Abstract
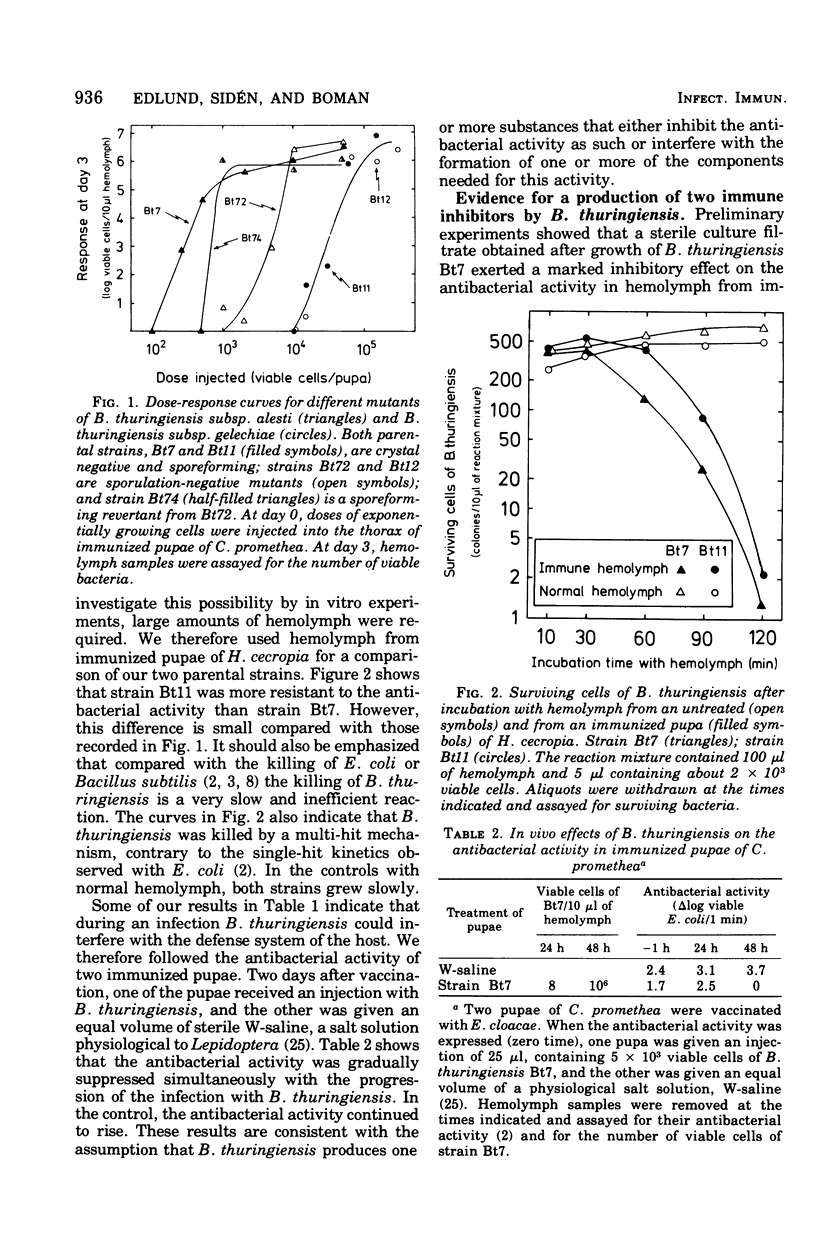
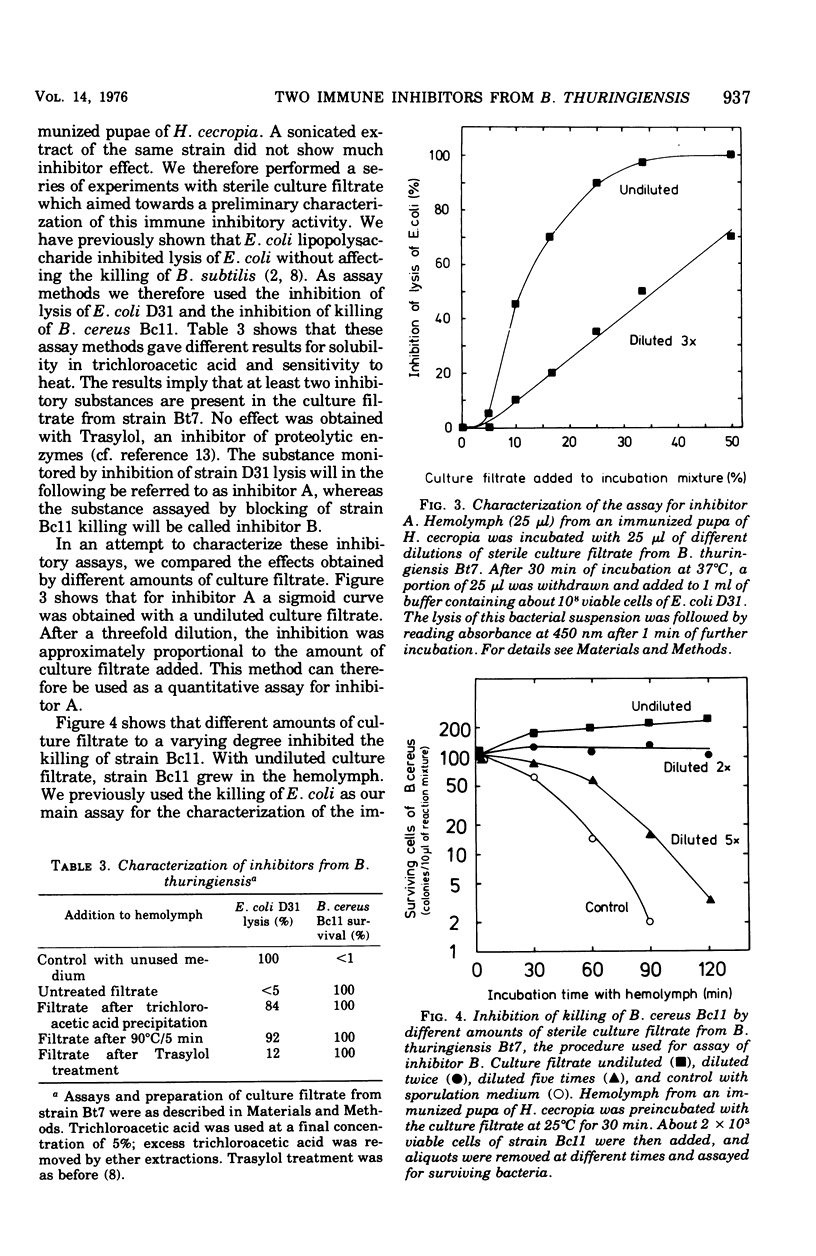
Mutants of Bacillus thuringiensis lacking either beta-exotoxin or gamma-endotoxin were compared for their virulence using pupae of a giant silk moth. Known doses of viable log-phase bacteria were injected, and the response was followed as the number of viable bacteria in the hemolymph. The results obtained imply that, in the system used, neither the beta-exotoxin nor the gamma-endotoxin and the sporeforming ability are of importance for virulence. Results with sterile culture filtrate from B. thuringiensis have given evidence for the production of two inhibitors, A and B, which interfere with the humoral defense system in pupae of Hyalophora cecropia. Inhibitor A, which blocked the lysis of Escherichia coli,was precipitated by trichloroacetic acid and sensitive to heating. Inhibitor B, which blocked the killing of Bacillus cereus, was soluble in trichloroacetic acid and resistant to 90 degrees C for 5 min. Both inhibitors are believed to contribute to the insecticidal nature of B. thuringiensis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beebee T., Korner A., Bond R. P. Differential inhibition of mammalian ribonucleic acid polymerases by an exotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis. The direct observation of nucleoplasmic ribonucleic acid polymerase activity in intact nuclei. Biochem J. 1972 May;127(4):619–634. doi: 10.1042/bj1270619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Nilsson-Faye I., Paul K., Rasmuson T., Jr Insect immunity. I. Characteristics of an inducible cell-free antibacterial reaction in hemolymph of Samia cynthia pupae. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):136–145. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.136-145.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulla L. A. Bacteria as insect pathogens. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:163–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delafield F. P., Somerville H. J., Rittenberg S. C. Immunological homology between crystal and spore protein of Bacillus thuringiensis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):713–720. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.713-720.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faye I., Pye A., Rasmuson T., Boman H. G., Boman I. A. Insect immunity. 11. Simultaneous induction of antibacterial activity and selection synthesis of some hemolymph proteins in diapausing pupae of Hyalophora cecropia and Samia cynthia. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1426–1438. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1426-1438.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Rietschel E. T., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Interaction of lipopolysaccharides and lipid A with complement. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Mar 1;19(1):143–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna E. E., Hale M. Deregulation of mouse antibody-forming cells in vivo in cell culture by streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):265–272. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.265-272.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li E., Yousten A. A. Metalloprotease from Bacillus thuringiensis. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Sep;30(3):354–361. doi: 10.1128/am.30.3.354-361.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendleton I. R., Bernheimer A. W., Grushoff P. Purification and partial characterization of hemolysins from Bacillus thuringiensis. J Invertebr Pathol. 1973 Mar;21(2):131–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(73)90192-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharmann W. Formation and isolation of leucocidin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Apr;93(2):283–291. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-2-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebesta K., Horská K. Mechanism of inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase by exotoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;209(2):357–376. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90734-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. A., Walker P. D., Thomson R. O., Somerville H. J. The fine structure of Bacillus finitimus and Bacillus thuringiensis spores with special reference to the location of crystal antigen. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Oct;84(2):261–276. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville H. J. Formation of the parasporal inclusion of Bacillus thuringiensis. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jan;18(2):226–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville H. J. Means for insect regulation. Microbial toxins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Jun 22;217:93–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb32752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville H. J., Pockett H. V. An insect toxin from spores of Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus cereus. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Apr;87(2):359–369. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-2-359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville H. J., Swain H. M. Temperature-dependent inhibition of polyphenylalanine formation by the exotoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jul 1;54(3):330–333. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80933-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenshein A. L., Cami B., Brevet J., Cote R. Isolation and characterization of rifampin-resistant and streptolydigin-resistant mutants of Bacillus subtilis with altered sporulation properties. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):253–265. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.253-265.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålenheim G., Götze O., Cooper N. R., Sjöquist J., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Consumption of human complement components by complexes of IgG with protein A of Staphylococcus aureus. Immunochemistry. 1973 Aug;10(8):501–507. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90221-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weevers R. D. A lepidopteran saline: effects of inorganic cation concentrations on sensory, reflex and motor responses in a herbivorous insect. J Exp Biol. 1966 Feb;44(1):163–175. doi: 10.1242/jeb.44.1.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



