Abstract
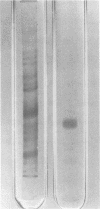
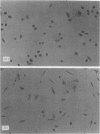
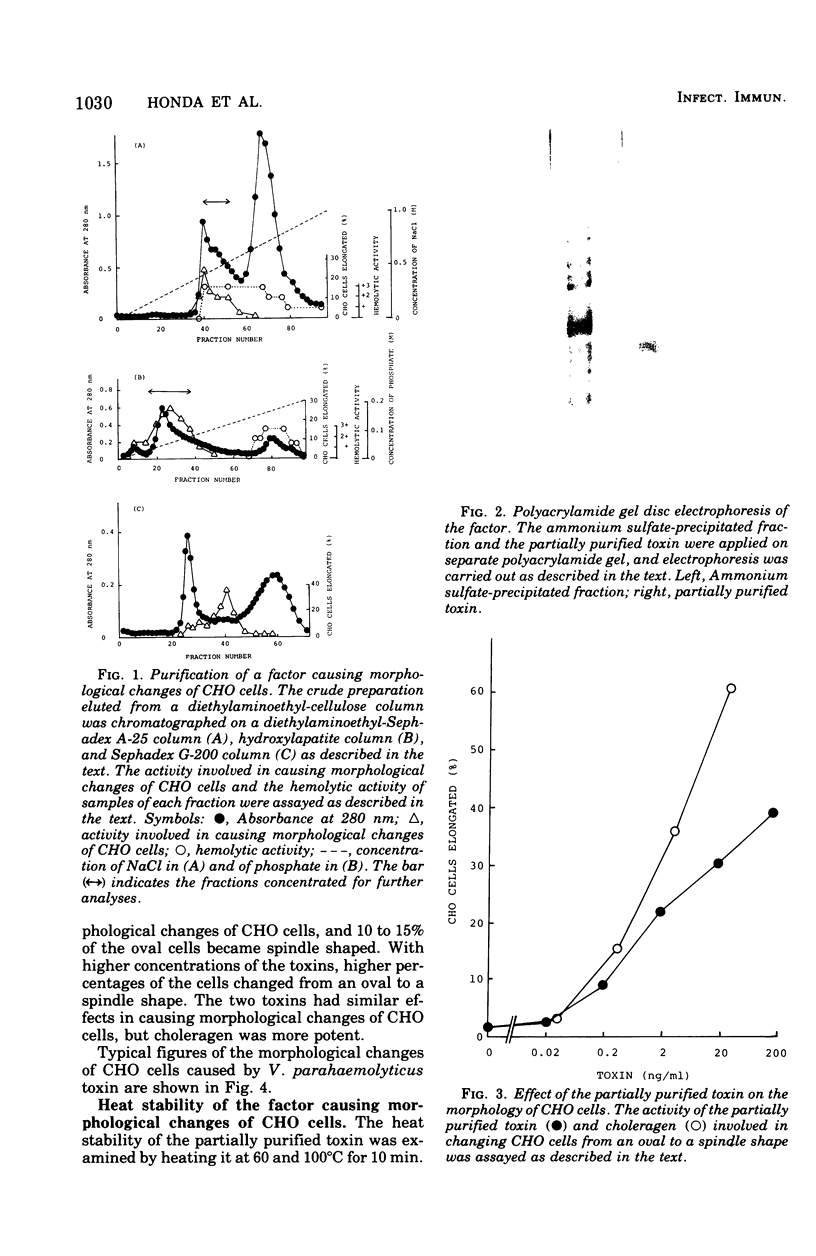
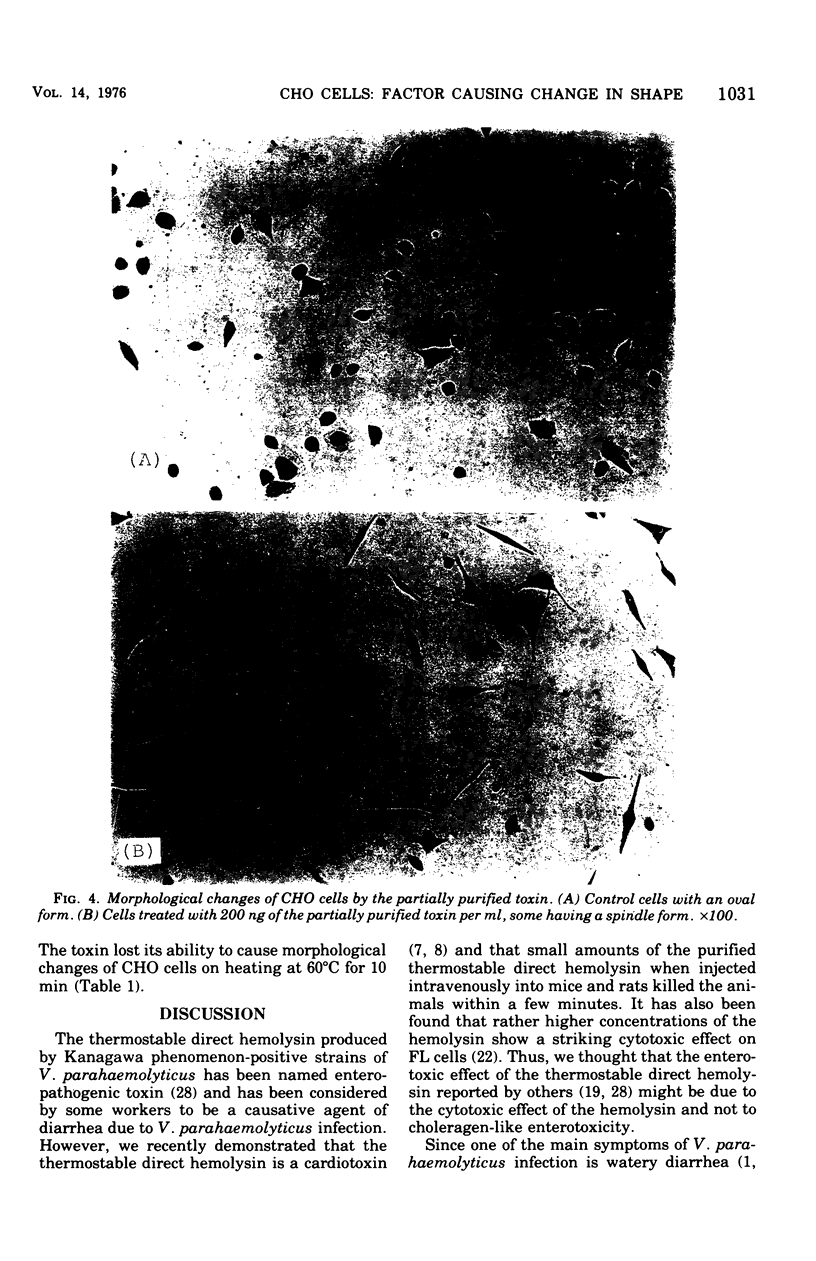
A factor changing Chinese hamster ovary cells from an oval to a spindle shape was isolated from the culture filtrate of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. It was partially purified by successive column chromatographies on diethylaminoethylcellulose, diethylaminoethyl-Sephadex A-25, hydroxylapatite, and Sephadex G-200. This factor was separated from thermostabl direct hemolysin and was heat labile.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., King M., Sloper K. Induction of steroidogenesis in tissue culture by cholera enterotoxin. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 20;243(129):246–247. doi: 10.1038/newbio243246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Smith D. M. Stimulation of steroidogenesis in tissue culture by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and its neutralization by specific antiserum. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):500–505. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.500-505.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M: Intestinal secretion: effect of cyclic AMP and its role in cholera. N Engl J Med. 1971 May 20;284(20):1137–1144. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197105202842008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Goshima K., Takeda Y., Sugino Y., Miwatani T. Demonstration of the cardiotoxicity of the thermostable direct hemolysin (lethal toxin) produced by Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):163–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.163-171.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Taga S., Takeda T., Hasibuan M. A., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Identification of lethal toxin with the thermostable direct hemolysin produced by Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and some physicochemical properties of the purified toxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):133–139. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.133-139.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsie A. W., Puck T. T. Morphological transformation of Chinese hamster cells by dibutyryl adenosine cyclic 3':5'-monophosphate and testosterone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):358–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsle A. W., Kawashima K., O'Neill J. P., Schröder C. H. Possible role of adenosine cyclic 3':5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase in the morphological transformation of Chinese hamster ovary cells mediated by N6,O2-dibutyryl adenosine cyclic 3':5"-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 10;250(3):984–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Johnson J., Henderson A., Gershon E. Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI106599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwatani T., Sakurai J., Takeda Y., Sugiyama S., Adachi T. [Antibody titers against the thermostable direct hemolysin in the sera of patients with Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1976 Feb;50(2):46–51. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.50.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwatani T., Takeda Y., Sakurai J., Yoshihara A., Taga S. Effect of heat (Arrhenius effect) on crude hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):1031–1033. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.1031-1033.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto Y., Kato T., Obara Y., Akiyama S., Takizawa K., Yamai S. In vitro hemolytic characteristic of Vibrio parahaemolyticus: its close correlation with human pathogenicity. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1147–1149. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1147-1149.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niikawa T., Obara Y., Yamai S., Miyamoto Y. Purification of a hemolysin from Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1972 Jun;25(3):197–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozawa R., Kon F., Yokota T., Ohashi M., Kuwahara S. Increased adhesion of Chinese hamster ovary cells to substratum by cholera enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):621–624. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.621-624.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai J., Honda T., Jinguji Y., Arita M., Miwatani T. Cytotoxic effect of the thermostable direct hemolysin produced by Vibrio parahaemolyticus on FL cells. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):876–883. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.876-883.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai J., Matsuzaki A., Miwatani T. Purification and characterization of thermostable direct hemolysin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):775–780. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.775-780.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai J., Matsuzaki A., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Existence of two distinct hemolysins in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):777–780. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.777-780.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer D. E., Lust W. D., Sircar B., Goldberg N. D. Elevated concentration of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in intestinal mucosa after treatment with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):851–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Hynie S. Stimulation of intestinal adenyl cyclase by cholera toxin. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):266–269. doi: 10.1038/229266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zen-Yoji H., Hitokoto H., Morozumi S., Le Clair R. A. Purification and characterization o;f a hemolysin produced by Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jun;123(6):665–667. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.6.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]