Abstract
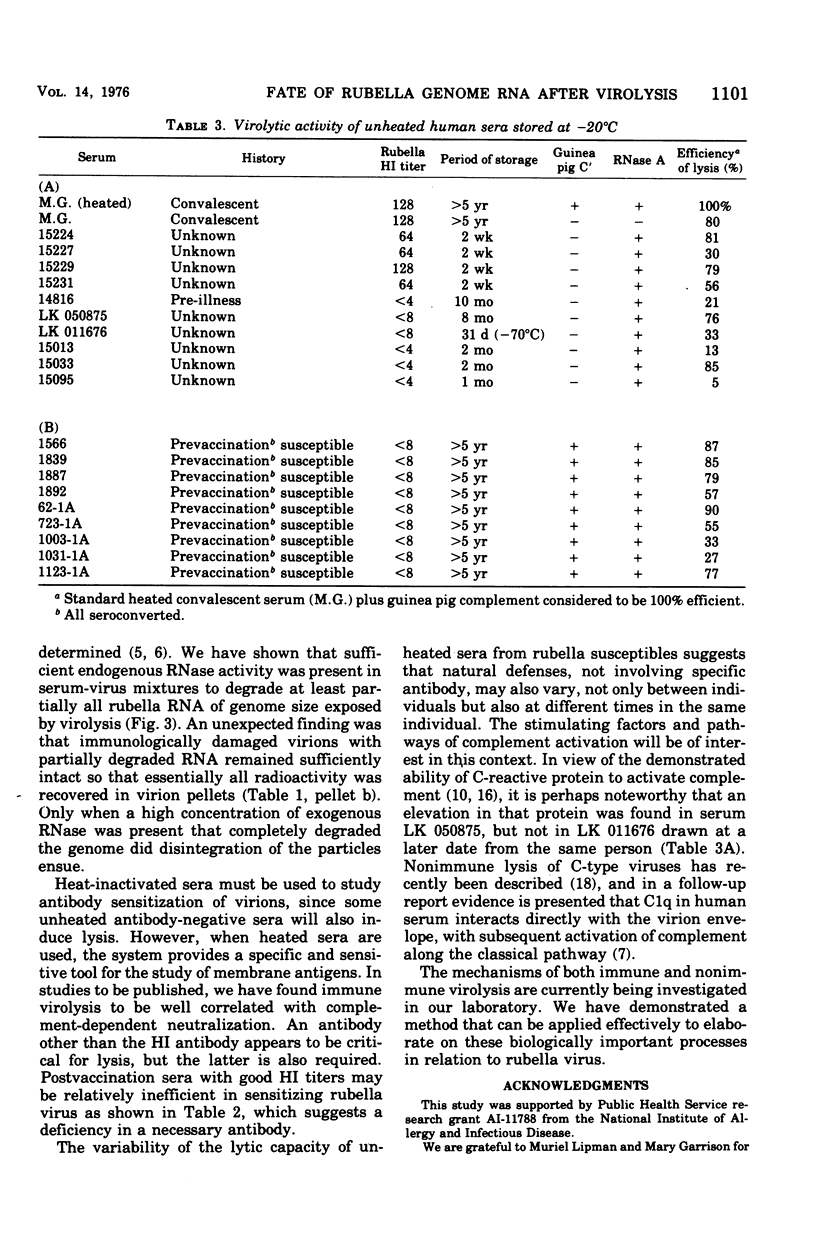
To determine whether rubella virion ribonucleic acid (RNA) becomes accessible to nuclease attack after immune lysis of the viral envelope, virions containing radioactively labeled RNA were examined in three ways with the following results. (i) Incubation of purified virus with heat-inactivated rubella convalescent human serum and guinea pig complement resulted in an increase in acid-soluble RNA. Antibody was required; the reaction was temperature dependent and was blocked by ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. When exogenous nuclease was added prior to lysis, radioactivity in virions was reduced to 15% of that in unlysed control pellets (ii) Sucrose gradient sedimentation profiles of RNA released from lysed and unlysed virions under controlled conditions showed that the nuclease content of serum-virus mixtures was sufficient to eliminate all RNA of genome size, although degradation was not complete. (iii) Virions were also lysed by unheated human immune sera in the absence of guinea pig complement and by some, but not all, unheated antibody-negative sera.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida J. D., Laurence G. D. Heated and unheated antiserum on rubella virus. Morphological effect. Am J Dis Child. 1969 Jul;118(1):101–106. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1969.02100040103017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida J. D., Waterson A. P. The morphology of virus-antibody interaction. Adv Virus Res. 1969;15:307–338. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60878-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORSOS T., DOURMASHKIN R. R., HUMPHREY J. H. LESIONS IN ERYTHROCYTE MEMBRANES CAUSED BY IMMUNE HAEMOLYSIS. Nature. 1964 Apr 18;202:251–252. doi: 10.1038/202251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry D. M., Almeida J. D. The morphological and biological effects of various antisera on avian infectious bronchitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1968 Jul;3(1):97–102. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNOLLY J. H., HERRIOTT R. M., GUPTA S. Deoxyribonuclease in human blood and platelets. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Aug;43:392–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONNOLLY J. H., HERRIOTT R. M., GUPTA S. Ribonuclease in normal and uraemic human blood. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Aug;43:402–408. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRIOTT R. M., CONNOLLY J. H., GUPTA S. Blood nucleases and infectious viral nucleic acids. Nature. 1961 Mar 11;189:817–820. doi: 10.1038/189817a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovi T. Release of rubella virus ribonucleic acid from ribonucleoprotein by polyanions. J Virol. 1972 May;9(5):879–882. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.5.879-882.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. H., Volanakis J. E. Interaction of C-reactive protein complexes with the complement system. I. Consumption of human complement associated with the reaction of C-reactive protein with pneumococcal C-polysaccharide and with the choline phosphatides, lecithin and sphingomyelin. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2135–2147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebhaber H. Measurement of rubella antibody by hemagglutination inhibition. II. Characteristics of an improved HAI test employing a new method for the removal of non-immunoglobulin HA inhibitors from serum. J Immunol. 1970 Apr;104(4):826–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebhaber H., Pajot T., Riordan J. T. Growth of high titered rubella virus in roller bottle cultures of Vero cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jan;130(1):12–14. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oroszlan S., Gilden R. V. Immune virolysis: effect of antibody and complement on C-type RNA virus. Science. 1970 Jun 19;168(3938):1478–1480. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3938.1478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radwan A. I., Burger D., Davis W. C. The fate of sensitized equine arteritis virus following neutralization by complement of anti-IgG serum. Virology. 1973 Jun;53(2):372–378. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90216-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawls W. E., Desmyter J., Melnick J. L. Rubella virus neutralization by plaque reduction. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jan;124(1):167–172. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J., Rent R., Gewurz H. Interactions of C-reactive protein with the complement system. I. Protamine-induced consumption of complement in acute phase sera. J Exp Med. 1974 Sep 1;140(3):631–647. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar V. Immune lysis of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1975 Aug;66(2):620–624. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Jr, Cooper N. R., Jensen F. C., Oldstone M. B. Human serum lyses RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1975 Oct 16;257(5527):612–614. doi: 10.1038/257612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]