Abstract
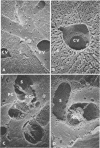
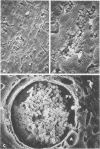
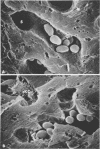
The initial clearance of Candida albicans from the blood stream of rats and from perfusion medium by perfused rat livers was characterized. Normal rats cleared over 90% of large doses of intravenously injected yeast cells in 5 min. All were recovered as viable cells among various reticulendothelial organs after 30 min. The perfused rat liver trapped an average of 85% of the yeast cells in a single pass. No significant killing occurred, even in the presence of 10% whole rat blood. Scanning electron microscopy of cryofractured livers revealed that the cells were trapped in liver sinusoids but outside phagocytic cells.
Full text
PDF

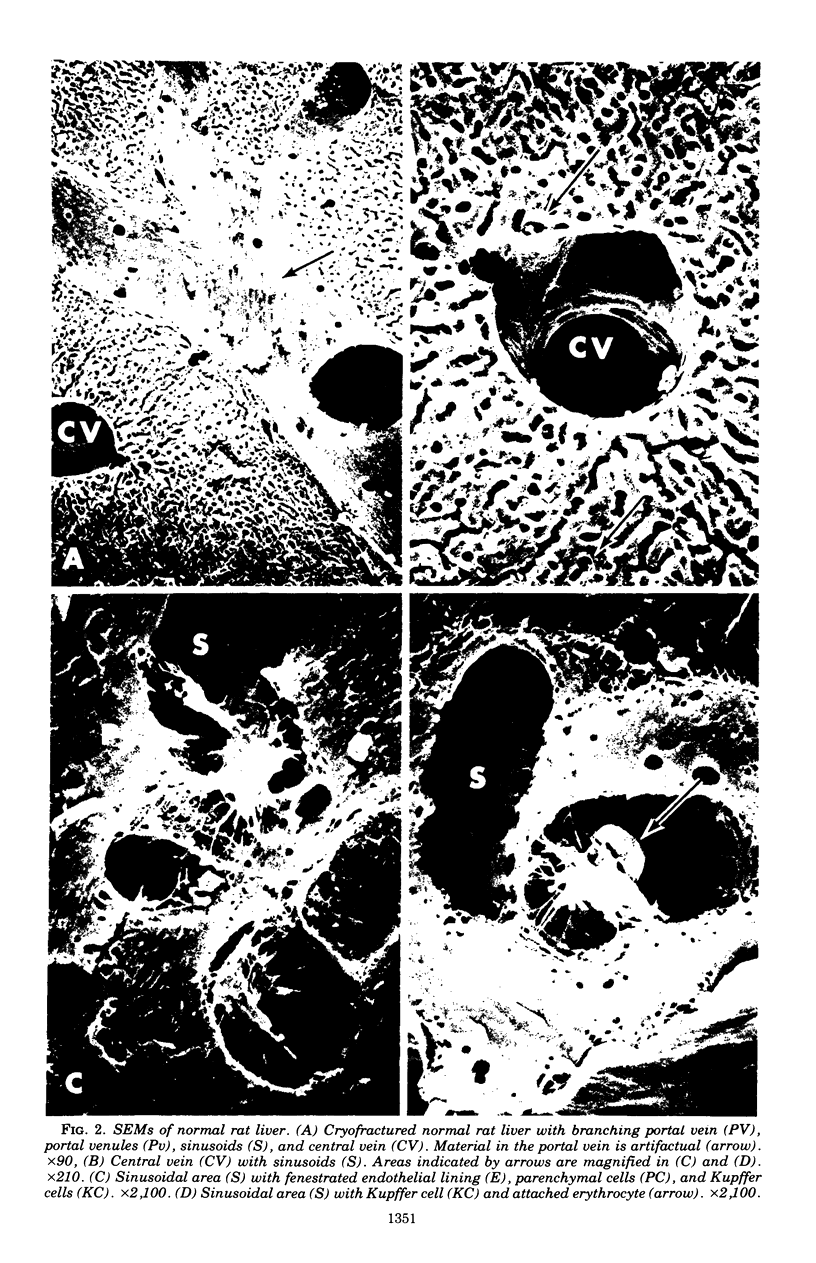
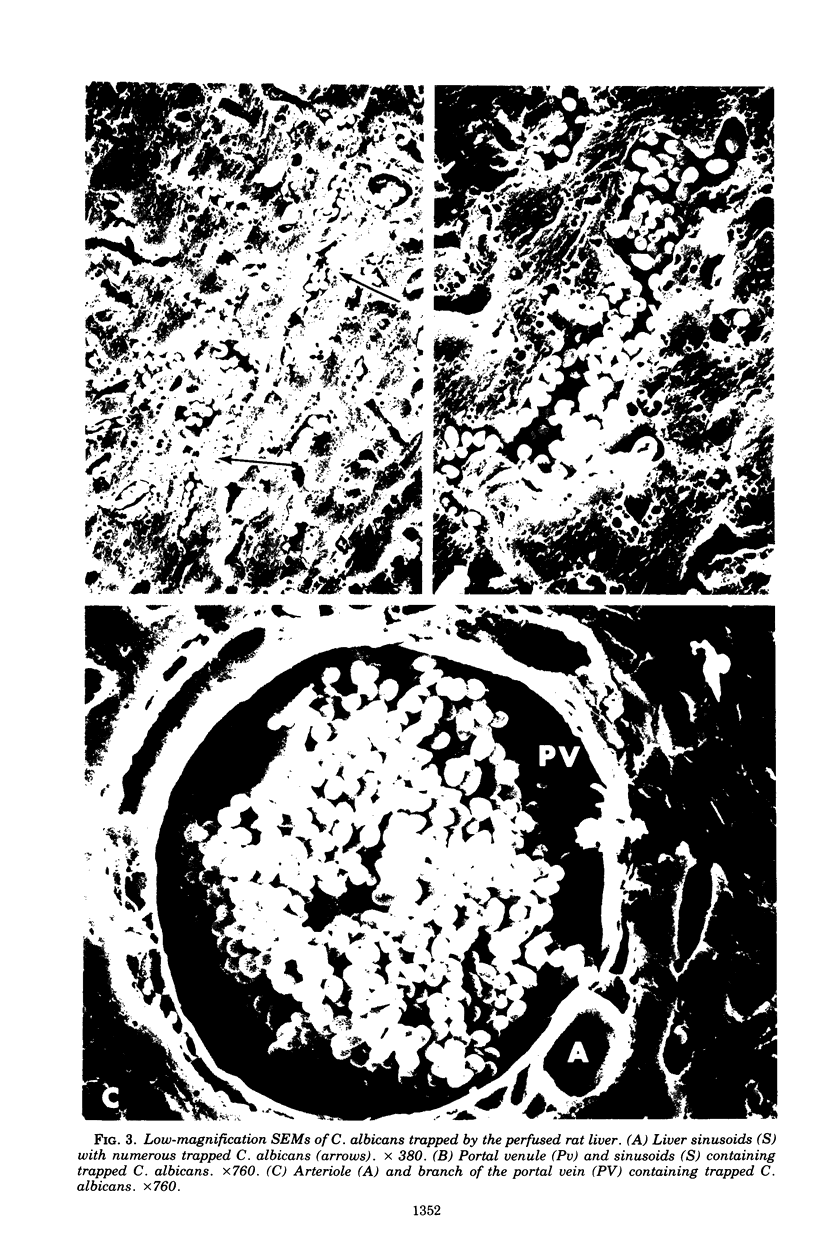
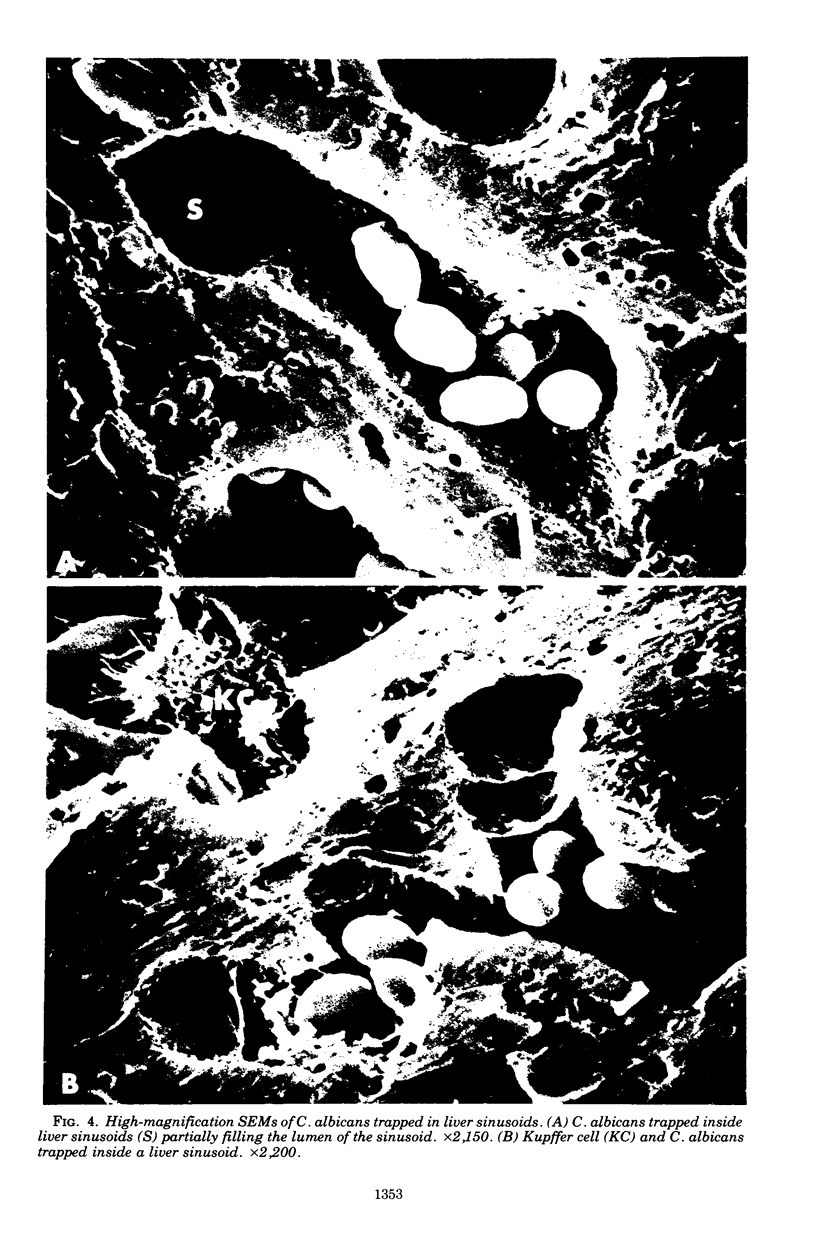
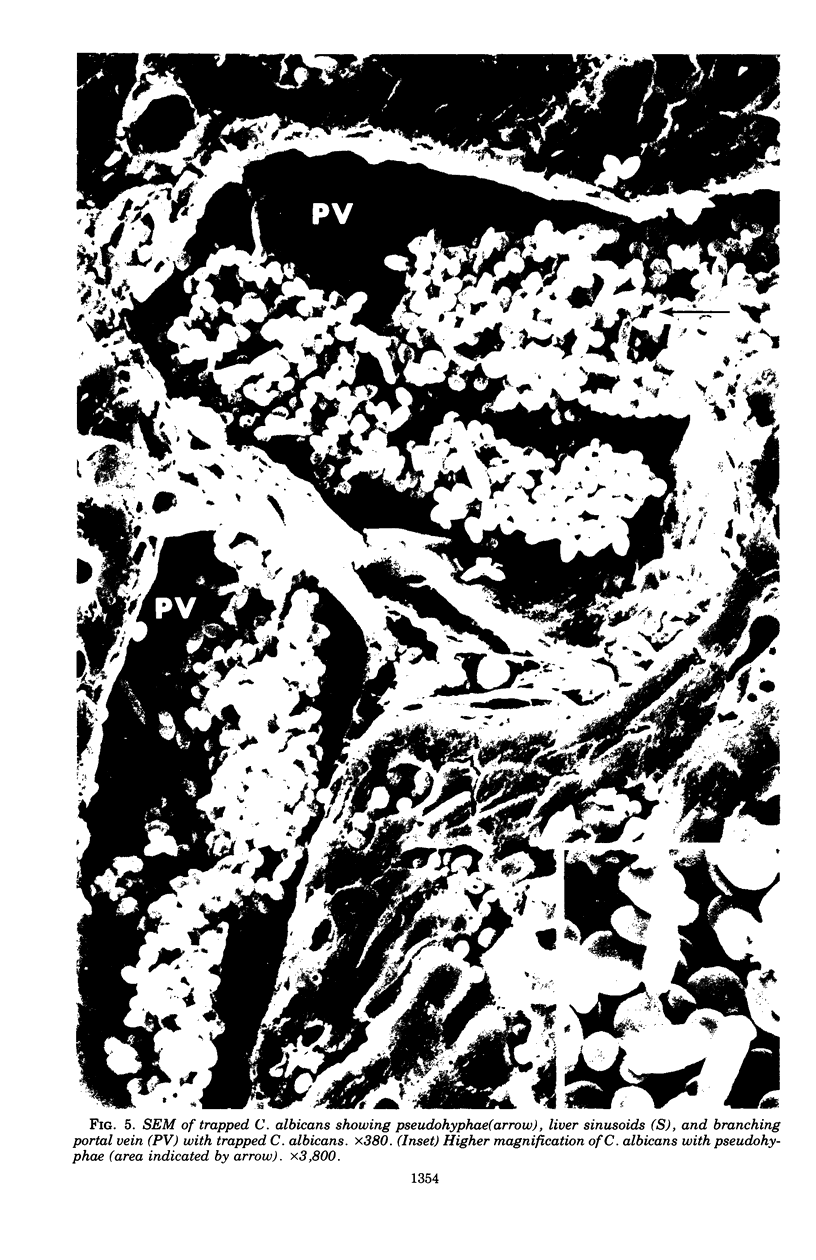

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baine W. B., Koenig M. G., Goodman J. S. Clearance of Candida albicans from the bloodstream of rabbits. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1420–1425. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1420-1425.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Oxman E. Phagocytosis and intracellular disposition of viable bacteria by the isolated perfused rat liver. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1965 Nov;2(4):313–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. R., Denning T. J. Candida albicans and the fungicidal activity of the blood. Sabouraudia. 1972 Nov;10(3):301–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning T. J., Davies R. R. Candida albicans and the chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Sabouraudia. 1973 Nov;11(3):210–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD J. G. The reticulo-endothelial system and resistance to bacterial infection. Scott Med J. 1961 Feb;6:60–82. doi: 10.1177/003693306100600203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD J. G., WARDLAW A. C. The opsonic effect of normal serum on the uptake of bacteria by the reticulo-endothelial system; perfusion studies with isolated rat liver. Immunology. 1958 Oct;1(4):338–352. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley R. Experimental infection with Candida albicans in modified hosts. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):57–67. doi: 10.1002/path.1700920108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeunet F. S., Cain W. A., Good R. A. Reticuloendothelial function in the isolated perfused liver. 3. Phagocytosis of Salmonella typhosa and Brucella melitensis and the blockade of the reticuloendothelial system. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1969 Aug;6(4):391–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeunet F. S., Cain W., Good R. A. Differential recognition of Brucella organisms by Kupffer cells: studies with isolated perfused liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Oct;129(1):187–190. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi K. R., Gavin J. B., Wheeler E. E. A scanning electron microscopic study of the morphogenesis of Candida albicans in vitro. Sabouraudia. 1973 Nov;11(3):263–266. doi: 10.1080/00362177385190531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOURIA D. B., FALLON N., BROWNE H. G. The influence of cortisone on experimental fungus infections in mice. J Clin Invest. 1960 Sep;39:1435–1449. doi: 10.1172/JCI104163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Cline M. J. Interaction of Candida albicans with human leukocytes and serum. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):996–1004. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.996-1004.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I. Measurement of candidacidal activity of specific leukocyte types in mixed cell populations I. Normal, myeloperoxidase-deficient, and chronic granulomatous disease neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1970 Jul;2(1):42–47. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.1.42-47.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon R. J., Vrable R. A., Broka J. A. In situ separation of bacterial trapping and killing functions of the perfused liver. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):411–418. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.411-418.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motta P., Porter K. R. Structure of rat liver sinusoids and associated tissue spaces as revealed by scanning electron microscopy. Cell Tissue Res. 1974 Mar 29;148(1):111–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00224322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The relative importance of blood monocytes and fixed macrophages to the expression of cell-mediated immunity to infection. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):521–534. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGERS D. E. Host mechanisms which act to remove bacteria from the blood stream. Bacteriol Rev. 1960 Mar;24(1):50–66. doi: 10.1128/br.24.1.50-66.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid L., Brune K. Assessment of phagocytic and antimicrobial activity of human granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1120–1126. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1120-1126.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkataraman M., Mohapatra L. N., Bhoyan U. N. Phagocytosis of Candida albicans by rabbit neutrophils. Sabouraudia. 1973 Jul;11(2):183–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]