Abstract
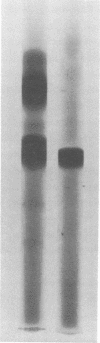
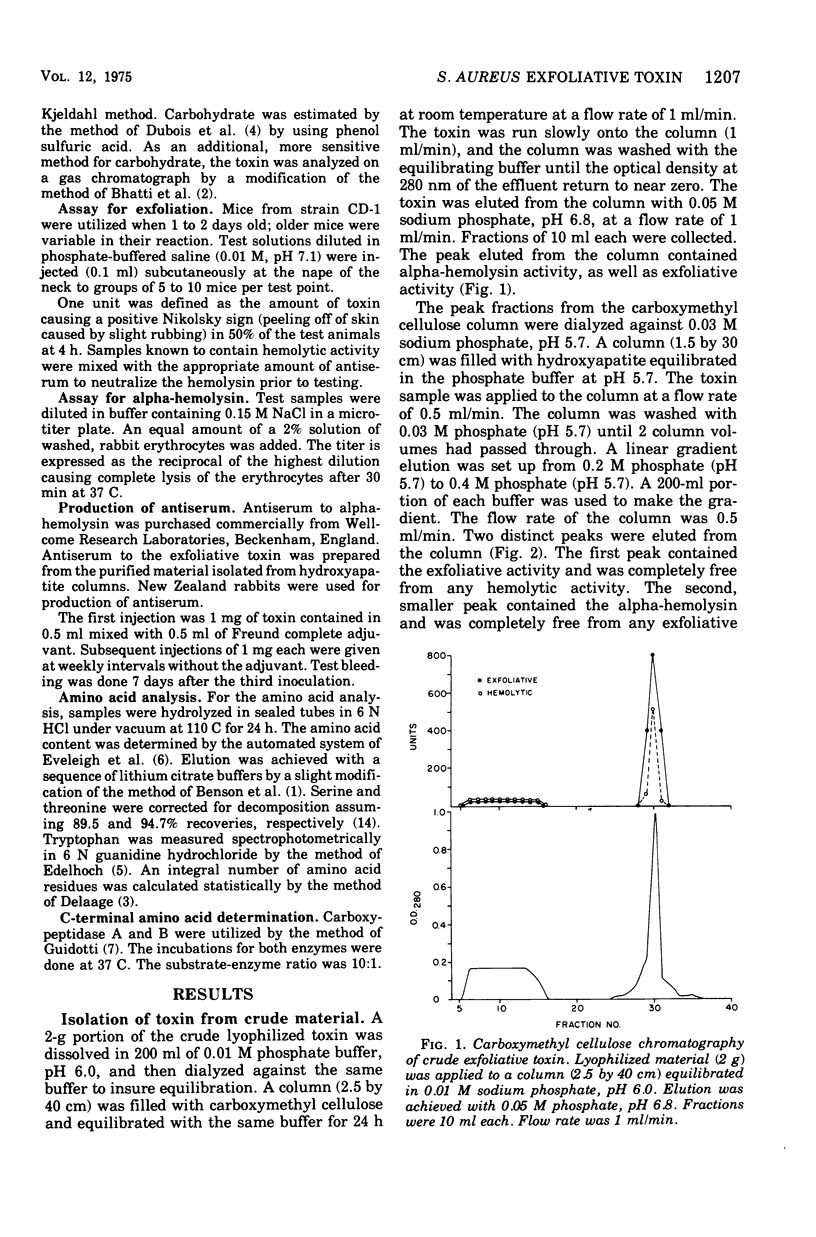
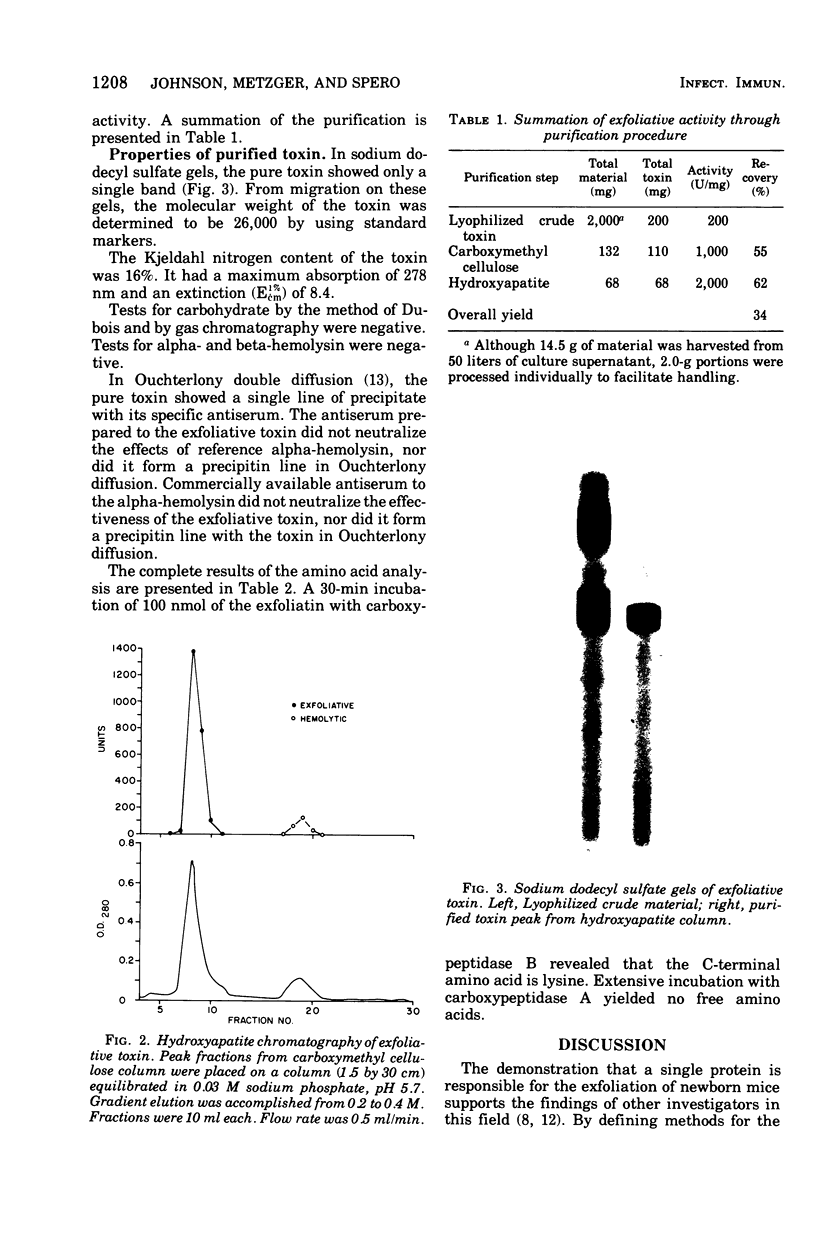
Methods for the production and isolation of exfoliative toxin are described. Fermentation conditions were established under which large quantities of the crude material can be produced. Column chromatography methods, including carboxymethyl cellulose and hydroxyapatite, were utilized to purify the toxic protein. The pure toxin had a molecular weight of 26,000 as determined by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate. The pure toxin is a simple protein composed of 17 amino acids. Tests for carbohydrate and for alpha- and beta-hemolysin were negative. The mean effective dose of the purified toxin was 0.5 mug per newborn mouse.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhatti T., Chambers R. E., Clamp J. R. The gas chromatographic properties of biologically important N-acetylglucosamine derivatives, monosaccharides, disaccharides, trisaccharides, tetrasaccharides and pentasaccharides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 24;222(2):339–347. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90122-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaage M. Sur la recherche du poids moléculaire le plus cohérent avec l'analyse des acides aminés d'une protéine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 3;168(3):573–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUIDOTTI G. The action of carboxypeptidases A and B on the separated alpha and beta chains of normal adult human hemoglobin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jul 29;42:177–179. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90774-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A., Miller M. M. Product of Staphylococcus aureus responsible for the scalded-skin syndrome. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):541–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.541-545.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo I., Sakurai S., Sarai Y. Purification of exfoliatin produced by Staphylococcus aureus of bacteriophage group 2 and its physicochemical properties. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):156–164. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.156-164.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowney E. D., Baublis J. V., Kreye G. M., Harrell E. R., McKenzie A. R. The scalded skin syndrome in small children. Arch Dermatol. 1967 Apr;95(4):359–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melish M. E., Glasgow L. A., Turner M. D. The staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome: isolation and partial characterization of the exfoliative toxin. J Infect Dis. 1972 Feb;125(2):129–140. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.2.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Antigen-antibody reactions in gels. IV. Types of reactions in coordinated systems of diffusion. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1953;32(2):230–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees M. W. The estimation of threonine and serine in proteins. Biochem J. 1946;40(5-6):632–640. doi: 10.1042/bj0400632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogolsky M., Wiley B. B., Keyhani M., Glasgow L. A. Interaction of staphylococcal exfoliative toxin with concanavalin A. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1260–1265. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1260-1265.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]