Abstract
AIM: To investigate the molecular mechanisms of the anti-cancer activity of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE).
METHODS: Protein profiles of human colorectal cancer SW480 cells treated with or without CAPE were analysed using a two-dimensional (2D) electrophoresis gel-based proteomics approach. After electrophoresis, the gels were stained with Coomassie brilliant blue R-250. Digital images were taken with a GS-800 Calibrated Densitometer, and image analysis was performed using PDQuest 2-D Analysis software. The altered proteins following CAPE treatment were further identified by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry following a database search. The identified proteins were validated by Western blot and immunofluorescence assay.
RESULTS: CAPE induced human colorectal cancer cell apoptosis. Four up-regulated proteins and seven down-regulated proteins in colorectal cancer cells treated with CAPE were found. The identified down-regulated proteins in CAPE-treated colorectal cancer cells were Triosephosphate Isomerase (Tim), Proteasome subunit alpha 4 (PSMA4) protein, Guanine nucleotide binding protein beta, Phosphoserine aminotransferase 1 (PSAT1), PSMA1, Myosin XVIIIB and Tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase. Notably, CAPE treatment led to the down-regulation of PSAT1 and PSMA1, two proteins that have been implicated in tumorigenesis. The identified up-regulated proteins were Annexin A4, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, Glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase 1 (GNPDA1), and Glutathione peroxidase (GPX-1). Based on high match scores and potential role in cell growth control, PSMA1, PSAT1, GNPDA1 and GPX-1 were further validated by Western blotting and immunofluorescence assay. PSMA1 and PSAT1 were down-regulated, while GNPDA1 and GPX-1 were up-regulated in CAPE-treated colorectal cancer cells.
CONCLUSION: These differentiated proteins in colorectal cancer cells following CAPE treatment, may be potential molecular targets of CAPE and involved in the anti-cancer effect of CAPE.
Keywords: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester, Colorectal cancer, Proteomics, Two-dimensional electrophoresis, Mass spectrometry
Core tip: To investigate the molecular mechanisms of the anti-cancer activity of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), CAPE-treated colorectal cancer SW480 cells were analysed by a 2D-gel based proteomics approach. Four up-regulated proteins and seven down-regulated proteins in CAPE-treated SW480 cells were found and further identified by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry following a database search. The down-regulated proteins, PSMA1 and PSAT1 and up-regulated proteins GNPDA1 and GPX-1 were validated by Western blotting. The two tumorigenesis associated proteins, PSMA1 and PSAT1, were further confirmed by immunofluorescence assay. These differentiated proteins in colorectal cancer cells following CAPE treatment, may be potential molecular targets of CAPE and involved in the anti-cancer effect of CAPE.
INTRODUCTION
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most commonly diagnosed malignancies and the third deadliest cancer in humans. In 2012, it was estimated that 143460 people in the United States had been diagnosed with colorectal cancer and that 51690 will die from this disease[1,2]. In the last few decades, enormous advances in the diagnosis and treatment of CRC have been made, and molecular biology has clarified some of the mechanisms involved in the carcinogenic process. However, patient prognosis is still poor; after curative resections, approximately 50% of patients succumb to recurrent and metastatic disease during the first 2 years of follow-up. For this reason, novel anti-cancer drugs for CRC are urgently needed.
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), a component of propolis is a phenolic antioxidant. CAPE has been shown to help in host defence through its anti-viral and anti-bacterial activity. In addition, the immunoregulatory properties, anti-inflammatory activity and anti-cancer activity of CAPE have been reported. Several studies have demonstrated that CAPE has anti-proliferative effects by inducing apoptosis in various tumour cells in vitro[3-7] and in vivo[8,9]. CAPE also inhibits the development of azoxymethane-induced aberrant crypts in the colon of rats[10].
Multiple molecular mechanisms seem to be involved in the anti-cancer effects of CAPE. We have previously shown that decreased β-catenin and associated signalling pathways may mediate the anti-cancer effects of CAPE[2]. It has been reported that CAPE inhibits tumor necrosis factor alpha-dependent nuclear factor kappa beta (NFκB) activation via direct inhibitory protein kappaB kinase inhibition and Nuclear factor-erythroid 2 p45 (NF-E2)-related factor 2 pathway activation[11]. Previous studies have also shown that Mcl-1 down-regulation, Bcl-2 expression, and Bax up-regulation, as well as activation of caspase-8, caspase-3, and PARP, are associated with CAPE-dependent cellular apoptosis[12,13]. However, the exact anti-tumour mechanism of CAPE is not fully understood.
To understand the mechanism of the anti-cancer activity of CAPE, CAPE-treated colorectal cancer SW480 cells were analysed by a 2D-gel based proteomics approach. Differentially expressed proteins were identified by mass spectrometry and then validated by Western blotting and confocal microscopy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell culture
The human CRC cell line SW480 was purchased from the American Type Culture Collection. The cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with penicillin G (100 U/mL), streptomycin (100 μg/mL), and 10% foetal calf serum. The cells were grown at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 and were routinely sub-cultured using 0.25% (w/v) trypsin-EDTA solution. All cell culture reagents were purchased from GIBCO (Carlsbad, United States). For CAPE treatment, CAPE was dissolved in DMSO and adjusted to a working concentration with culture medium before use (DMSO concentration was 0.1%). CAPE was added to the culture medium on the second day at a working concentration of 10 μg/mL.
TUNEL staining
SW480 cells were grown on poly-L-lysine coated slides in a six-well plate. After treatment with or without CAPE for 48 h, the slides were gently washed three times in 0.1 mol/L PBS (pH = 7.4) and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde. To determine cellular apoptosis, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labelling (TUNEL) assays were performed using the TUNEL Detection kit (Boehringer Mannheim, Mannheim, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. All samples were observed under a microscope. Cell apoptosis was determined by counting TUNEL positive cells under a light microscope at × 40 objective.
Protein separation by 2-D electrophoresis
SW480 cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium with or without CAPE (10 μg/mL) for 48 h. The cells were carefully collected using a cell scraper. All reagents for 2D electrophoresis were obtained from Amersham Pharmacia Biotech (Uppsala, Sweden), except those otherwise indicated. To perform 2D electrophoresis, SW480 tumour cells were suspended in lysis buffer containing 40 mmol/L Tris, 8 mol/L urea, 4% CHAPS, 60 mmol/L DTT, 0.8% IPG buffer (pH = 3-10), and protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche, Mannheim, Germany). Protein concentration was measured with the DC Protein Assay (BioRad, United States). Proteins (500 mg/gel) were loaded into IEF gels (pH = 3-10). The gels were immersed overnight in hydration buffer containing 8 M urea, 4% CHAPS, 60 mmol/L DTT, and 0.5% IPG buffer. After sample loading, IEF gels were run at 200 V for 1 h, 500 V for 1 h, 1000 V for 1 h and then were gradually increased to 8000 V for 5-6 h. Focusing was carried out at 35000 V·h. After IEF, IPG strips were equilibrated twice in equilibration buffer (50 mmol/L Tris-HCl (pH = 8.8), 6 mol/L urea, 30% glycerol, 2% SDS). In the first equilibration, 100 mg of DTT was dissolved in 10 mL of equilibration buffer, and 400 mg of iodoacetamide was added in the second equilibration. The strips were then transferred onto vertical slab 12.5% SDS-PAGE gels and sealed with 0.5% low melting point agarose.
Image analysis
After electrophoresis, the gels were stained with Coomassie brilliant blue R-250. Digital images were taken with a GS-800 Calibrated Densitometer (BioRad, USA), and image analysis was performed with PDQuest 2-D Analysis software (BioRad, United States).
Protein in-gel enzyme digestion and identification
In-gel digestion was performed as described by Rosenfeld[14]. Briefly, spots were excised from the stained gel, destained with 25 mmol/L ammonium bicarbonate/50% acetonitrile (ACN), and then dried with a SpeedVac plus SC1 10 (Savant Holbook, United States). The dried gels were rehydrated in trypsin solution (Promega, United States) at 37 °C overnight. After rehydration, peptides were first eluted with 5% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) at 40 °C for 1 h, and then eluted with 2.5% TFA/50% ACN at 30 °C for 1 h. ACN was removed by centrifugation in a vacuum centrifuge. The peptides were concentrated using C18 pipette tips (Millipore, Bedford, MA, United States). Analysis was performed primarily using the matrix-assisted laser desorption ionisation time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometer (Bruker, Germany). Peptide mixtures were analysed using a saturated solution of α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (Sigma, United States) in acetone containing 1% TFA. Peptides were selected in the mass range of 800-4000 Da. The peptide sequence was determined with MASCOT software. Sequence homology was analysed using the MASCOT program and the NCBI BLAST online search service. The database NCBInr 20060731 was used.
Western blotting
SW480 cells were treated with or without CAPE (10 μg/mL) for 48 h. The cells were lysed in SDS-sample loading buffer and boiled at 100 °C for 5 min. The cell lysates were then subjected to SDS-PAGE. Proteins in the gel were then transferred onto PVDF membranes. The PVDF membranes were incubated for 2 h in blocking buffer (5% milk in 10 mmol/L Tris-HCl (pH = 7.5), 2.5 mmol/L EDTA (pH = 8.0), 50 mmol/L NaCl). The membranes were then incubated in antibodies against PSMA1, PSAT1, GNPDA1 or GPX1 (Sigma-Aldrich, United States) at a dilution of 1:1000 for 2 h at room temperature. After washing three times with washing buffer (TBS buffer containing 0.01% Tween 20), the membranes were incubated with HRP-conjugated anti-human IgG antibodies (Zhongshan Inc., Beijing, China) at a dilution of 1:5000 for 1 h at room temperature. Immunodetection was determined using the ECL-plus kit (Roche, United States) and autoradiography.
Immunofluorescence assay
SW480 cells grown on glass coverslips were treated with or without CAPE (10 μg/mL) for 48 h under standard culture conditions as described above. The cells were washed with PBS and fixed with methanol for 20 min. Incubation with anti-PSMA1, and anti-PSAT1 monoclonal antibody (1:500) was carried out overnight at 4 °C. This step was followed by incubation with FITC-conjugated secondary antibody (1:1000) for 1 h at room temperature. DAPI was used to stain the nucleus. Images were captured using a laser scanning confocal microscope (Leica, Germany).
RESULTS
CAPE inhibits tumour cell growth and induces apoptosis
To set up the cell culture system with CAPE treatment, SW480 cells were treated with CAPE at 5 μg/mL or 10 μg/mL, and cell growth was monitored daily by cell counting for a few days. Similar to a previous study[2], 10 μg/mL of CAPE effectively inhibited cell growth when compared to untreated control cells (data not shown). To determine if cell growth inhibition was caused by cell apoptosis, TUNEL assay was performed. We found a dose-dependent increase in cell apoptosis following treatment with CAPE (Figure 1A-D). Our data suggest that the growth inhibitory effect of CAPE may be associated with an increase in cell apoptosis.
Figure 1.
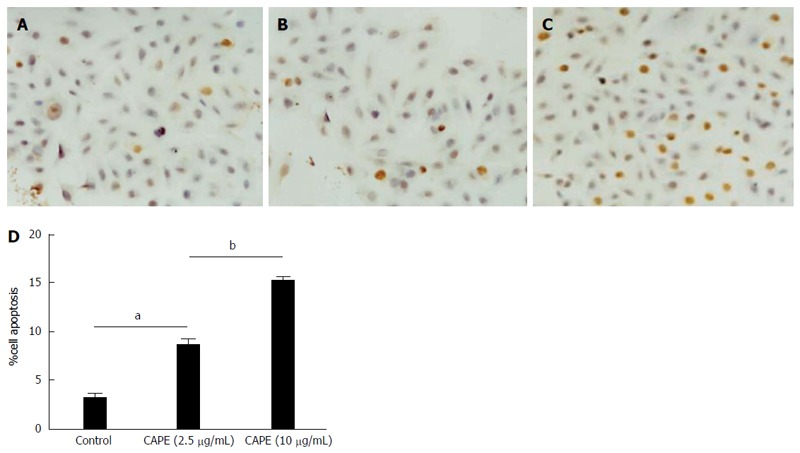
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester induces colorectal cancer cell apoptosis. SW480 cells were treated with caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) in 24-well plates. For TUNEL staining, cells were treated without (A), with 2.5 μg/mL (B), or 10 μg/mL (C) CAPE for 48 h and cell apoptosis was examined using the TUNEL detection kit. Cell apoptosis was determined by counting TUNEL positive cells under a light microscope at × 40 objective (D). Results are representative of 3 independent experiments with similar results. aP < 0.05 vs controls; bP < 0.01, CAPE (2.5 μg/mL) vs CAPE (10 μg/mL).
Identification of differentially expressed proteins by the proteomics approach
To investigate the molecular mechanisms of the anti-cancer activity of CAPE, CAPE-treated colorectal cancer SW480 cells were analysed by a 2D-gel based proteomics approach. We used a cell viability assay to determine the optimum CAPE concentration of 10 μg/mL for cell treatment over 48 h.
Protein expression profiles in SW480 cells with or without CAPE treatment were compared by 2D electrophoresis (2-DE). Approximately 250 protein spots in untreated (Figure 2A) and treated cells (Figure 2B) were detected on the Coomassie stained gels. All spots were matched by gel-to-gel comparison using PDQuest software, and the difference in the relative abundance of each protein spot was analysed. Four up-regulated and seven down-regulated protein spots in the treated SW480 cells were found repeatedly (Figure 2C). Those eleven highly repeatable proteins were excised and then identified by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and a database search. The seven down-regulated proteins in response to CAPE treatment were Triosephosphate isomerase, PSMA4 protein, guanine nucleotide-binding protein, PSAT1, PSMA1, myosin WVIIIB, and human tryptophanal-tRNA synthetase (Table 1). The up-regulated proteins were Annexin A4, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, Glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase 1 (GNPDA1), and glutathione peroxidase (GPX-1) (Table 2).
Figure 2.
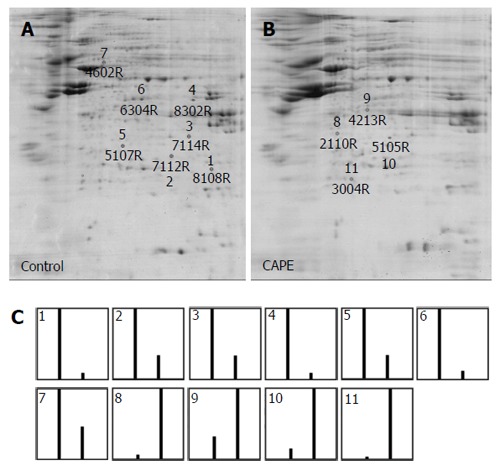
Protein profiles of SW480 cells treated with caffeic acid phenethyl ester by two-dimensional PAGE. SW480 cells were treated without (A) or with (B) 10 μg/mL caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) for 48 h and then harvested for 2D-PAGE analysis. 500 mg of cellular protein was applied to the IEF gel. After electrophoresis, the gels were stained with Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 and the proteins were analysed by PDQuest 2-D analysis software. The marked spots shown on the gels were the down-regulated proteins (shown by numbers 1-7) and the up-regulated proteins (shown by numbers 8-11). The relative abundance of each differentially expressed protein in the 2 gels was analysed by PDQuest (C). The first bar shown in the graph is the relative abundance of the proteins in untreated cells and the second bar is the relative abundance of the proteins in CAPE-treated cells. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments with similar results.
Table 1.
Identification of down-regulated proteins in SW480 cells treated with caffeic acid phenethyl ester
| No. | Protein name | Accession No. | Matched peptides | Protein sequence coverage | Mascot score | MW/pI |
| 1 | Triosephosphate Isomerase (Tim) | gi|15079533 | FFVGGNWK | 79% | 131 | 26.8/6.51 |
| KQSLGELIGTLNAAK | ||||||
| VPADTEVVCAPPTAYIDFAR | ||||||
| IAVAAQNCYK | ||||||
| VTNGAFTGEISPGMIK | ||||||
| DCGATWVVLGHSER | ||||||
| RHVFGESDELIGQK | ||||||
| HVFGESDELIGQK | ||||||
| VAHALAEGLGVIACIGEK | ||||||
| VVLAYEPVWAIGTGK | ||||||
| TATPQQAQEVHEK | ||||||
| SNVSDAVAQSTR | ||||||
| IIYGGSVTGATCK | ||||||
| ELASQPDVDGFLVGGASLKPEFVDIINAK | ||||||
| 2 | PSMA4 protein | gi|34783332 | TTIFSPEGR | 50% | 70 | 29.6/7.56 |
| LLDEVFFSEK | ||||||
| LNEDMACSVAGITSDANVLTNELR | ||||||
| YLLQYQEPIPCEQLVTALCDIK | ||||||
| RPFGVSLLYIGWDK | ||||||
| HYGFQLYQSDPSGNYGGWK | ||||||
| ATCIGNNSAAAVSMLK | ||||||
| QKEVEQLIK | ||||||
| KHEEEEAK | ||||||
| 3 | Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), beta polypeptide 2-like 1 | gi|5174447 | GHNGWVTQIATTPQFPDMILSASR | 80% | 154 | 35.5/7.6 |
| DETNYGIPQR | ||||||
| GHSHFVSDVVISSDGQFALSGSWDGTLR | ||||||
| LWDLTTGTTTR | ||||||
| DVLSVAFSSDNR | ||||||
| YTVQDESHSEWVSCVR | ||||||
| FSPNSSNPIIVSCGWDK | ||||||
| FSPNSSNPIIVSCGWDKLVK | ||||||
| VWNLANCK | ||||||
| TNHIGHTGYLNTVTVSPDGSLCASGGK | ||||||
| DGQAMLWDLNEGK | ||||||
| HLYTLDGGDIINALCFSPNR | ||||||
| YWLCAATGPSIK | ||||||
| IIVDELKQEVISTSSK | ||||||
| AEPPQCTSLAWSADGQTLFAGYTDNLVR | ||||||
| VWQVTIGTR | ||||||
| 4 | Phosphoserine aminotransferase 1 (PSAT1) | gi|17390289 | QVVNFGPGPAK | 38% | 79 | 40.9/7.56 |
| LPHSVLLEIQK | ||||||
| GVGISVLEMSHR | ||||||
| CADYVVTGAWSAK | ||||||
| FGTINIVHPK | ||||||
| FGTINIVHPKLGSYTK | ||||||
| GAVLVCDMSSNFLSKPVDVSK | ||||||
| NVGSAGVTVVIVR | ||||||
| DDLLGFALR | ||||||
| SQTIYEIIDNSQGFYVCPVEPQNR | ||||||
| ASLYNAVTIEDVQK | ||||||
| 5 | Proteasome (prosome, macropain) subunit, alpha type, 1 (PSMA1) | gi|18490859 | NQYDNDVTVWSPQGR | 50% | 81 | 29.8/6.15 |
| IHQIEYAMEAVK | ||||||
| IHQIEYAMEAVKQGSATVGLK | ||||||
| ILHVDNHIGISIAGLTADAR | ||||||
| LLCNFMR | ||||||
| FVFDRPLPVSR | ||||||
| HMSEFMECNLNELVK | ||||||
| DLEFTIYDDDDVSPFLEGLEERPQR | ||||||
| AQPAQPADEPAEKADEPMEH | ||||||
| 6 | Myosin XVIIIB | gi|51317366 | DRQGTRPQAQGPGEGVRPGK | 14% | 75 | 28.7/6.45 |
| EGAEPTNTVEKGNVSK | ||||||
| STTGKAGESWDK | ||||||
| MGQPQGKSGNAGEAR | ||||||
| AGDGAGALETELEGPSQPALEK | ||||||
| AGDGAGALETELEGPSQPALEKDAERPR | ||||||
| RDQSIVALGWSGAGK | ||||||
| QKAAAAFAQLQGAMEMLGISESEQR | ||||||
| AAAAFAQLQGAMEMLGISESEQRAVWR | ||||||
| QIIQQMTFGPSR+ Oxidation (M) | ||||||
| SFSSHHLSMASIMVVDSPGFQNPR + 2 Oxidation (M);Pyro-glu (N-term Q) | ||||||
| LQLLFYQRTFVSTLQR | ||||||
| AVAGLEGTSQQALQR | ||||||
| LQMDALTSMIK+ 2 Oxidation (M) | ||||||
| NPTGGADEWQMR + 2 Oxidation (M) | ||||||
| FDLQLAQALGESVFEK | ||||||
| WELGQLQQQLKQK | ||||||
| FELEIERMK+ Oxidation (M) | ||||||
| RTHALLSDVQLLLGTMEDGK | ||||||
| HKLQEQLQVAQMR+ Oxidation (M) | ||||||
| DSLIKMGEELSQAATSESQQR+ Oxidation (M) | ||||||
| CMELEKYVEELAAVR + Oxidation (M) | ||||||
| INEEAGDTERTQSALALSR + Oxidation (M) | ||||||
| DMLLSPTLRPR+ Oxidation (M) | ||||||
| DMLLSPTLRPRR | ||||||
| 7 | Chain B, A Short Peptide Insertion Crucial For Angiostatic Activity Of Human Tryptophanyl-tRNA Synthetase | gi|42543731 | EDFVDPWTVQTSSAKGIDYDK | 56% | 79 | 44.9/6.41 |
| ATGQRPHHFLR | ||||||
| GIFFSHR | ||||||
| GIFFSHRDMNQVLDAYENK | ||||||
| KPFYLYTGR | ||||||
| GPSSEAMHVGHLIPFIFTK | ||||||
| WLQDVFNVPLVIQMTDDEK+ Oxidation (M) | ||||||
| TFIFSDLDYMGMSSGFYK + Oxidation (M) | ||||||
| HVTFNQVK | ||||||
| GIFGFTDSDCIGK | ||||||
| ISFPAIQAAPSFSNSFPQIFR | ||||||
| IGYPKPALLHSTFFPALQGAQTK | ||||||
| MSASDPNSSIFLTDTAK | ||||||
| ALIEVLQPLIAEHQAR | ||||||
| KLSFDFQ |
Table 2.
Identification of up-regulated proteins in SW480 cells treated with caffeic acid phenethyl ester
| No. | Protein name | Accession No. | Matched peptides | Protein sequence coverage | Mascot score | MW/pI |
| 8 | Annexin A4 | gi|12652859 | AASGFNAMEDAQTLR | 56% | 105 | 36.2/5.65 |
| GLGTDEDAIISVLAYR | ||||||
| GAGTDEGCLIEILASR | ||||||
| ISQTYQQQYGR | ||||||
| SLEDDIRSDTSFMFQR + Oxidation (M) | ||||||
| SDTSFMFQR+ Oxidation (M) | ||||||
| VLVSLSAGGR | ||||||
| DEGNYLDDALVR | ||||||
| QDAQDLYEAGEK | ||||||
| FLTVLCSR | ||||||
| NRNHLLHVFDEYK | ||||||
| NHLLHVFDEYK | ||||||
| NHLLHVFDEYKR | ||||||
| SETSGSFEDALLAIVK | ||||||
| NKSAYFAEK | ||||||
| GLGTDDNTLIR | ||||||
| VMVSRAEIDMLDIR+2 Oxidation (M) | ||||||
| AEIDMLDIR | ||||||
| 9 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | gi|31645 | LVINGNPITIFQERDPSK | 46% | 76 | 36.2/8.28 |
| WGDAGAEYVVESTGVFTTMEK | ||||||
| RVIISAPSADAPMFVMGVNHEK | ||||||
| IISNASCTTNCLAPLAK | ||||||
| VIHDNFGIVEGLMTTVHAITATQK | ||||||
| GALQNIIPASTGAAK | ||||||
| VPTANVSVVDLTCR | ||||||
| LISWYDNEFGYSNR | ||||||
| VVDLMAHMASK+2 Oxidation (M) | ||||||
| 10 | Glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase 1 (GNPDA1) | gi|18490843 | IIQFNPGPEK | 54% | 90 | 32.8/6.42 |
| YFTLGLPTGSTPLGCYK | ||||||
| TFNMDEYVGLPR | ||||||
| AAGGIELFVGGIGPDGHIAFNEPGSSLVSR | ||||||
| TLAMDTILANAR | ||||||
| VPTMALTVGVGTVMDAR | ||||||
| EVMILITGAHKAFALYK | ||||||
| AIEEGVNHMWTVSAFQQHPR | ||||||
| TVFVCDEDATLELK | ||||||
| ETEKSQSSK | ||||||
| 11 | Glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPX1) | gi|14717805 | GLVVLGFPCNQFGHQENAK | 56% | 70 | 22.2/6.15 |
| YVRPGGGFEPNFMLFEK | ||||||
| CEVNGAGAHPLFAFLR | ||||||
| EALPAPSDDATALMTDPKLITWSPVCR | ||||||
| LITWSPVCR | ||||||
| FLVGPDGVPLR | ||||||
| FLVGPDGVPLRR | ||||||
| RFQTIDIEPDIEALLSQGPSCA |
Validation of differentially expressed proteins
To validate the above proteomic findings, the expression levels of some identified proteins were examined by Western blot analysis. Proteins were selected for further analysis based on both their high match score and their probable role in cell growth control. Similar to our earlier observation (Figure 2), the expression of PSMA1 and PSAT1 was down-regulated, and the expression of GNPDA1 and GPX-1 was up-regulated in CAPE-treated cells (Figure 3A and B). The identity of the two tumorigenesis associated proteins, PSMA1 and PSAT1, were further confirmed by immunofluorescence assay. PSMA1 and PSAT1 were mainly expressed on the cell membrane and in the cytosol (Figure 3B and C). After CAPE treatment, the expression levels of PSMA1 and PSAT1 were altered, although the cellular localisation of these proteins did not change (Figure 3B and C).
Figure 3.
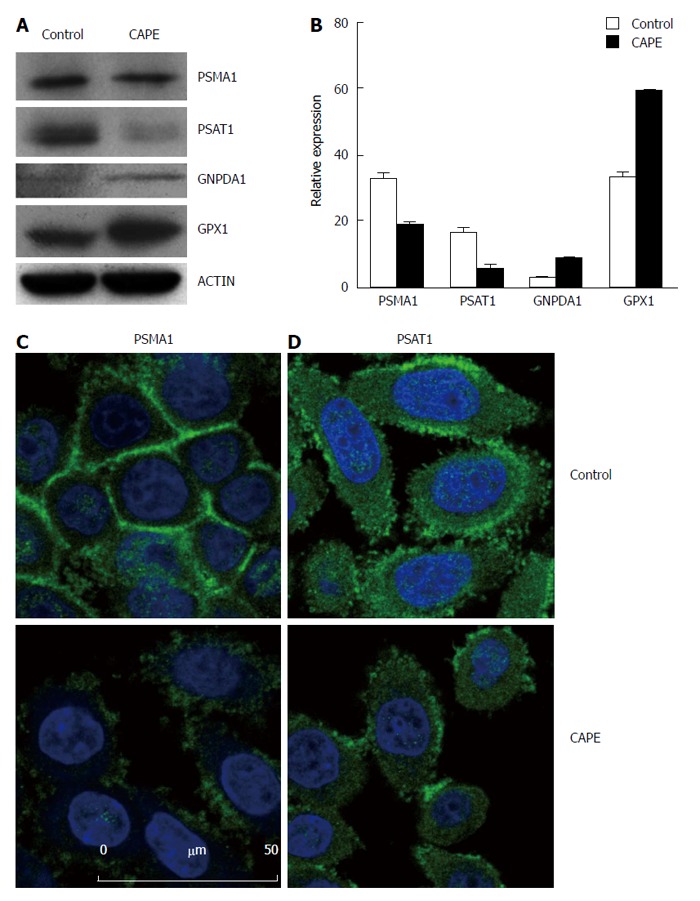
Validation of differentially expressed proteins in SW480 treated with caffeic acid phenethyl ester. SW480 cells were treated without (control) and with 10 μg/mL CAPE for 48 h and then harvested for Western blotting (A and B) or immunofluorescence assay (C and D). For Western blotting, beta-actin was included as the internal control. Densitometric analysis was performed and the integrated density values are presented as the ratio of each protein over the beta-actin protein (B). For the immunofluorescence assay, SW480 cells were grown on glass coverslips and treated without (control) or with CAPE (10 μg/mL) for 48 h. The cells were washed with PBS and fixed with methanol. Anti-PSMA1 (A), and anti-PSAT1 (B) monoclonal antibodies were applied as the primary antibodies, and then, FITC-conjugated secondary antibodies were used. DAPI was used to stain the nucleus. Results are representative of 2 independent experiments with similar results. PSMA1: Proteasome subunit alpha 1; PSAT1: Phosphoserine aminotransferase 1.
DISCUSSION
Propolis has been used in folk medicine since ancient times and has been noted to exhibit immunoregulatory, anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumorigenic activities in different models[15-17]. CAPE is a component of propolis and is therefore implicated in the activity of propolis. CAPE has been shown to selectively target tumour cells and to inhibit tumour cell proliferation. In addition, CAPE has been demonstrated to induce apoptosis in different types of tumours including breast cancer[18], myeloid leukaemia[13], cervical cancer[12], hepatocarcinoma cell[19], cholangiocarcinoma[7], and glioma[20].
In our previous studies, we demonstrated that CAPE could inhibit colorectal cancer cell proliferation by inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis[2]. Recently, it was shown that CAPE was a specific inhibitor of nuclear factor κB, inducing apoptosis via activation of the Fas signalling pathway in human tumour cells[21]. Other signalling pathways may also be involved[2,11,13,19]. To investigate the molecular mechanisms of the anti-cancer activity of CAPE, we compared the protein expression profiles of treated SW480 cells using 2D electrophoresis. Highly repeatable protein spots were selected and identified by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and online database searching.
PSAT1 belongs to subgroup IV of the aminotransferases and plays a crucial role in linking the central catabolic pathways (glycolysis) and amino acid biosynthesis pathways. PSAT1 catalyses the second step in the biosynthesis of the amino acid, serine, which in turn, is the crucial carbon source for purine nucleotides, phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylserine, and other cellular metabolites. PSAT1 is weakly expressed in the normal colon, but overexpressed in colon cancer with increased expression as disease progresses[22,23]. PSAT1 expression was shown to be up-regulated during the colorectal adenoma-to-carcinoma sequence by proteomic technology[24]. Recently, it has been reported that the overexpression of PSAT1 stimulates cell growth and increases the chemoresistance of colon cancer cells[25], indicating that overexpression of PSAT1 may be involved in tumorigenesis and promotes cell growth. In contrast, down-regulation of PAST1 in CAPE-treated colorectal cancer cells may be associated with cell growth inhibition.
Proteasomes are distributed throughout eukaryotic cells at a high concentration and cleave peptides in an ATP/ubiquitin-dependent process in non-lysosomal pathways. PSMA1 is a subunit that is strategically located at the mouth of the core of the proteasome barrel. While PSMA1 is not part of the catalytic machinery of the proteasome, it likely plays a role in gating the entry of proteins into the barrel. PSMA1 has been shown to bind specifically with Notch 3 protein in a yeast two-hybrid assay, which results in the inhibition of proteasome activity[26]. PSMA1 has been reported to be overexpressed in breast cancer tissue compared to adjacent normal tissue[27], suggesting that PSMA1 may be involved in tumorigenesis. Similar to PSAT1, PSMA1 was down-regulated in CAPE-treated CRC cells, suggesting that PSMA1 is not only an important regulator of biological processes, but also involved in the anti-cancer activity of CAPE.
GNPDA or glucosamine-6-phosphate isomerase (GNPI) is an allosteric enzyme that catalyses the reversible conversion of D-glucosamine-6-phosphate into D-fructose-6-phosphate and ammonium[28]. Although GNPI has been found to be expressed in human tissues and some cancer cell lines ubiquitously[29], its role in tumorigenesis and the anti-cancer effect of CAPE is unknown. However, lower expression of another up-regulated protein, GPX1, a selenium-containing antioxidant enzyme, is associated with aggressiveness and poor survival in patients with cancer[30-32]. GPX-1 may have cancer-supressing effects and up-regulation of GPX1 in CAPE-treated colorectal cancer cells might also be associated with the anti-cancer effect of CAPE.
In conclusion, we found that CAPE induced cell apoptosis and a differential protein expression profile. In particular, CAPE treatment resulted in down-regulation of proteins previously implicated in tumorigenesis. Down-regulated PSAT1 and PSMA1 and up-regulated GPX-1 in CAPE treated-colorectal cancer cells may be potential molecular targets of CAPE and involved in the anti-cancer effect of CAPE.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Lei Zhang for excellent technical assistance and Emeka Okeke at the University of Manitoba in Canada for English language editing.
COMMENTS
Background
Colorectal cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed malignancies and the third deadliest cancer in humans. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) is a phenolic antioxidant, which is known to suppress the growth of tumor cells and induce cell apoptosis. However, the molecular mechanisms of the anti-cancer activity of CAPE are unclear.
Research frontiers
CAPE is an active component of propolis and has various biological and pharmacological functions including immunoregulatory, anti-inflammatory, anti-viral, anti-bacterial, and anti-cancer activities. Several studies have demonstrated that CAPE has anti-proliferative effects by inducing apoptosis in various tumour cells in vitro and in vivo. CAPE also inhibits the development of azoxymethane-induced aberrant crypts in the colon of rats.
Innovations and breakthroughs
Based on a proteomic approach, several altered proteins were identified in CAPE-treated human colorectal cancer cells. Phosphoserine aminotransferase 1 (PSAT1) and Proteasome subunit alpha 1 (PSMA1), have been shown to be overexpressed in human cancer tissues, while low expression of Glutathione peroxidase (GPX-1) is known to be associated with aggressiveness and poor survival in patients with cancer. Down-regulated PSAT1 and PSMA1 and up-regulated GPX-1 in CAPE treated-colorectal cancer cells may be potential molecular targets of CAPE and involved in the anti-cancer effect of CAPE.
Applications
These findings suggest that CAPE mediates its anti-cancer effect by regulating the expression of important molecules.
Terminology
Proteomics is the study of the structure and function of proteins in a cell or tissue at a specific time under certain pre-defined conditions. CAPE is a natural phenolic chemical compound. It is found in a variety of plants and is also a component of propolis found in honeybee hives.
Peer review
The authors of this paper studied the mechanism involved in the inhibition by CAPE of colorectal cancer cells, and identified differential protein expression with or without CAPE-treatment. They concluded that CAPE-treatment down-regulated 7 proteins including PSAT1 and PSMA1 that played important roles in tumorigenesis but up-regulated 4 proteins including GNPDA1 and GPX1. The article is well written. Experimental design was logically followed through. Method and results were well presented.
Footnotes
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China No. 30872466 and No. 30801096, the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing No. 2011BB5032, and PLA Logistics Science Research during the 12th Five-Year Plan Period No. BWS11J041
P- Reviewer: Pichler M S- Editor: Qi Y L- Editor: Webster JR E- Editor: Wang CH
References
- 1.Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29. doi: 10.3322/caac.20138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.He YJ, Liu BH, Xiang DB, Qiao ZY, Fu T, He YH. Inhibitory effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on the growth of SW480 colorectal tumor cells involves beta-catenin associated signaling pathway down-regulation. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:4981–4985. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i31.4981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lee YJ, Liao PH, Chen WK, Yang CY. Preferential cytotoxicity of caffeic acid phenethyl ester analogues on oral cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2000;153:51–56. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(00)00389-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chen YJ, Shiao MS, Wang SY. The antioxidant caffeic acid phenethyl ester induces apoptosis associated with selective scavenging of hydrogen peroxide in human leukemic HL-60 cells. Anticancer Drugs. 2001;12:143–149. doi: 10.1097/00001813-200102000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nagaoka T, Banskota AH, Tezuka Y, Saiki I, Kadota S. Selective antiproliferative activity of caffeic acid phenethyl ester analogues on highly liver-metastatic murine colon 26-L5 carcinoma cell line. Bioorg Med Chem. 2002;10:3351–3359. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(02)00138-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Usia T, Banskota AH, Tezuka Y, Midorikawa K, Matsushige K, Kadota S. Constituents of Chinese propolis and their antiproliferative activities. J Nat Prod. 2002;65:673–676. doi: 10.1021/np010486c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Onori P, DeMorrow S, Gaudio E, Franchitto A, Mancinelli R, Venter J, Kopriva S, Ueno Y, Alvaro D, Savage J, et al. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester decreases cholangiocarcinoma growth by inhibition of NF-kappaB and induction of apoptosis. Int J Cancer. 2009;125:565–576. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Orsolić N, Terzić S, Mihaljević Z, Sver L, Basić I. Effects of local administration of propolis and its polyphenolic compounds on tumor formation and growth. Biol Pharm Bull. 2005;28:1928–1933. doi: 10.1248/bpb.28.1928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kuo HC, Kuo WH, Lee YJ, Lin WL, Chou FP, Tseng TH. Inhibitory effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on the growth of C6 glioma cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2006;234:199–208. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2005.03.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Borrelli F, Izzo AA, Di Carlo G, Maffia P, Russo A, Maiello FM, Capasso F, Mascolo N. Effect of a propolis extract and caffeic acid phenethyl ester on formation of aberrant crypt foci and tumors in the rat colon. Fitoterapia. 2002;73 Suppl 1:S38–S43. doi: 10.1016/s0367-326x(02)00189-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lee Y, Shin DH, Kim JH, Hong S, Choi D, Kim YJ, Kwak MK, Jung Y. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester-mediated Nrf2 activation and IkappaB kinase inhibition are involved in NFkappaB inhibitory effect: structural analysis for NFkappaB inhibition. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010;643:21–28. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.06.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hung MW, Shiao MS, Tsai LC, Chang GG, Chang TC. Apoptotic effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester and its ester and amide analogues in human cervical cancer ME180 cells. Anticancer Res. 2003;23:4773–4780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jin UH, Song KH, Motomura M, Suzuki I, Gu YH, Kang YJ, Moon TC, Kim CH. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia U937 cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2008;310:43–48. doi: 10.1007/s11010-007-9663-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rosenfeld J, Capdevielle J, Guillemot JC, Ferrara P. In-gel digestion of proteins for internal sequence analysis after one- or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1992;203:173–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90061-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Orsolić N, Knezević AH, Sver L, Terzić S, Basić I. Immunomodulatory and antimetastatic action of propolis and related polyphenolic compounds. J Ethnopharmacol. 2004;94:307–315. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2004.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Orsolić N, Saranović AB, Basić I. Direct and indirect mechanism(s) of antitumour activity of propolis and its polyphenolic compounds. Planta Med. 2006;72:20–27. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-873167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sforcin JM, Bankova V. Propolis: is there a potential for the development of new drugs? J Ethnopharmacol. 2011;133:253–260. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.10.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wu J, Omene C, Karkoszka J, Bosland M, Eckard J, Klein CB, Frenkel K. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), derived from a honeybee product propolis, exhibits a diversity of anti-tumor effects in pre-clinical models of human breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2011;308:43–53. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2011.04.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chung TW, Moon SK, Chang YC, Ko JH, Lee YC, Cho G, Kim SH, Kim JG, Kim CH. Novel and therapeutic effect of caffeic acid and caffeic acid phenyl ester on hepatocarcinoma cells: complete regression of hepatoma growth and metastasis by dual mechanism. FASEB J. 2004;18:1670–1681. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-2126com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lee YJ, Kuo HC, Chu CY, Wang CJ, Lin WC, Tseng TH. Involvement of tumor suppressor protein p53 and p38 MAPK in caffeic acid phenethyl ester-induced apoptosis of C6 glioma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;66:2281–2289. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2003.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Watabe M, Hishikawa K, Takayanagi A, Shimizu N, Nakaki T. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester induces apoptosis by inhibition of NFkappaB and activation of Fas in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:6017–6026. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306040200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ojala P, Sundström J, Grönroos JM, Virtanen E, Talvinen K, Nevalainen TJ. mRNA differential display of gene expression in colonic carcinoma. Electrophoresis. 2002;23:1667–1676. doi: 10.1002/1522-2683(200206)23:11<1667::AID-ELPS1667>3.0.CO;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Friederichs J, Rosenberg R, Mages J, Janssen KP, Maeckl C, Nekarda H, Holzmann B, Siewert JR. Gene expression profiles of different clinical stages of colorectal carcinoma: toward a molecular genetic understanding of tumor progression. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2005;20:391–402. doi: 10.1007/s00384-004-0722-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Roth U, Razawi H, Hommer J, Engelmann K, Schwientek T, Müller S, Baldus SE, Patsos G, Corfield AP, Paraskeva C, et al. Differential expression proteomics of human colorectal cancer based on a syngeneic cellular model for the progression of adenoma to carcinoma. Proteomics. 2010;10:194–202. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200900614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vié N, Copois V, Bascoul-Mollevi C, Denis V, Bec N, Robert B, Fraslon C, Conseiller E, Molina F, Larroque C, et al. Overexpression of phosphoserine aminotransferase PSAT1 stimulates cell growth and increases chemoresistance of colon cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 2008;7:14. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-7-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhang Y, Jia L, Lee SJ, Wang MM. Conserved signal peptide of Notch3 inhibits interaction with proteasome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;355:245–251. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.01.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Deng S, Zhou H, Xiong R, Lu Y, Yan D, Xing T, Dong L, Tang E, Yang H. Over-expression of genes and proteins of ubiquitin specific peptidases (USPs) and proteasome subunits (PSs) in breast cancer tissue observed by the methods of RFDD-PCR and proteomics. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007;104:21–30. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9393-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Arreola R, Valderrama B, Morante ML, Horjales E. Two mammalian glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminases: a structural and genetic study. FEBS Lett. 2003;551:63–70. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00896-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhang J, Zhang W, Zou D, Chen G, Wan T, Li N, Cao X. Cloning and functional characterization of GNPI2, a novel human homolog of glucosamine-6-phosphate isomerase/oscillin. J Cell Biochem. 2003;88:932–940. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Min SY, Kim HS, Jung EJ, Jung EJ, Jee CD, Kim WH. Prognostic significance of glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPX1) down-regulation and correlation with aberrant promoter methylation in human gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2012;32:3169–3175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lei XG, Cheng WH, McClung JP. Metabolic regulation and function of glutathione peroxidase-1. Annu Rev Nutr. 2007;27:41–61. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.27.061406.093716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hu Y, Benya RV, Carroll RE, Diamond AM. Allelic loss of the gene for the GPX1 selenium-containing protein is a common event in cancer. J Nutr. 2005;135:3021S–3024S. doi: 10.1093/jn/135.12.3021S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


