Abstract
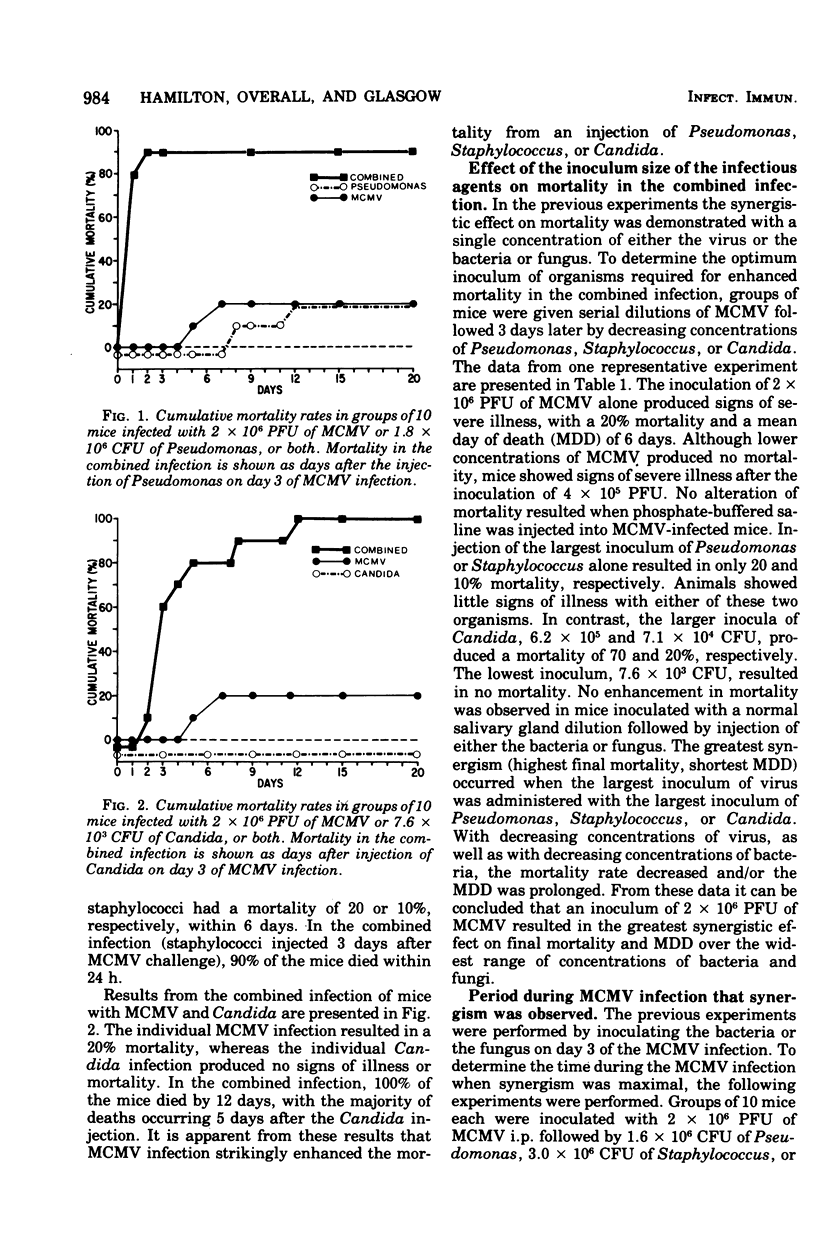
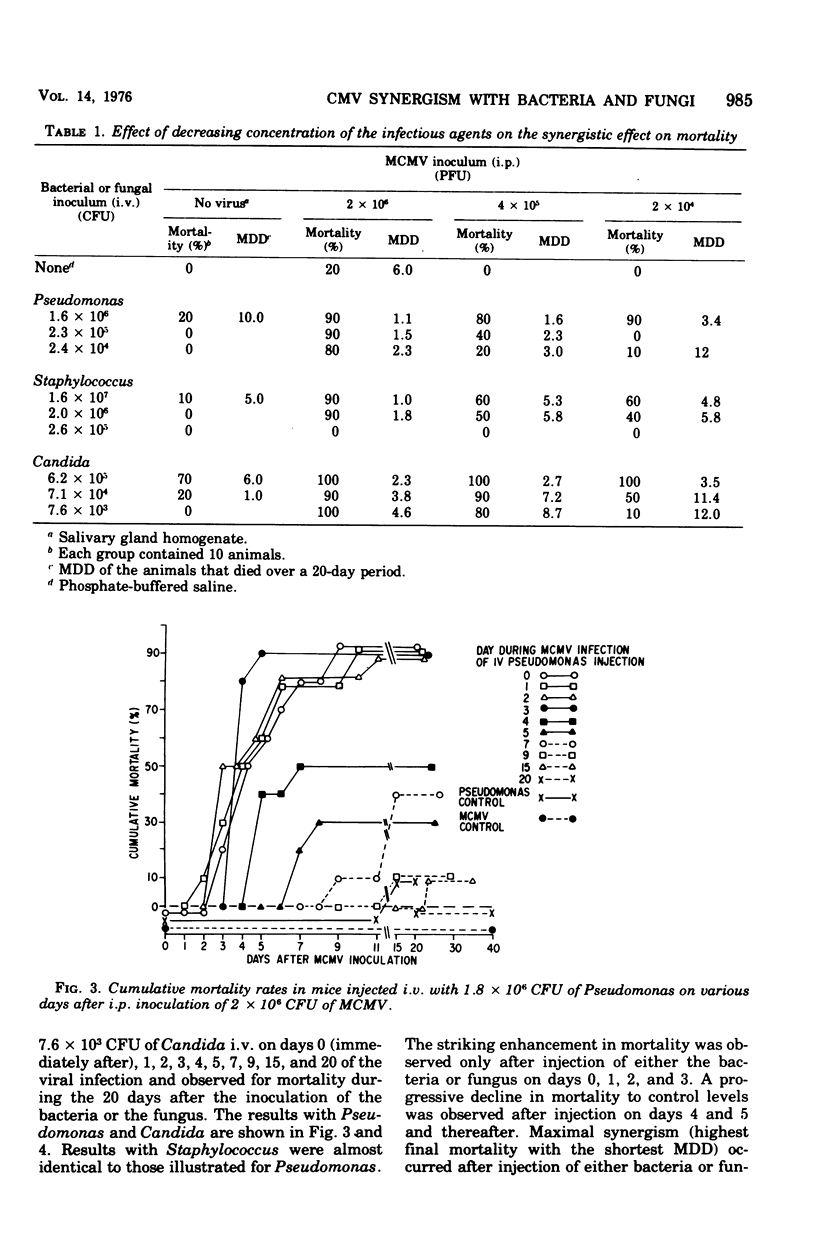
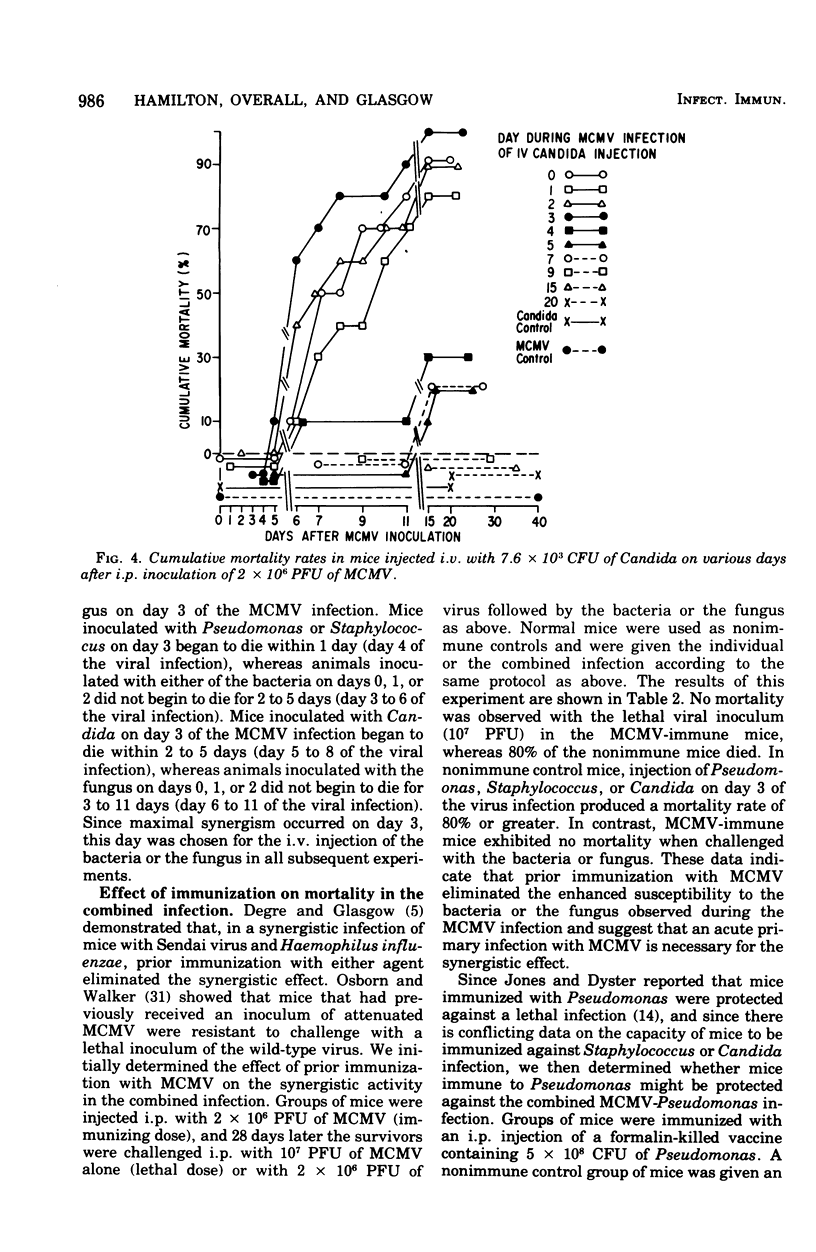
A synergistic effect on mortality was demonstrated in a combined infection of mice with murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, or Candida albicans. Mice infected intraperitoneally with a 0 to 20% lethal dose inoculum of MCMV 3 days prior to the intravenous injection of a 0 to 20% lethal dose inoculum of either the bacteria or fungus demonstrated a striking enhancement of mortality. MCMV-infected mice given Pseudomonas or Staphylococcus exhibited a 90 to 100% mortality within 24 to 48 h, whereas 80% of viral-infected animals injected with Candida died in 5 days. Injection of the bacteria or fungus at various times during the MCMV infection resulted in enhanced mortality on days 0,1,2, and 3 of the viral infection. Greatest synergism was observed on day 3, with a progressive decline in death rates thereafter. Immunization with MCMV abrogated the synergistic effect on mortality in all three combined infections. Immunization with Pseudomonas reduced mortality in the combined MCMV-Pseudomonas infection. These results indicate that mice exhibit a markedly enhanced susceptibility to bacterial and fungal infections during the course of the MCMV infection and suggest that the enhancement may be related to viral-induced alterations in host resistance.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balakrishnan S. L., Armstrong D., Rubin A. L., Stenzel K. H. Cytomegalovirus infection after renal transplantation. Report of a case with viremia and atypical lymphocytosis. JAMA. 1969 Mar 3;207(9):1712–1714. doi: 10.1001/jama.207.9.1712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjornson A. B., Michael J. G. Contribution of humoral and cellular factors to the resistance to experimental infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice. I. Interaction between immunoglobulins, heat-labile serum factors, and phagocytic cells in the killing of bacteria. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):462–467. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.462-467.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjornson A. B., Michael J. G. Contribution of humoral and cellular factors to the resistance to experimental infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice. II. Opsonic, agglutinative, and protective capacities of immunoglobulin G anti-Pseudomonas antibodies. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.775-782.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degré M., Glasgow L. A. Synergistic effect in viral-bacterial infection. I. Combined infection of the respiratory tract in mice with parainfluenza virus and Hemophilus influenza. J Infect Dis. 1968 Dec;118(5):449–462. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.5.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emödi G., Just M. Impaired interferon response of children with congenital cytomegalovirus disease. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1974 Mar;63(2):183–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1974.tb04781.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyckmans L., Billiau A. Inhibition of bactericidal capacity in mice after administration of Newcastle disease virus. Scand J Infect Dis. 1972;4(2):101–104. doi: 10.3109/inf.1972.4.issue-2.06. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine R. N., Grushkin C. M., Malekzadeh M., Wright H. T., Jr Cytomegalovirus syndrome following renal transplantation. Arch Surg. 1972 Oct;105(4):564–570. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1972.04180100015006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINDER D. R. INCREASED SUSCEPTIBILITY OF MICE INFECTED WITH MOUSE ADENOVIRUS TO ESCHERICHIA COLI-INDUCED PYELONEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1964 Dec 1;120:1117–1128. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.6.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSHAW J. B., BETTS R. F., SIMON G., BOYNTON R. C. ACQUIRED CYTOMEGALOVIRUS INFECTION: ASSOCIATION WITH HEPATOMEGALY AND ABNORMAL LIVER-FUNCTION TESTS. N Engl J Med. 1965 Mar 25;272:602–609. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196503252721202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Miller J., Najarian J. S. Cytomegalovirus-induced immune suppression. II. Cell-mediated immunity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):119–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Najarian J. S. Cytomegalovirus-induced immune suppression. I. Humoral immunity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):109–118. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugh R., Huang K. Y., Elliott T. B. Enhancement of bacterial infections in mice by newcastle disease virus. Infect Immun. 1971 Mar;3(3):488–493. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.3.488-493.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. J., Dyster R. E. The role of polymorphonuclear leucocytes in protecting mice vaccinated against Pseudomon as aeruginosa infections. Br J Exp Pathol. 1973 Aug;54(4):416–421. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. C., Rousseau W., Stewart J. A., Noble G. R., Chin T. D. Spontaneous cytomegalovirus mononucleosis. Clinical and laboratory observations in nine cases. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Aug;79(2):153–160. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-2-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman C. A., Phair J. P., Linnemann C. C., Jr, Schiff G. M. Cell-mediated immunity in humans during viral infection. I. Effect of rubella on dermal hypersensitivity, phytohemagglutinin response, and T lymphocyte numbers. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):212–215. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.212-215.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern E. R., Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Herpesvirus hominis infection in newborn mice. I. An experimental model and therapy with iododeoxyuridine. J Infect Dis. 1973 Sep;128(3):290–299. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.3.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinerman E. S., Snyderman R., Daniels C. A. Depression of human monocyte chemotaxis by herpes simplex and influenza viruses. J Immunol. 1974 Nov;113(5):1562–1567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemola E. Cytomegalovirus infection in previously healthy adults. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Aug;79(2):267–268. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-2-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemola E., Käriäinen L. Cytomegalovirus as a possible cause of a disease resembling infectious mononucleosis. Br Med J. 1965 Nov 6;2(5470):1099–1102. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5470.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemola E., von Essen R., Wager O., Haltia K., Koivuniemi A., Salmi I. Cytomegalovirus mononucleosis in previously healthy individuals. Five new cases and follow-up of 13 previously published cases. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Jul;71(1):11–19. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-71-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loosli C. G. Influenza and the interaction of viruses and bacteria in respiratory infections. Medicine (Baltimore) 1973 Sep;52(5):369–384. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197309000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez C., Simmons R. L., Mauer S. M., Najarian J. S., Good R. A., Gentry S. Association of renal allograft rejection with virus infections. Am J Med. 1974 Mar;56(3):280–289. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90609-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luby J. P., Burnett W., Hull A. R., Ware A. J., Shorey J. W., Peters P. C. Relationship between cytomegalovirus and hepatic function abnormalities in the period after renal transplant. J Infect Dis. 1974 May;129(5):511–518. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.5.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millard P. R., Herbertson B. M., Nagington J., Evans D. B. The morphological consequences and the significance of cytomegalovirus infection in renal transplant patients. Q J Med. 1973 Jul;42(167):585–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notkins A. L. Enzymatic and immunologic alterations in mice infected with lactic dehydrogenase virus. Am J Pathol. 1971 Sep;64(3):733–746. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Blazkovec A. A., Walker D. L. Immunosuppression during acute murine cytomegalovirus infection. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):835–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Medearis D. N., Jr Suppression of interferon and antibody and multiplication of Newcastle disease virus in cytomegalovirus infected mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Feb;124(2):347–353. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Shahidi N. T. Thrombocytopenia in murine cytomegalovirus infection. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Jan;81(1):53–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Walker D. L. Virulence and attenuation of murine cytomegalovirus. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):228–236. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.228-236.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Virus infections of the fetus and newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1970 Aug;77(2):315–333. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80346-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWE W. P., HARTLEY J. W., WATERMAN S., TURNER H. C., HUEBNER R. J. Cytopathogenic agent resembling human salivary gland virus recovered from tissue cultures of human adenoids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Jun;92(2):418–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUEBNER B. H., MIYAI K., SLUSSER R. J., WEDEMEYER P., MEDEARIS D. N., Jr MOUSE CYTOMEGALOVIRUS INFECTION. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF HEPATIC PARENCHYMAL CELLS. Am J Pathol. 1964 May;44:799–821. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruebner B. H., Hirano T., Slusser R., Osborn J., Medearis D. N., Jr Cytomegalovirus infection. Viral ultrastructure with particular reference to the relationship of lysosomes to cytoplasmic inclusions. Am J Pathol. 1966 Jun;48(6):971–989. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERN H., ELEK S. D. THE INCIDENCE OF INFECTION WITH CYTOMEGALOVIRUS IN A NORMAL POPULATION. A SEROLOGICAL STUDY IN GREATER LONDON. J Hyg (Lond) 1965 Mar;63:79–87. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400044983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selgrade M. K., Osborn J. E. Role of macrophages in resistance to murine cytomegalovirus. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1383–1390. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1383-1390.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Lactic dehydrogenase activity in blood. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):210–213. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller T. H. The cytomegaloviruses: ubiquitous agents with protean clinical manifestations. I. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 22;285(4):203–214. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107222850406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



