Abstract
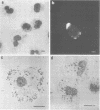
Antibodies in both mouse and human Rickettsia mooseri (Rickettsia typhi) convalescent serum that were cytophilic for mouse macrophages were demonstrated by the rosette technique. Mouse peritoneal macrophages, passively sensitized with early and late serum from mice with a sublethal infection of R. mooseri, were washed and exposed to rickettsiae. Rosettes of rickettsiae were found around macrophages, maintained at 4 degrees C, which had been sensitized with immune serum (direct sensitization of macrophages), but no rosettes were found around macrophages sensitized with serum from normal mice. When the macrophages were maintained at 34 degrees C after addition of the rickettsiae, phagocytosis of rickettsiae occurred, indicating one probable role for cytophilic antibodies in typhus infections. If the rickettsiae were mixed with serum from infected mice, washed, and then added to macrophages (indirect sensitization of macrophages), more rosettes were found around the macrophages than around directly sensitized macrophages. The presence of mouse immunoglobulin G on the macrophage surface was also shown by staining living sensitized macrophages with rabbit fluroescein-conjugated anti-mouse immunoglobulin G.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYDEN S. V. CYTOPHILIC ANTIBODY IN GUINEA-PIGS WITH DELAYED-TYPE HYPERSENSITIVITY. Immunology. 1964 Jul;7:474–483. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L., Wisseman C. L., Jr Mechanisms of immunity in typhus infections. VI. Differential opsonizing and neutralizing action of human typhus rickettsia-specific cytophilic antibodies in cultures of human macrophages. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1071–1076. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1071-1076.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berken A., Benacerraf B. Properties of antibodies cytophilic for macrophages. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):119–144. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambrill M. R., Wisseman C. L., Jr Mechanisms of immunity in typhus infections. 3. Influence of human immune serum and complement on the fate of Rickettsia mooseri within the human macrophages. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):631–640. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.631-640.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchley C., Grey H. M., Uhr J. W. The cytophilic activity of human immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1970 Aug;105(2):362–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lay W. H., Nussenzweig V. Ca++-dependent binding of antigen-19 S antibody complexes to macrophages. J Immunol. 1969 May;102(5):1172–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lay W. H., Nussenzweig V. Receptors for complement of leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):991–1009. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis J. M., Bigley N. J. Cytophilic macroglobulin reactive with bacterial protein in mice immunized with ribonucleic acid-protein fractions of virulent Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):390–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.390-397.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M. The dissociation of the attachment and ingestion phases of phagocytosis by macrophages. Exp Cell Res. 1967 Apr;46(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90405-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberman R., Fiset P. Method for counting Rickettsiae and Chlamydiae in purified suspensions. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):259–261. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.259-261.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tizard I. R. Macrophage cytophilic antibodies in mice: inability to induce ingestion of sheep erythrocytes by mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):931–936. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.931-936.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tizard I. R. Macrophage cytophilic antibody in mice. The relationship between the adherence of antigen to macrophages mediated by macrophage-cytophilic antibodies and opsonic adherence antibodies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;39(2-3):201–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. D., Walsh W. T. Mechanisms of immunity in typhus infections. IV. Failure of chicken embryo cells in culture to restrict growth of antibody-sensitized Rickettsia prowazeki. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):571–575. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.571-575.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]