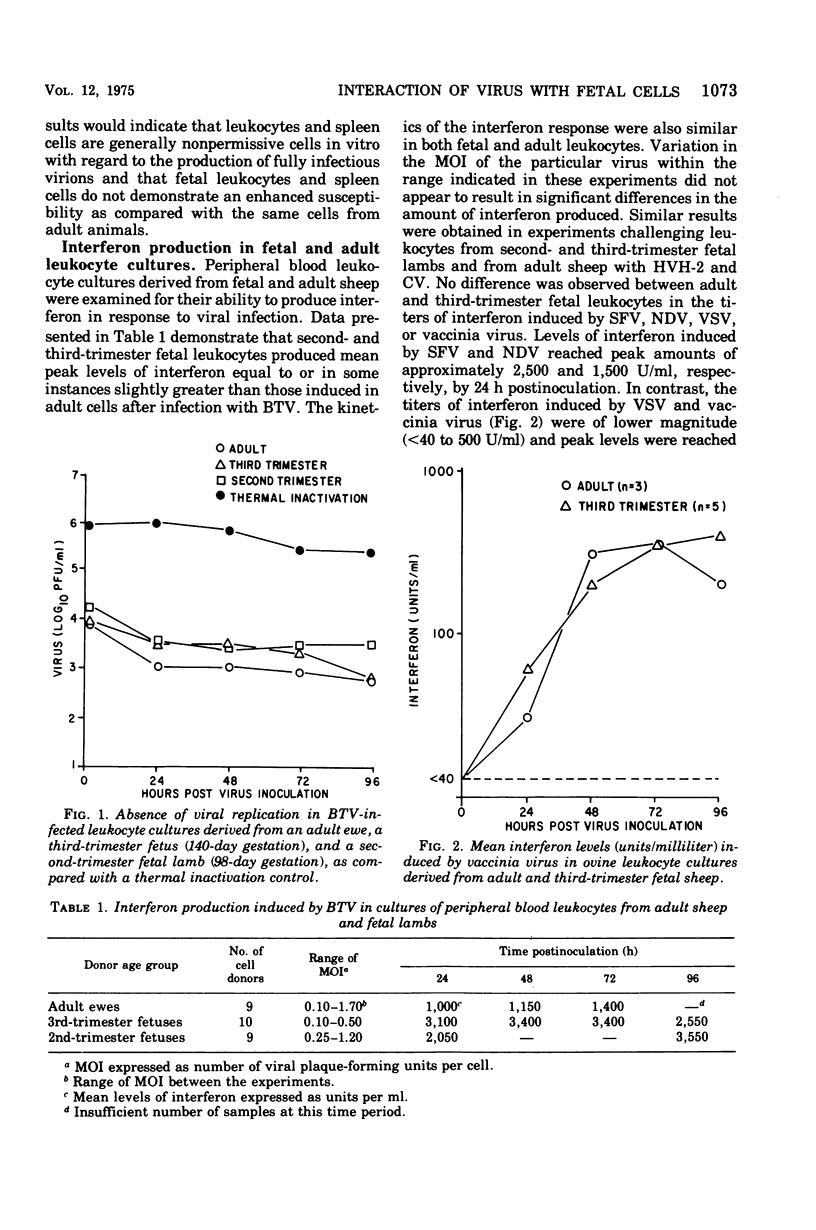
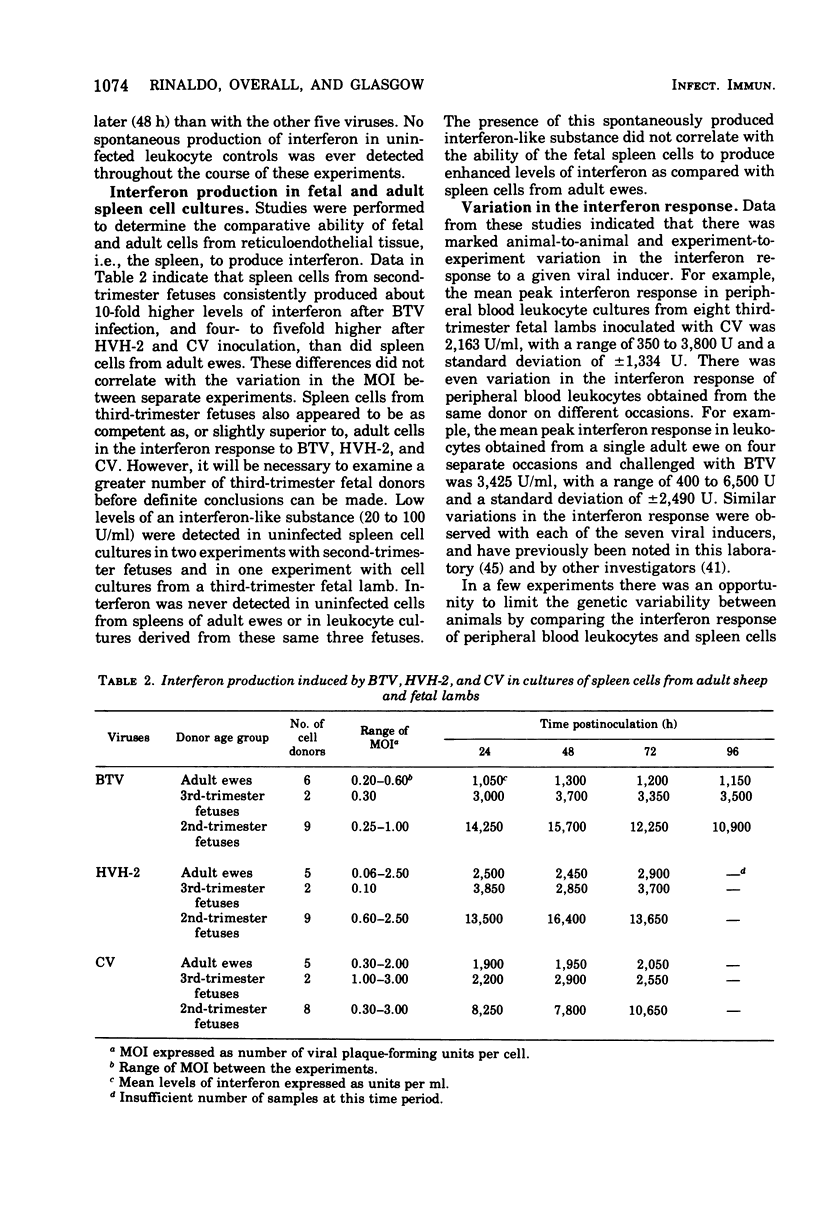
Peripheral blood leukocyte and spleen cell cultures derived from adult sheep and from third-trimester (107 to 145 days of gestation) and second-trimester (70 to 98 days of gestation) fetal lambs were examined for their ability to support viral replication and to produce interferon. Bluetongue virus, Herpesvirus hominis type 2, and Chikungunya virus failed to replicate in either leukocyte or spleen cell cultures derived from adult ewes or in cultures from second- or third-trimester fetal lambs. Similarly, peripheral blood leukocytes from adult sheep or third-trimester fetal lambs did not support the replication of Semliki Forest virus, vesicular stomatitis virus, Newcastle disease virus, or vaccinia virus. No major differences were observed in the ability of fetal and adult leukocytes to produce interferon in response to viral infection. In contrast, mean interferon titers induced by bluetongue virus, H. hominis type 2, and Chikungunya virus in spleen cells from second-trimester fetuses were 4- to 10-fold greater than those induced in spleen cells from adult ewes. Variations in interferon levels induced on separate occasions with cells from the same donor age group were observed. The antiviral substance induced in both the fetal and adult cell cultures fulfilled the usual criteria for characterization as interferon.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acton J. D. The lymphoreticular system and interferon production. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1973 Nov;14(5):449–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARON S., ISAACS A. Mechanism of recovery from viral infection in the chick embryo. Nature. 1961 Jul 1;191:97–98. doi: 10.1038/191097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banatvala J. E., Potter J. E., Best J. M. Interferon response to sendai and rubella viruses in human foetal cultures, leucocytes and placental cultures. J Gen Virol. 1971 Nov;13(2):193–201. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-13-2-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa L. H., London W. T., Hamilton R., Buckler C. Interferon response of the fetal Rhesus monkey after viral infection. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Jun;146(2):398–400. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantell K., Strander H., Saxén L., Meyer B. Interferon response of human leukocytes during intrauterine and postnatal life. J Immunol. 1968 Jun;100(6):1304–1309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. C., Stites D. P., Fudenberg H. H. Cellular immune aspects of the human fetal-maternal relationship. I. In vitro response of cord blood lymphocytes to phytohemagglutinin. Cell Immunol. 1972 Sep;5(1):21–29. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. A., Hande K. R., Essien B., Prochownik E., Kaback M. M. Comparative production of interferon by human fetal, neonatal, and maternal cells. Infect Immun. 1971 May;3(5):671–677. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.5.671-677.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano L. W., Jr, Sever J. L. The role of viruses as causes of congenital diseases. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:255–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.001351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmyter J., Rawls W. E., Melnick J. L., Yow M. D., Barrett F. F. Interferon in congenital rubella: response to live attenuated measles vaccine. J Immunol. 1967 Oct;99(4):771–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diosi P., Moldovan E., Tomescu N. Latent cytomegalovirus infection in blood donors. Br Med J. 1969 Dec 13;4(5684):660–662. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5684.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudgeon J. A. Congenital rubella. Pathogenesis and immunology. Am J Dis Child. 1969 Jul;118(1):35–44. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1969.02100040037007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne H. W., Clark C. D. Embryonic death, fetal mummification, stillbirth, and neonatal death in pigs of gilts vaccinated with attenuated live-virus hog cholera vaccine. Am J Vet Res. 1968 Apr;29(4):787–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallily R., Warwick A., Bang F. B. Ontogeny of macrophage resistance to mouse hepatitis in vivo and in vitro. J Exp Med. 1967 Apr 1;125(4):537–548. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.4.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Lang D. J. Relationships between viruses and leucocytes. Prog Med Virol. 1966;8:62–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEINEBERG H., GOLD E., ROBBINS F. C. DIFFERENCES IN INTERFERON CONTENT IN TISSUES OF MICE OF VARIOUS AGES INFECTED WITH COXSACKIE B1 VIRUS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Apr;115:947–953. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-29086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackbarth S. A., Reinarz A. B., Sagik B. P. Age-dependent resistance of mice to sindbis virus infection: reticuloendothelial role. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1973 Nov;14(5):405–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanshaw J. B. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection: a fifteen year perspective. J Infect Dis. 1971 May;123(5):555–561. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.5.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. S., Zisman B., Allison A. C. Macrophages and age-dependent resistance to Herpes simplex virus in mice. J Immunol. 1970 May;104(5):1160–1165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell P. G., Verwoerd D. W. Bluetongue virus. Virol Monogr. 1971;9:35–74. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-3987-5_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS A., BARON S. Antiviral action of interferon in embryonic cells. Lancet. 1960 Oct 29;2(7157):946–947. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)92022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON R. T. THE PATHOGENESIS OF HERPES VIRUS ENCEPHALITIS. II. A CELLULAR BASIS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF RESISTANCE WITH AGE. J Exp Med. 1964 Sep 1;120:359–374. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.3.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack I., Grutzner J. Cellular viraemia in babies infected with rubella virus before birth. Br Med J. 1969 Feb 1;1(5639):289–292. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5639.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. J., Noren B. Cytomegaloviremia following congenital infection. J Pediatr. 1968 Dec;73(6):812–819. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80233-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavelle G. C., Starr T. J. Interferon response and age-related resistance of germfree mice to mouse hepatitis virus. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1968 Oct;5(5):422–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luedke A. J. Bluetongue in sheep: viral assay and viremia. Am J Vet Res. 1969 Apr;30(4):499–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARENNIKOVA S. S., KAPTSOVA T. I. AGE-DEPENDENCE OF SUSCEPTIBILITY OF WHITE MICE TO VARIOLA VIRUS. Acta Virol. 1965 May;9:230–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIMS C. A. ASPECTS OF THE PATHOGENESIS OF VIRUS DISEASES. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Mar;28:30–71. doi: 10.1128/br.28.1.30-71.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONIF G. R., AVERY G. B., KORONES S. B., SEVER J. L. POSTMORTEM ISOLATION OF RUBELLA VIRUS FROM THREE CHILDREN WITH RUBELLA-SYNDROME DEFECTS. Lancet. 1965 Apr 3;1(7388):723–724. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson J., Kapusta R., Dick V. Maternal and fetal interferon production in the rat. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1970 Jul 15;107(6):902–907. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)34044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mims C. A. Pathogenesis of viral infections of the fetus. Prog Med Virol. 1968;10:194–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morahan P. S., Grossberg S. E. Age-related cellular resistance of the chicken embryo to viral infections. I. Interferon and natural resistance to myxoviruses and vesicular stomatitis virus. J Infect Dis. 1970 Jun;121(6):615–623. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.6.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson G. B., Dent P. B., Rawls W. E., South M. A., Montgomery J. R., Melnick J. L., Good R. A. Abnormalities of in vitro lymphocyte responses during rubella virus infections. J Exp Med. 1968 Jul 1;128(1):47–68. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson L. C., Sithisarn P., Djinawi N. K. Role of macrophages in Wesselsbron and Germiston virus infections of mice. J Infect Dis. 1975 Feb;131(2):119–128. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osburn B. I., Johnson R. T., Silverstein A. M., Prendergast R. A., Jochim M. M., Levy S. E. Experimental viral-induced congenital encephalopathies. II. The pathogenesis of bluetongue vaccine virus infection in fetal lambs. Lab Invest. 1971 Sep;25(3):206–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osburn B. I., Silverstein A. M., Prendergast R. A., Johnson R. T., Parshall C. J., Jr Experimental viral-induced congenital encephalopathies. I. Pathology of hydranencephaly and porencephaly caused by bluetongue vaccine virus. Lab Invest. 1971 Sep;25(3):197–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Fetal response to viral infection: interferon production in sheep. Science. 1970 Feb 20;167(3921):1139–1141. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3921.1139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Virus infections of the fetus and newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1970 Aug;77(2):315–333. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80346-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pidot A. L., O'Keefe G., 3rd, McManus N., McIntyre O. R. Human leukocyte interferon: the variation in normals and correlation with PHA transformation. 1. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Sep;140(4):1263–1269. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pini A., Coackley W., Ohder H. Concentration of bluetongue virus in experimentally infected sheep and virus identification by immune fluorescence technique. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1966;18(4):385–390. doi: 10.1007/BF01246571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawls W. E. Congenital rubella: the significance of virus persistence. Prog Med Virol. 1968;10:238–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray C. G. The ontogeny of interferon production by human leukocytes. J Pediatr. 1970 Jan;76(1):94–98. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Overall J. C., Jr, Cole B. C., Glasgow L. A. Mycoplasma-associated induction of interferon in ovine leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):796–803. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.796-803.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWICKI L. Influence of age of mice on the recovery from experimental Sendal virus infection. Nature. 1961 Dec 30;192:1258–1259. doi: 10.1038/1921258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIGEL M. M. Influence of age on susceptibility to virus infections with particular reference to laboratory animals. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1952;6:247–280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.06.100152.001335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siewers C. M., John C. E., Medearis D. N., Jr Sensitivity of human cell strains to interferon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Apr;133(4):1178–1183. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons M. J. Congenital rubella: an immunological paradox? Lancet. 1968 Dec 14;2(7581):1275–1278. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91765-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subrahmanyan T. P. A study of the possible basis of age-dependent resistance of mice to poxvirus diseases. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1968 Jun;46(3):251–265. doi: 10.1038/icb.1968.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber T. H., Santesson B., Skoog V. T. The activation of fetal lymphocytes. Scand J Haematol. 1973;11(3):177–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1973.tb00113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheelock E. F., Toy S. T. Participation of lymphocytes in viral infections. Adv Immunol. 1973;16:123–184. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



