Abstract
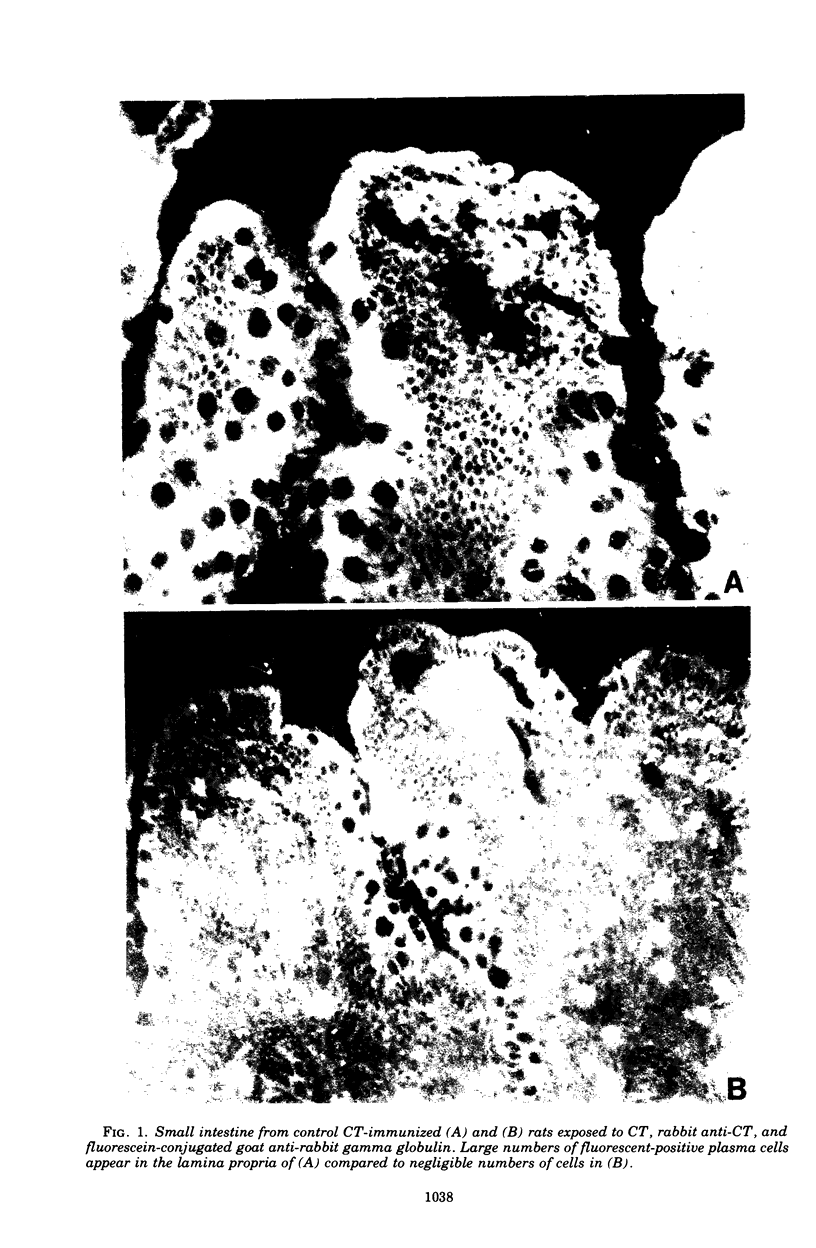
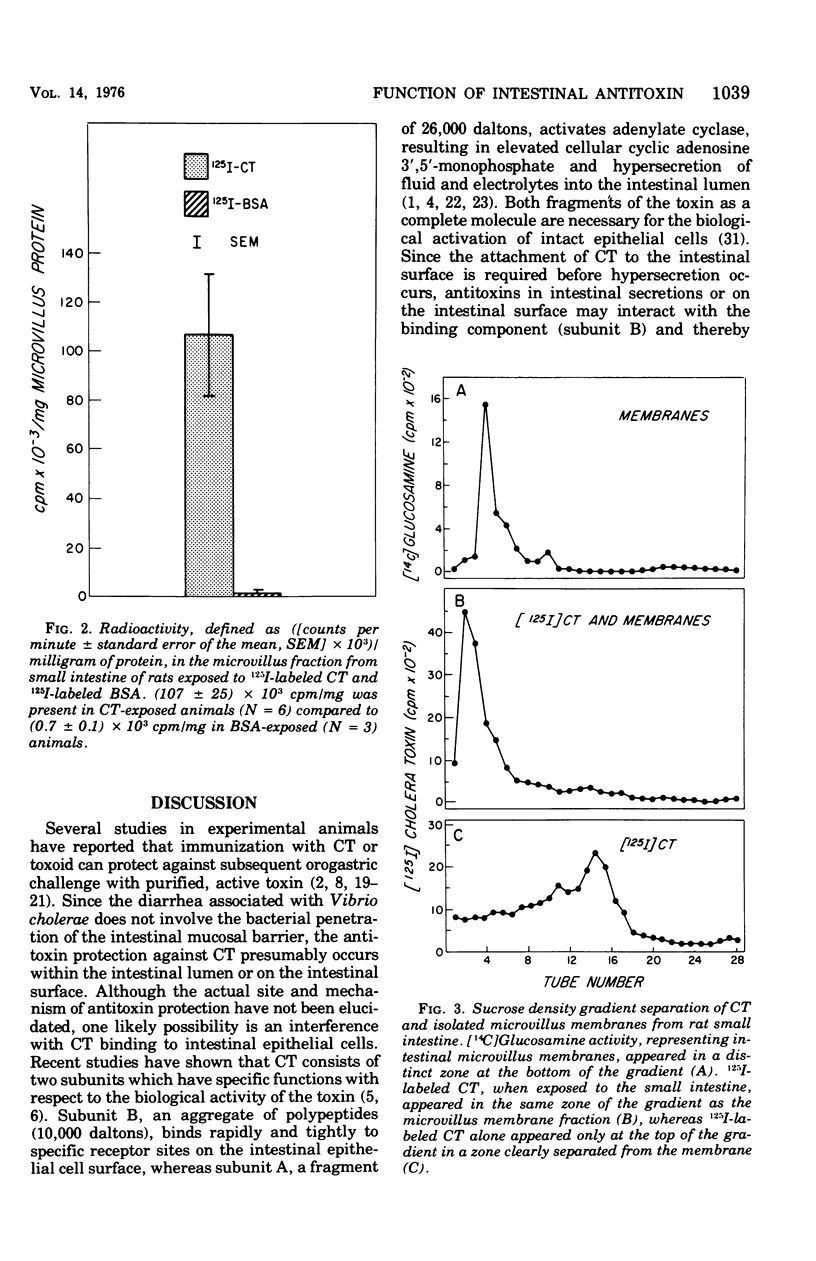
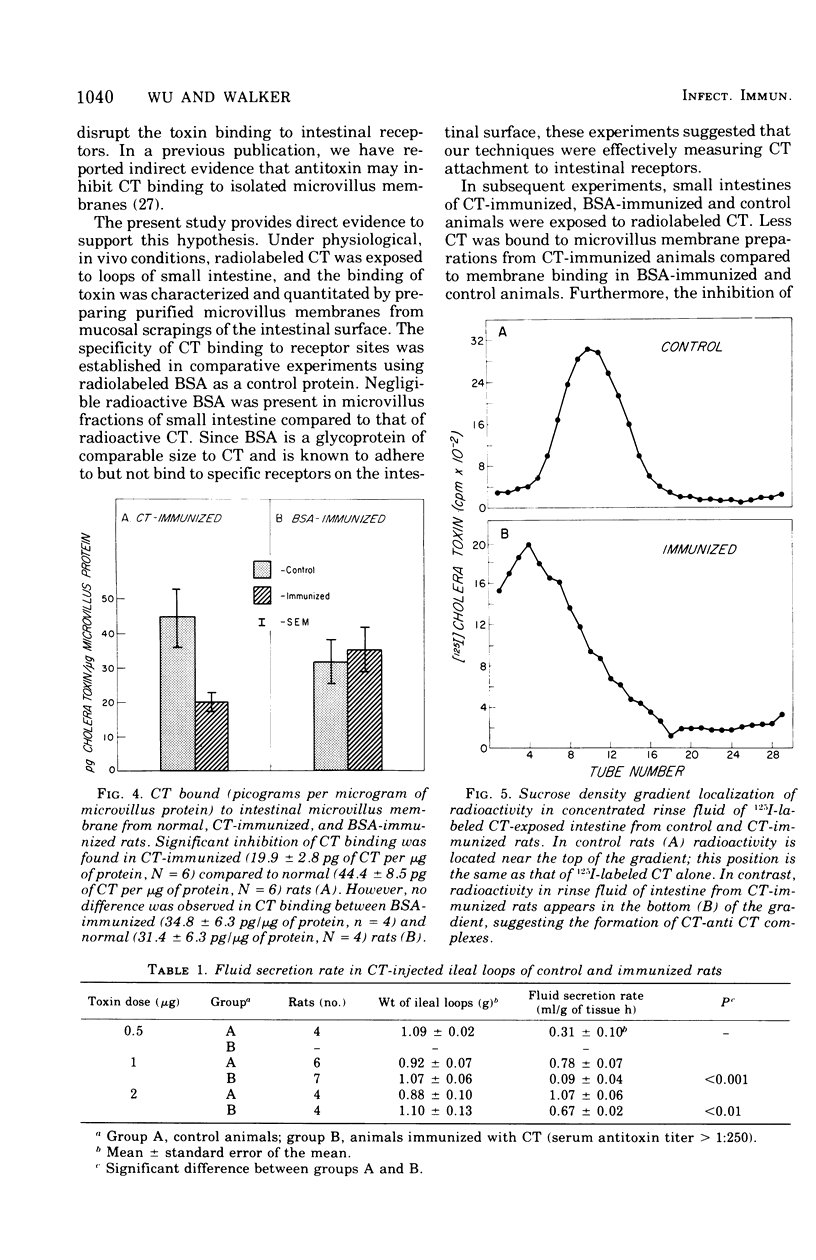
The immunological control mechanism against cholera toxin (CT) in the small intestine of rats was studied in vivo. CT binding to intestinal receptors was determined by injected radiolabeled CT into the loops of rat small intestine and subsequently separating purified microvillus membranes from mucosal scrapings of those loops. substantial radioactivity (10(5) cpm/mg of microvillus protein) was present in microvillus fractions of small intestine exposed to 125I-labeled CT compared to radioactivity (10(2) cpm/mg) in fractions from intestine exposed to radiolabeled bovine serum albumin (BSA) used as a control. CT binding to intestinal receptors was significantly inhibited (P less than 0.02) in rats immunized with crude toxin by a combined intraperitoneal and oral method compared to CT binding in animals immunized with BSA or controls, suggesting a specific relationship between intestinal antitoxin and inhibition of binding. Furthermore, ligated ileal loops from CT-immunized animals showed a significant decrease in fluid accumulation when exposed to CT compared to loops from control or BSA-immunized animals, suggesting that antitoxins also interfered with the biological action of CT under conditions of immunization. These studies provide direct evidence that intestinal antitoxins protect against CT-induced diarrhea by interfering with the attachment of the toxin to the intestinal microvillus surface.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carpenter C. C. Cholera and other enterotoxin-related diarrheal diseases. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):551–564. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlqvist A. Assay of intestinal disaccharidases. Anal Biochem. 1968 Jan;22(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90263-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. Intestinal secretion. Gastroenterology. 1974 May;66(5):1063–1084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Boesman M., Neoh S. H., LaRue M. K., Delaney R. Dissociation and recombination of the subunits of the cholera enterotoxin (choleragen). J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):145–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fubara E. S., Freter R. Protection against enteric bacterial infection by secretory IgA antibodies. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):395–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita K., Finkelstein R. A. Antitoxic immunity in experimental cholera: comparison of immunity induced perorally and parenterally in mice. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):647–655. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyningen S Van Cholera toxin: interaction of subunits with ganglioside GM1. Science. 1974 Feb 15;183(4125):656–657. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4125.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lönnroth I., Månsson J., Svennerholm L. Interaction of cholera toxin and membrane GM1 ganglioside of small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2520–2524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfer U., Nelson K., Perrotto J., Isselbacher K. J. Glucose transport in isolated brush border membrane from rat small intestine. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):25–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Gershon E., Henderson A. Effects of prostaglandins and cholera enterotoxin on intestinal mucosal cyclic AMP accumulation. Evidence against an essential role for prostaglandins in the action of toxin. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):941–949. doi: 10.1172/JCI107635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Johnson J., Henderson A., Gershon E. Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI106599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lospalluto J. J., Finkelstein R. A. Chemical and physical properties of cholera exo-enterotoxin (choleragen) and its spontaneously formed toxoid (choleragenoid). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 26;257(1):158–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90265-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Gowans J. L. Cellular kinetics of the intestinal immune response to cholera toxoid in rats. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1550–1563. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Kaniecki E. A., Northrup R. S. Protection against experimental cholera by antitoxin. J Infect Dis. 1972 Dec;126(6):606–616. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.6.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Reynolds H. Y. Immunity to experimental cholera. I. Protective effect of humoral IgG antitoxin demonstrated by passive immunization. J Immunol. 1974 Sep;113(3):1017–1023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Reynolds H. Y. Immunity to experimental cholera. II. Secretory and humoral antitoxin response to local and systemic toxoid administration. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):383–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer D. E., Lust W. D., Sircar B., Goldberg N. D. Elevated concentration of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in intestinal mucosa after treatment with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):851–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W. Action of cholera toxin on fluid and electrolyte movement in the small intestine. Annu Rev Med. 1973;24:19–23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.24.020173.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Hynie S. Stimulation of intestinal adenyl cyclase by cholera toxin. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):266–269. doi: 10.1038/229266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stechschulte D. J., Austen K. F. Immunoglobulins of rat colostrum. J Immunol. 1970 May;104(5):1052–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Field M., Isselbacher K. J. Specific binding of cholera toxin to isolated intestinal microvillous membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):320–324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Isselbacher K. J., Bloch K. J. Intestinal uptake of macromolecules. II. Effect of parenteral immunization. J Immunol. 1973 Jul;111(1):221–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Wu M., Isselbacher K. J., Bloch K. J. Intestinal uptake of macromolecules. III. Studies on the mechanism by which immunization interferes with antigen uptake. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):854–861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Wu M., Isselbacher K. J., Bloch K. J. Intestinal uptake of macromolecules. IV.--The effect of pancreatic duct ligation on the breakdown of antigen and antigen-antibody complexes on the intestinal surface. Gastroenterology. 1975 Dec;69(6):1223–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser M. M., Quill H. Intestinal villus and crypt cell responses to cholera toxin. Gastroenterology. 1975 Aug;69(2):479–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Gibbons R. J. Inhibition of bacterial adherence by secretory immunoglobulin A: a mechanism of antigen disposal. Science. 1972 Aug 25;177(4050):697–699. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4050.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]