Dear Editor
Factors affecting hemodynamic significance of symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis (ICAS), for instance, collateralization, could alter subsequent stroke risk (1), so hemodynamic significance of ICAS may yield a good predictor for stroke risk in patients with symptomatic ICAS. Based on the signal contrast mechanism, flow-related enhancement (2) of time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), and hemodynamic features of flowing blood in the case of stenosis, we assumed that changes of signal intensities (SIs) across an arterial stenosis might yield information on its hemodynamic significance. Therefore, in a pilot study, we developed and evaluated a novel index, named SI ratio (SIR), to quantify the hemodynamic significance of ICAS using TOF MRA.
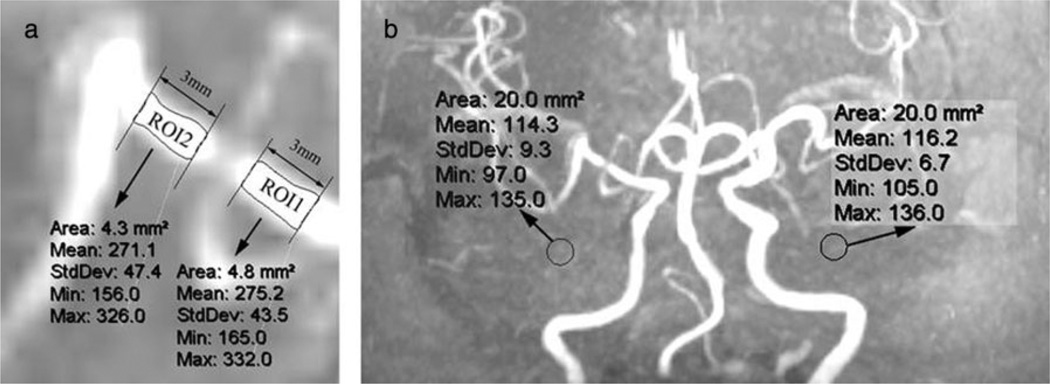
The index SIR was calculated as follows: SIR = (mean poststenotic SI – mean background SI)/(mean prestenotic SI – mean background SI), where mean prestenotic, mean poststenotic (Fig. 1a), and left/right background SIs (Fig. 1b) were measured as shown in Fig. 1. SIRs of 26 arteries (18 middle cerebral arteries and eight intracranial internal carotid arteries) selected from patients with 50–99% symptomatic ICAS identified by three-dimensional TOF MRA (3·0 T) were measured and calculated by the same expert twice, and reproducibility of repeated measures was evaluated.
Figure 1.
MRA maximum intensity projections (MIPs) of an ischemic stroke patient with a short flow void of right MCA. Mean prestenotic and poststenotic SIs were measured using regions of interest (ROI) on the MIP showing the greatest degree of stenosis as follows (a): (1) determine the first anatomically normal diameters both proximal and distal to the stenosis; (2) draw a line parallel and distal to the first normal poststenotic diameter, with a distance of three-millimeter in between, similar for the prestenotic vessel segment; and (3) select a ROI (ROI 2) covering the entire vessel lumen between the two lines distal to the stenosis, similar for placement of the prestenotic ROI (ROI 1). Background SIs (b) were measured within the left and right halves of the anterior–posterior direction MIP, with ROIs (20 mm2) beside ICAs and avoiding vessel signals. Mean background SI was the mean value of bilateral background SIs, 115·3 for this case. Hence, SIR for this stenosis = (mean poststenotic SI – mean background SI)/(mean prestenotic SI – mean background SI) = (271·1 – 115·3)/(275·2 – 115·3) = 0·97. ICA, intracranial arterial stenosis; MCA, middle cerebral artery; MRA, magnetic resonance angiography; SI, signal intensity; SIR, signal intensity ratio.
Mean SIRs were both 0·84 for repeated measures, with ranges of 0·35–1·25 and 0·39–1·25, respectively. Mean absolute and relative differences between repeated measures were 0·037 and 5%, respectively. Intrarater agreement was 88% for the 26 arteries studied, and Pearson’s correlation coefficient for repetitive measures was 0·975.
Measurement and calculation of the index SIR on TOF MRA were easy to perform and highly reproducible, which makes it feasible to be carried out in clinical practice. Future studies are warranted to further test this novel method for evaluating hemodynamic significance of ICAS and to find out whether it is related to outcomes of patients with symptomatic ICAS.
References
- 1.Liebeskind DS, Cotsonis GA, Saver JL, et al. Collaterals dramatically alter stroke risk in intracranial atherosclerosis. Ann Neurol. 2011;69:963–974. doi: 10.1002/ana.22354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bradley W, Waluch V, Lai K, et al. The appearance of rapidly flowing blood on magnetic-resonance images. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984;143:1167–1174. doi: 10.2214/ajr.143.6.1167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]