Abstract
Background
Neuroticism is frequently discussed as a risk factor for psychopathology. According to the maturity principle, neuroticism decreases over the course of life, but not uniformly across individuals. However, the implications of differences in personality maturation on mental health have not been well studied so far. Hence, we hypothesized that different forms of neuroticism development from adolescence to young adulthood are associated with differences in depression, anxiety and everyday emotional experience at the age of 25.
Methods
A sample of 266 adolescents from the general population was examined three times over ten years (age at T0: 15, T1: 20 and T2: 25) using questionnaires, interviews and ecological momentary assessment (EMA). At all measurement points, neuroticism was assessed with the NEO inventory. At T2, diagnoses of major depression and anxiety disorders were captured with a structured clinical interview (M-CIDI). Phone-based EMA was used to assess emotional experience and affective instability over a two-week period at T2.
Results
The best fitting model was a latent class growth analysis with two groups of neuroticism development. Most individuals (n = 205) showed moderate values whereas 61 participants were clustered into a group with elevated neuroticism levels. In both groups neuroticism significantly changed during the ten year period with a peak at the age of 20. Individuals with a higher absolute level were at 14-fold increased risk for depression and 7-fold risk for anxiety disorders at the age of 25. In EMA, increased negative affect and arousal as well as decreased positive emotions were found in this high group.
Conclusions
Other than expected, personality did not mature in our sample. However, there was a significant change of neuroticism values from adolescence to young adulthood. Further, over 20% of our participants showed a neuroticism development which was associated with adverse outcomes such as negatively toned emotional experience and a heightened risk to suffer from depressive and anxiety disorders in young adulthood. These high-risk persons need to be identified early to provide interventions supporting continuous personality maturation.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12888-014-0210-2) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Neuroticism, Anxiety, Depression, Ecological momentary assessment, Emotional experience
Background
Personality traits are frequently discussed as risk factors for various psychopathological complaints [1],[2]. Especially, neuroticism is often examined in the context of psychopathology [3],[4]. Individuals scoring high on this personality dimension can be characterized as worried, emotionally unstable, overly reactive or nervous [5]. Particularly, the association between high neuroticism and internalizing disorders like depression [6],[7] or anxiety disorders [8],[9] is well established.
Originally, personality traits were described to reflect genetically determined and relatively stable interindividual differences e.g., [10],[11]. However, by now there is increasing evidence that personality changes in all periods of life (for reviews see [12],[13]) with great developmental steps during adolescence/young adulthood and again in old age [14]-[16]. For instance, Littlefield, Sher, and Wood [17] found mean-level decreases of neuroticism in young adulthood. Similar results were obtained by Specht, Egloff, and Schmukle [16]. They reported that emotional stability, which is often used as synonym for low neuroticism, rises during a four year interval in different age groups in the general population. Such developmental changes of personality are summarized in the maturity principle[13],[18],[19]. This principle states that in most people personality matures over time. Regarding neuroticism, a decrease of neuroticism is expected. Importantly, Caspi et al. [13] emphasize that this maturation process is not uniform across individuals. Instead the authors argue that not all individuals achieve a mature personality or at least not at the same time. This should in turn be associated with differences in outcomes such as mental health or well-being, for example [13].
Thus, the maturity principle emphasizes the possibility that individuals do not mature at the same pace. Therefore, individual courses of personality maturation and their impact on mental health need to be focused on [20]. Nevertheless, only few studies examined personality changes by differentiating developmental courses (e.g., [21],[22]). For instance, three developmental groups were identified by Robins, Fraley, Roberts, and Trzesniewski [23]: in 23% of participants neuroticism levels decreased over a 4-year-interval, in 4% they increased and in 73% neuroticism remained stable. However, in this study the implications of group membership on possible outcomes like psychopathology or well-being were not examined.
Johnson, Hicks, McGue, and Iacono [24] focused on the temperament factor harm avoidance (HA), which is strongly associated with neuroticism [25], in a female twin sample. In their study, they found four different forms of development from age 14 to age 24: Three groups showed increasing HA-values, but differed in absolute level, whereas in the fourth group a decrease of HA was found. In addition, these developmental groups differed significantly regarding the prevalence of antisocial behaviour or substance dependence at the age of 24. Mroczek and Spiro [26] even found different mortality rates dependent on neuroticism level and course in middle-aged to old men. Men who scored high on this trait at baseline and who increased over a period of 18 years were less likely to survive.
Of course, this review of studies is not exhaustive. Nevertheless it gives first evidence for the serious consequences of missed personality maturation, albeit studies longitudinally relating changes in neuroticism to psychopathology are still rare. It must be noted, that, except for Johnson et al. [24] all above mentioned studies assessed psychopathology on a subsyndromal level using self-reports. In contrast, the influence of personality maturation on diagnoses of psychiatric disorders, as measurable with structured clinical interviews, has been neglected so far.
In addition, self-reports often generate global indices of impairments in general and are prone to retrospective bias [27]. It remains unclear how different forms of development influence everyday life. Such shortcomings could be overcome by ecological momentary assessment (EMA); [28]. This approach allows capturing real-time information while individuals go about their normal lives. As alterations in affectivity can be found in most mental disorders [29], the assessment of emotional experience using EMA could provide valuable additional information. With this method, emotions can be recorded in the moment they are experienced without being subject to recollection bias or other systematic distortions [30]. Further, affect dynamics such as instability or variability can be examined aside from mean levels [31],[32]. Due to its high ecological validity and enhanced flexibility compared to traditional assessment methods, EMA has gained increased application in the context of mood and affective components of mental disorders [33],[34].
When it comes to neuroticism and emotional experience, EMA is also increasing in importance [35]-[40]. For instance, Miller, Vachon, and Lynam [41] contacted undergraduate students via palm computers eight times a day over one week. In doing so, they found questionnaire-based neuroticism to be positively associated with mean negative affect and negative affect instability in daily measures. Similar results were obtained in other studies in which the authors reported more frequent, more intense and longer lasting unpleasant affect in EMA in association with neuroticism [42]-[44]. In several studies, Suls et al. [45] found that individuals with high neuroticism values strongly respond to daily problems – a pattern which they call the neurotic cascade. Further, in one study that assessed neuroticism at multiple measurement points, these values were aggregated over time for further analyses [46]. The authors reported lower positive affect and increased negative affect variability in individuals with high neuroticism values. To sum up, EMA methods are applied more and more frequently in research on the association between neuroticism and affect in everyday life. However, none of the above mentioned studies examined the longitudinal relationship between neuroticism and affectivity in everyday life in a representative sample taking changes in personality into account.
In line with the existing literature, we hypothesized that neuroticism values change from adolescence to young adulthood. In particular, we assumed that these changes in neuroticism are not uniform across individuals. Instead, groups of different courses should be identifiable. As all but one study examined outcomes of personality maturation using self-reports, in our study we aimed at describing the implications of group membership more precisely. Therefore, a multimethod approach was chosen: first, we examined whether belonging to a specific developmental group is associated with different degrees of psychopathology assessed by structured clinical interviews and self-ratings. Further, we tested the influences of group membership on emotions in everyday life using EMA.
Methods
Participants
The sample was drawn from the population-based Greifswald family study [47],[48], a subpopulation of the Study of Health in Pomerania, Germany (SHIP; John et al., [49]). In SHIP, 4308 people aged 20 to 79 were randomly selected between March 1997 and May 2000, proportional to the population size of each community, and stratified by age and gender. From this sample, 527 families who lived in a household with at least one offspring between the ages of 11 and 18 years were invited to take part in the family study. 141 families could not be located or did not answer our phone calls and letters. Further, 71 families refused to participate, resulting in a final sample of 315 families with whom assessments of parents and offspring (n = 381, mean age 15.1, SD = 2.3) were conducted (T0).
Parents and offspring were again investigated about five years later between 2005 and 2008 (T1): 87.7% of offspring (n = 334, mean age 19.6, SD = 2.4) took part in this follow-up. Since May 2011 offspring were examined for a third time (T2). Data of this second follow-up are available from 85.0% (n = 284) of T1 participants. 23 former participants were not available via post sendings or telephone calls because they moved away. 25 individuals were contacted but refused to participate and two persons died between T1 and T2. Individuals who took part in all assessments did not differ from those who dropped out after T0 regarding sex (χ2 = 2.37, p = .146), age (F = 2.05, p = .153), neuroticism (F = 0.73, p = .395; operationalized as harm avoidance in children younger than 16 years: F = 0.10, p = .747) and psychopathology (F = 0.16, p = .690) at T0. In 18 participants, at least one relevant questionnaire or interview was missing completely. These individuals were excluded from our analyses, resulting in a final sample of 266 young adults (56.4% female, mean age 24.9, SD = 2.3). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants after the study has been fully explained. The study was approved by the local ethics committee of the Ruprecht-Karls-University Heidelberg, Germany.
Materials and procedure
An overview over all constructs and their assessment at each measurement point can be seen in Table 1.
Table 1.
Constructs, measures and measurement mode for the three measurement points
| Measure | Mode | Transformation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neuroticism | |||
| T0 | |||
| • age < 16 | harm avoidance scale of the J-TCI | self-report | scale 1 to 5 |
| • age ≥ 16 | NEO-FFI | self-report | - |
| T1 | NEO-PI-R (only corresponding FFI-Items) | self-report | - |
| T2 | NEO-FFI | self-report | - |
| Subsyndromal psychopathology | |||
| T0 | YSR total score | self-report | scale 1 to 5 |
| T1 | SCL-90-R: GSI | self-report | scale 1 to 5 |
| T2 | BSI: GSI | self-report | scale 1 to 5 |
| Diagnoses of depression and anxiety disorders | |||
| T0 lifetime | |||
| • age < 16 | children version of the DIPS | structured clinical interview | |
| • age ≥ 16 | DIA-X | standardized clinical interview | |
| T1lifetime | DIA-X | standardized clinical interview | |
| T2 current & lifetime | DIA-X | standardized clinical interview | |
| Emotions in everyday life | |||
| T2 | ecological momentary assessment | phone-based self-report | |
Notes. J-TCI: Junior Temperament and Character Inventory; NEO-FFI: NEO Five Factor Inventory; NEO-PI-R: NEO Personality Inventory Revised; YSR: Youth Self Report; SCL-90-R: Symptom Checklist 90 Revised; GSI: Global Severity Index; BSI: Brief Symptom Inventory; DIPS: Diagnostic Interview for Mental Disorders.
Assessment of neuroticism
At all points of measurement, neuroticism was assessed with versions of the NEO personality inventory [49]. The NEO measures the Big-Five personality traits extraversion, neuroticism, openness, agreeableness and conscientiousness on a 5-point likert-type scale. The versions solely differ in their item number: whereas the NEO-Five-Factor-Inventory (T0 & T2; NEO-FFI; [50]) consists of 60 items, the NEO-Personality-Inventory-Revised (T1; NEO-PI-R; [51]) has 240 items. We only included the corresponding NEO-FFI-items from the NEO-PI-R in our analyses. Validity [52] and reliability of the NEO-FFI were found to be satisfying (Cronbach’s α T0: 0.716, T1: 0.870, T2: 0.868).
As the NEO is not applicable in children younger than 16 years [53], we used the harm avoidance subscale of the Junior Temperament and Character Inventory J-TCI; [54] in younger participants at T0 instead. This is an adapted version of Cloninger’s Temperament and Character Inventory (TCI); [55]. The harm avoidance scale comprises the subscales anticipatory worry, fear of uncertainty, shyness, and fatigability. Cronbach’s α in our sample was 0.775. Studies examining personality with multiple questionnaires found harm avoidance and neuroticism to be highly correlated and to compose a common dimension in factor analysis [56],[57]. Thus, Aluja and Blanch [25] concluded that both scales measure equivalent constructs. In our study, individuals older than 16 years answered both the NEO and the TCI at T0 and harm avoidance and neuroticism were highly correlated (r = .614, p = .000). To enhance comparability between measurements, we transformed the J-TCI harm avoidance scale into the NEO 1 to 5 answering mode.
Assessment of psychopathology
Diagnoses of depression and anxiety disorders
At all measurement points, diagnoses of depressive and anxiety disorders were assessed with the standardized Munich-Composite International Diagnostic Interview (DIA-X/M-CIDI); [58] in individuals older than 15 years. All interviews were conducted by trained clinical psychologists either in person or via telephone if a participant was living too far away. Unfortunately, we were not able to tape our interviews. Hence, inter-rater-reliability of our diagnostic interviews could not be calculated. However, according to the developers of the DIA-X, inter-rater reliability of this interview is high (κ = .81 - 1.0) and validity according to comparison with clinical diagnoses is at least satisfying (κ = .39 - .82) [59]. As the DIA-X is not applicable in children younger than 16, at T0 the child version of the Diagnostic Interview for Mental Disorders (DIPS); [60] was used. The DIPS is a structured clinical interview with satisfying to good psychometric properties [60].
General psychopathological complaints
At first assessment, the German version of the Youth Self Report (YSR); [61],[62] was used for examination of general psychopathological complaints. The YSR is a self-report instrument and consists of 112 items assessing behavioural and emotional problems on eight scales in adolescents aged 11 to 18. A general psychopathology score was calculated from 101 items. In our study, reliability was excellent (Cronbach’s α = 0.921).
At T1, general psychopathology was measured with the German version of the Symptom Checklist-Revised (SCL-90-R); [63],[64] and at T2 with its short form, the Brief Symptom Inventory (BSI); [65], respectively. Both are self-rating inventories with nine scales assessing different symptoms during the last seven days and were found to be comparable [66]. Reliability and validity were found to be excellent for both, the SCL-90-R and the BSI (T1 SCL-90-R: Cronbach’s α = 0.965; T2 BSI: Cronbach’s α = 0.963) [67],[68]. To assess general psychopathology, the Global Severity Index (GSI); [63] was calculated for both questionnaires. In order to enhance comparability with neuroticism and interpretability of these different measurements, all instruments were transformed into a 1 to 5 response format.
Emotional experience in everyday life
An ecological momentary approach was used to gather information regarding emotional experience in everyday life at T2. Computer-based phone calls were made with the SmartQ/DialQ software package (© Telesage Inc.), and recorded questions were red out by a staff member. Participants were called on their cell phones three times a day, every second day during a two week period. If the call was not answered, two additional trials were made 30, respectively 60, minutes later. Besides other questions, we asked the participants how they felt in the current moment. First, the emotional state was examined in general by indicating current valence (from good to bad) and arousal (from relaxed to tense). Answers were given on likert-type scales ranging from 0 to 6 by pressing the according number on the keyboard. Second, we asked more specifically for the experience of eight different emotions (happiness, sadness, disgust, anxiety, anger, interest, shame, boredom) again using scales from 0 to 6. Higher values indicated stronger momentary experience of this particular emotion. To date, methodology in EMA studies is manifold, and standardized questions and instruments are missing so far [33]. Nevertheless, as mentioned above, these designs are meant to diminish recall biases and increase ecological validity compared to self-report questionnaires. Further, there is some literature reporting good reliability and validity of EMA in clinical psychology research [69],[70].
Data analyses
When it comes to modelling longitudinal growth data, various approaches can be used [71]. In this study we examined two different models, namely latent class growth analysis (LCGA) and growth mixture modelling (GMM). Both models were conducted with neuroticism at the three measurement points using Mplus version 6 [72]. As an extension to conventional latent growth models, LCGA and GMM allow to identify latent groups with different developmental trajectories. Individuals are grouped based on latent growth factors, namely intercept (initial status) and slope. In our models the factor loading for the slope growth factor on T2 was freely estimated. Due to our relatively large age range as well as differences in neuroticism assessment depending on age at T0, age was included as a covariate. Further, the error variances of T1 and T2 neuroticism were set to be equal because at these assessments the same instrument was used as opposed to T0. LCGA is a specific form of GMM in which trajectories within a class are defined to be homogenous, i.e., the variance of the slope factor is fixed to zero within groups (see Figure 1). In contrast, in GMM the variance of the slope factor is freely estimated. Thus, the slope factor can covariate with other variables such as the intercept, (for example for a detailed description of LCGA and GMM see [73]). In Mplus, a variety of indices is provided to evaluate model fit. In this study, the best group solution was identified on the basis of the following criteria [74]: the Bayesian information criterion (BIC, lowest values considered best), the Lo-Mendell-Rubin-test (LMR); [75] and bootstrapped parametric likelihood ratio tests (BLRT); [76]. LMR and BLRT were applied to test whether a solution with k + 1 groups fits the data significantly better than the solution with k groups. Further, relative entropy should be at least 0.8 as with a value of 1.0 indicating perfect classification [77]. However, there is no binding criterion to decide the number of trajectory classes. Instead, a variety of factors like theoretical considerations, interpretability or replicability among others should be considered [73].
Figure 1.
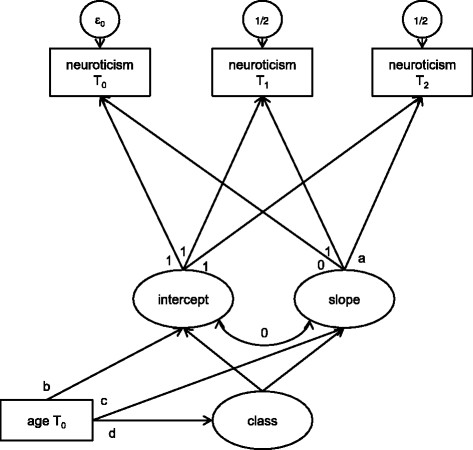
Latent class growth analysis model for neuroticism at three measurements points. Legend: estimated path coefficients for a 2-class-solution: a = 0.655, p ≤ .001; b = -0.001, p = .972; c = -0.063, p = .003; d(Nmoderate) = -0.233, p = .049; d(N high) = 0.233, p = .049.
Second, repeated measures analysis of variances with time as within-subjects factor and group membership as between-subjects factor was performed for general psychopathology for the three measurement points. In addition, survival analyses were run to examine the courses of lifetime diagnoses of depression and anxiety disorders over the ten year period. Further, we conducted logistic regression analyses to examine odds ratios (OR) for the T2 diagnoses of current depressive and anxiety disorders depending on developmental group and controlled for depression and anxiety symptoms at T0 (as measured with the YSR).
Third, data from EMA were aggregated into a mean experience score for valence, arousal and each specific emotion. Further, exploratory factor analysis with oblimin rotation was conducted with the specific emotion scores. In addition, mean squared successive differences (MSSD) within a day were calculated as a marker for emotional instability for a detailed description of the MSSD see [78],[79]. MSSDs were averaged over the assessment days for each participant and weighted by the emotion level, as there is evidence that absolute level and affect dynamics are interrelated [41]. Finally, a multivariate analysis of variances (MANOVA) was performed to identify group differences regarding valence, arousal, emotional factor values and emotional instability.
Results
Descriptive statistics regarding demographic variables as well as neuroticism, psychopathology and everyday emotional experience can be seen in Table 2.
Table 2.
Descriptive statistics regarding demographics, neuroticism, psychopathology, prevalences of depression and anxiety disorders and emotional experience (n = 266)
| % | n | |
|---|---|---|
| T 2 demographics | ||
| education | ||
| university degree | 17.6 | 47 |
| A-Levels | 41.0 | 109 |
| secondary school diploma | 36.5 | 97 |
| others | 4.9 | 13 |
| living in partnership | 64.3 | 171 |
| having children | 12.8 | 34 |
| T 2 current diagnosis | ||
| depression | 9.8 | 26 |
| anxiety | 4.5 | 12 |
| M | SD | |
| Neuroticism | ||
| T0 | 2.26 | (0.69) |
| T1 | 2.77 | (0.58) |
| T2 | 2.55 | (0.64) |
| General psychopathology | ||
| T0 | 1.42 | (0.25) |
| T1 | 1.39 | (0.35) |
| T2 | 1.32 | (0.40) |
| T 2 everyday emotional experience a | ||
| valenceb | 1.89 | (0.96) |
| arousalc | 1.81 | (0.87) |
Notes. an = 222 due to missing values in ecological momentary assessment; b scaled from feeling good (0) to feeling bad (6); cscaled from being relaxed (0) to being tense (6).
Using LCGA our models converged and fit indices for different class solutions can be seen in Table 3. In GMM, a non-significant negative residual variance (estimate -0.151, p = 0.07) of the slope factor occurred in the two group solution. This pattern did not change after modification of starting values and thus may indicate that there is no substantial variance of the slope factor within groups. Thus, for further examination we decided to go with the LCGA in which the variance of the slope factor is fixed to zero as this seemed to be a more proper model. In LCGA, differences in BIC were not wide, but it was the lowest for a three group solution (see Table 3). However, in this model entropy was slightly lower than 0.8 and the LMRT did not reach significance, indicating deficits in classification. Further, in this solution one class consisted of less than 10% of our sample which limits our confidence regarding the replicability of these results. As entropy was good in the two-group solution and LMR as well as BLRT were also significant in this model, we chose two trajectory classes for further analysesa. Estimated path coefficients for the model with two classes can be seen in Figure 1.
Table 3.
Fit indices for latent class growth analysis with neuroticism values at the three measurement points
| Number of groups | BICa | Entropy | Lo-Mendell-Rubin likelihood ratio test | Bootstrapped parametric likelihood ratio test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pb | pb | |||
| 2 | 1430.303 | 0.833 | .0005 | .0000 |
| 3 | 1413.441 | 0.750 | .1119 | .0000 |
| 4 | 1417.614 | 0.687 | .0655 | .0000 |
Notes. aBayesian Information Criterion; btesting if a model with k groups fits the data better than the model with k-1 groups; group sizes: 2 class solution: n1 = 205, n2 = 61; 3 class solution: n1 = 162, n2 = 23, n3 = 81; 4 class solution: n1 = 48, n2 = 113, n3 = 98, n4 = 7.
In both groups, neuroticism significantly changed from T0 to T2 with a peak at T1. However, the groups differed regarding absolute neuroticism levels. The majority of participants (77.1%; mean age T0 14.75, SD = 2.20; mean age T1 19.20, SD = 2.26; mean age T2 24.73, SD = 2.31; 51.0% female) showed a pattern of moderate neuroticism values. Thus, this group was labelled “neuroticism (N) moderate” (mean intercept 2.084, SE = 0.362, p ≤ .001; mean slope 1.380, SE = 0.309, p ≤ .001). Individuals clustered into the second group (22.9%; mean age T0 15.75, SD 2.04; mean age T1 19.89, SD 1.76, mean age T2 25.26, SD 1.96; 77.0% female) showed higher neuroticism levels (mean intercept 2.844, SE = 0.428, p ≤. 001) as well as slightly greater change over ten years (mean slope 1.666, SE = 0.377, p ≤. 001). This group was named “N high”. Neuroticism means for the trajectory groups are visualized in Figure 2.
Figure 2.
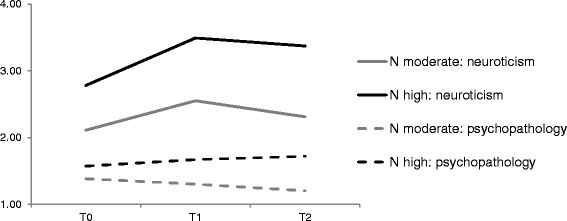
Neuroticism and psychopathology course over the three measurement points for the two trajectory groups. Legend: N(Nmoderate) = 205; N(N high) = 61.
Repeated measures analysis of variances revealed a significant main effect for trajectory group (F = 132.01, p ≤. 001, effect size partial eta squared (ƞP2) = .33) as well as a significant interaction effect of group x time (F = 31.59, p ≤ .001, ƞP2 = .11) on general psychopathology. The main effect for time did not yield significance (F = 0.21, p = .644, ƞP2 = .001). Across the three assessments, the group “N high” showed higher psychopathological burden than individuals with stable moderate neuroticism values (see Figure 2). Further, in individuals with high neuroticism, psychopathology slightly increased in our ten year period whereas it decreased in the “N moderate” group.
The results of survival analyses regarding the lifetime prevalences of depressive and anxiety disorders for groups can be seen in the morbidity curves in Figure 3. Curves differed significantly between groups (depression χ2 = 41.44, df = 1, p ≤ .001; anxiety χ2 = 28.84, df = 1, p ≤ .001) with elevated prevalences in the “N high” group. The gap between groups widened with increasing age. The estimated course shows that at an age of 28 or older nearly every person in the “N high” group suffered from depression or anxiety disorders at least once during their lives. Further, logistic regression analyses predicting current diagnoses at T2 revealed a 14-fold increased risk for depressive disorders in the “N high” compared to the “N moderate” group (β = 2.64, SE = 0.52, p ≤ .001, OR 14.00, confidence interval (CI) 5.08 - 38.34) controlled for internalizing symptoms at T0 (regression without trajectory group: β = 0.08, SE = 0.04, p = .035; regression with trajectory group: β = -0.02, SE = 0.05, p = .669). Regarding anxiety disorders a 7-fold risk was found for this high group (β = 1.92, SE = 0.74, p ≤. 01, OR 6.84, confidence interval (CI) 1.61 - 29.07; coefficients for the control variable internalizing symptoms at T0: without trajectory group: β = 0.17, SE = 0.05, p ≤ .001; regression with trajectory group: β = 0.11, SE = 0.05, p = .035).
Figure 3.
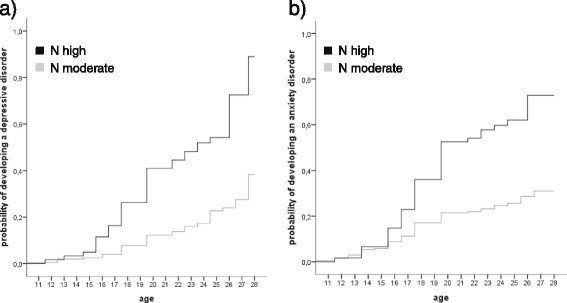
Morbidity curves for depression (a) and anxiety disorders (b) according to neuroticism developmental group. Legend: N = neuroticism; N(Nmoderate) = 205; N(N high) = 61; the age 28 includes individuals who are 28 and older.
In the next step, we focused on information about emotional experience in everyday life as assessed by EMA. Completion rate was 88% with a mean of 18 answered calls. Data were analysed if at least 50% of calls were answered resulting in a sample of 208 individuals (“N moderate”: 162; “N high”: 46). A MANOVA revealed significant group differences in the global emotional indices valence (F = 17.54, p ≤. 001, ƞP2 = .08) and arousal (F = 15.57, p ≤ .001, ƞP2 = .07). Individuals with a neuroticism course on a moderate level felt better and were more relaxed during a two week period than individuals whose neuroticism values were higher (see Figure 4).
Figure 4.
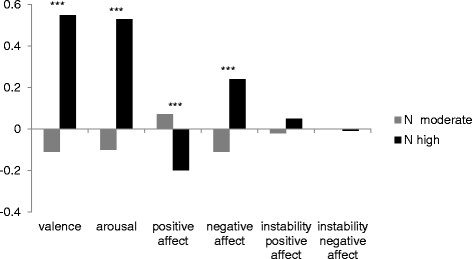
Means of emotional experience in everyday life (EMA) according to neuroticism trajectory group. Legend: N = neuroticism; N(Nmoderate) = 166; N(N high) = 46; valence: higher values indicate feeling bad; arousal: higher values indicate being tense; instability is assessed with the MSSD; all values are z-standardized; ***p ≤ .001.
Further, exploratory factor analysis was conducted with ratings of specific emotions. Here, a two factor solution emerged. The first factor consisted of ratings for sadness, disgust, anxiety, anger, shame and boredom, and accounted for 57% of variance. This factor was labelled “negative affect”. Happiness and interest ratings constituted a second factor which accounted for 20% of variance and was named “positive affect”. As can also be seen in Figure 3, groups differed significantly in negative (F = 10.71, p ≤ .001, ƞP2 = .05) and in positive affect (F = 10.39, p ≤ .001, ƞP2 = .05). Individuals with high neuroticism values experienced more negative and less positive affect in everyday life than the “N moderate” group. According to the results of the factor analysis, the MSSD was calculated separately for positive and negative affect. However, groups did not differ regarding emotional instability, neither in positive (F = 0.17, p = .682, ƞP2 = .001) nor in negative affect (F = 0.01, p = .929, ƞP2 = .000).
Discussion
In this study we longitudinally examined differential developmental courses of neuroticism from adolescence to young adulthood, and their association to psychopathology and emotional experience in a general population sample. In particular, various levels of psychopathology were assessed using self-reports, structured clinical interviews, and an ecological momentary assessment approach.
As hypothesized, neuroticism course was not uniform across individuals in our general population sample. Instead, over a period of ten years, two different forms of neuroticism development were revealed. In both groups, neuroticism was not stable, but changed from adolescence to young adulthood as indicated by the significant slope factors. Interestingly, the shape of the neuroticism course was similar in both groups with a peak around the age of 20. In contrast, courses differed regarding absolute neuroticism level. The majority of individuals showed neuroticism values on a moderate absolute level. However, there was also a group with higher absolute neuroticism levels. This higher pattern was associated with an elevated level of psychopathology from adolescence to young adulthood. Further, individuals who stood out from the masses by being more timid, nervous and emotionally unstable were at 14-fold increased risk for developing depressive and at 7-fold risk for anxiety disorders compared to persons with moderate neuroticism levels. These results are in line with studies associating lower levels of neuroticism with positive outcomes such as life satisfaction [80] or subjective well-being [81].
According to the maturity principle [13], a decrease of neuroticism values would have been expected in the majority of individuals. This pattern could not be observed in our data. Instead, neuroticism increased from 15 to 20 and decreased afterwards in both groups. This pattern might be explained by the model of Ormel et al. [82]. Here, the authors provide evidence that personality development bases on two factors: on the one hand, there is an individually fixed set point. On the other hand, there are experience-dependent alterations in personality. Hence, it can be assumed that in line with personality models some individuals do have a higher neuroticism set point than others [5]. At the same time, the age of 20 reflects an important developmental step associated with experiences that potentially lead to an increase in neuroticism values. It is easily imaginable that moving out, finding a job and perhaps starting an own family can fuel fears, worries and negative emotions. Perhaps, five years later individuals become more settled which is reflected in a decrease of neuroticism values back to the respective set point. This assumption is in line with findings showing a decrease in neuroticism between 20 and 40 [14]. In fact, lots of studies reporting decreases in neuroticism assess individuals older than 18 years [23],[83]. Hence, it seems plausible that hypothesized personality maturation is just about to start in our sample. Of course, this must be clarified in future studies which should also account for potentially different paces of such maturation processes.
In parallel to the neuroticism course, morbidity rates of anxiety and depressive disorders strongly rose from T0 to T1 but the increase slowed down from T1 to T2, particularly in the “N high” group. This is in line with other studies showing increases in depressive symptoms starting in the ages between 12 and 14 [84],[85]. Hence, our data might suggest that in parallel with increasing neuroticism values from T0 to T1, depressive and anxiety symptoms reach the threshold of diagnoses at the age of 20, particularly in individuals with a higher absolute level of neuroticism. However, it could be argued, that these associations result from the conceptual overlap of neuroticism and psychopathology measures [86]. Yet, there is evidence suggesting that content overlap is not the main explanation for associations between neuroticism and depression/anxiety [9]. Instead, neuroticism seems to reflect more than depressive and anxious symptoms, as a general neuroticism factor including all of its facets is a better predictor for depression and anxiety than the disorder-specific subscales [9]. Further, general psychopathology measures also include externalizing symptomatology and thus are supposed to be sufficiently distinct from neuroticism. Nevertheless, it is possible that the strength of the association is a little overestimated. Hence, in line with Nicholls et al. [87], we decided not to exclude overlapping items but to include a variety of outcome assessment methods to account for potential conceptual overlap.
Further, it could be assumed that retrospective recall of symptoms and personality is biased by current psychopathology and mood [88],[89]. Therefore, we additionally used EMA to assess implications of neuroticism developmental groups. This method minimizes recall biases and other systematic distortions, as individuals spontaneously indicate their current emotional experience at multiple random assessment points. However, this method was only applicable at T2, so recall biases at T0 and T1 cannot be ruled out.
Using EMA at T2, we found high neuroticism course from adolescence to adulthood to be associated with increased negative affect and arousal at the age of 25. In addition, levels of positive affect were reduced. This is of particular importance, as there is evidence that negative emotions in everyday life are associated with various adverse outcomes, such as an increased vulnerability for depression [90], smoking relapse [91], or binge eating [92], for instance. Further, Wichers et al. [93] found positive emotions in everyday life to buffer the disadvantageous effects of stress on depression development. Hence, the high neuroticism group is affected in two ways: first, by its increased negative affectivity, and second, through the lack of possibly protecting positive emotions. In sum, it can be assumed that alterations in emotional experience constitute a mechanism relating neuroticism development to psychopathology. This idea needs clarification in future research.
Interestingly, no group differences emerged regarding emotional instability. This is in contrast to other studies reporting significant associations between neuroticism and affect instability [41],[46],[94]. However, these studies did not test the influence of longitudinal neuroticism courses on emotional instability, but assessed or averaged concurrent neuroticism levels instead. Another methodological explanation for these inconsistent findings is provided in a recent study of Koval, Pe, Meers, and Kuppens [31]. They argue that overlap in conceptualizations (variability, instability, inertia) and measures (SD, MSSD, autocorrelation) of affect dynamics account for inconsistencies in results (in their case regarding depression). Thus, it would be interesting to test whether neuroticism courses differentially influence diverse measures of affect dynamics in future studies.
Our results have to be interpreted in the light of several limitations. Although data were collected longitudinally, causal statements cannot be made. Whereas in our argumentation the developmental course of neuroticism is interpreted as risk factor for different negative outcomes, it is also plausible that differences in mental stress influence personality (for review see [95]). For instance, evidence is inconsistent regarding depression: whereas the vulnerability hypothesis states that personality constitutes a risk factor for depressive disorders [96],[97] the scar hypothesis arguments that an episode of depression leads to alterations in personality [98]. In our study we found evidence for the vulnerability hypothesis, as a neuroticism course with high absolute levels led to an increased risk of depression in adulthood. However, it would be promising to examine whether previous depressive episodes influenced personality development in a future study.
Further, it is also imaginable that third factors like a family history of mental illness [99], treatment experiences [100], significant life events [101] or traumas [102] influence the associations between neuroticism course and mental health. Hence, such mechanisms should be considered in further research. In addition, the concurrent assessment of personality and psychopathology might lead to mood-state distortions [103]. Hence, for the future it might be promising to assess personality and psychopathology at different time points controlling for current mood-state.
Moreover, in our EMA-design we did not capture the context in which emotions were experienced. However, there is increasing evidence emphasizing the importance of context-specific information on emotions [104],[105]. Therefore including a few questions on the activities, stressors and interactions partners in everyday situations might help to get a more detailed insight in the emotionality of individuals at risk for depression and anxiety disorders. However, EMA research is still at its very beginning and our results give a first idea of the association between trait affectivity and affective experience in everyday life.
Further, in this study we focused on the personality trait neuroticism, as this trait is frequently examined in the context of internalizing psychopathology [106],[107]. Of course, the development of other traits such as extraversion or impulsivity would also be interesting as these traits are discussed as risk factors of mental disorders, too [8],[108]. In addition, future research should examine the association between the development of trait combinations in terms of personality profiles and psychopathology.
Methodologically, varying assessment methods for neuroticism and general psychopathology were used at the different measurement points. This adaption was inevitable due to age-specific application of the questionnaires. However, we included age as a covariate in our models to account for possible assessment effects. Still, method-specific biases cannot completely be ruled out. Thus, overcoming measurement problems is a major challenge for future research on personality development in the transition from adolescence to adulthood.
Nevertheless, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first study differentiating courses of neuroticism development in this phase of life and longitudinally linking them to different forms and severities of psychological impairment. Therefore, a multimethod approach with self-reports, interview data and ecological momentary assessment was used. Further, our data were collected in both sexes in the general population instead of patient samples or college students, thus enhancing the generalizability of our findings.
Conclusions
This study highlights that neuroticism changes in the transition from adolescence to young adulthood. However, personality maturation as indicated by a decrease of neuroticism could not be observed. Instead, neuroticism peaked at the age of 20. Interestingly, this form of development was similar across individuals. However, the absolute neuroticism level strongly differed between two groups. Over 20% of our participants showed elevated neuroticism levels over all assessments which were associated with adverse outcomes such as negatively toned emotional experience, increased general psychopathology over ten years, and a heightened risk to suffer from depression and anxiety disorders in young adulthood. Thus, these high-risk persons need to be identified early to be able to provide individually suited interventions to support continuous personality maturation. At the same time, the assessment of possible negative outcomes needs to be refined in order to detect specific patterns increasing the risk for mental disorders, such as increased experience of negative emotions in everyday life.
Endnote
aWe also tested a model including a dummy-coded control variable, indicating whether J-TCI or NEO was used to assess neuroticism at T0 instead of age (results not shown). Here, a similar 2-class-solution was obtained and further results were comparable. As it was age-dependent whether the J-TCI or the NEO was used, age and the control variable were highly interrelated (r = 0.862, p ≤ .001). Hence, we decided to display the age-controlled model only.
Authors’ contributions
MA made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the study, acquisition, statistical analyses and interpretation of the data (particularly EMA), and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. MS made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the study as well as to statistical analyses and revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. IU made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the study, and revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. KA made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the study, had the lead in diagnostics and revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. ER made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the study, and revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. SW made substantial contributions to the acquisition of data, and revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. HJG made substantial contributions to the acquisition of data, and revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. SL revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. SB made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the study, the analysis and interpretation of the data, and revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. All authors contributed to and have approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The Greifswald family study was supported by the German Research Foundation (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, BA-2172/2-1, BA2172.8-1.GR1912.7-1). Further, we acknowledge financial support by the German Research Foundation and the Ruprecht-Karls-University Heidelberg within the funding program Open Access Publishing.
Abbreviations
- BIC
Bayesian information criterion
- BLRT
Bootstrapped parametric likelihood ratio tests
- EMA
Ecological momentary assessment
- HA
Harm avoidance
- LCGA
Latent class growth analysis
- LMR
Lo-Mendell-Rubin-test
- MSSD
Mean squared successive differences
- N
Neuroticism
- OR
Odds ratio
- SHIP
Study of health in Pomerania
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Footnotes
Competing interests
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Contributor Information
Maren Aldinger, Email: maren.aldinger@psychologie.uni-heidelberg.
Malte Stopsack, Email: malte.stopsack@psychologie.uni-heidelberg.de.
Ines Ulrich, Email: ines.ulrich@psychologie.uni-heidelberg.de.
Katja Appel, Email: katappel@uni-greifswald.de.
Eva Reinelt, Email: eva.reinelt@psychologie.uni-heidelberg.de.
Sebastian Wolff, Email: sebastian.wolff@psychologie.uni-heidelberg.de.
Hans Jörgen Grabe, Email: grabeh@uni-greifswald.de.
Simone Lang, Email: simone.lang@psychologie.uni-heidelberg.de.
Sven Barnow, Email: sven.barnow@psychologie.uni-heidelberg.de.
References
- 1.Kotov R, Gamez W, Schmidt F, Watson D. Linking “big” personality traits to anxiety, depressive, and substance use disorders: a meta-analysis. Psychol Bull. 2010;136:768–821. doi: 10.1037/a0020327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Barnow S, Spitzer C, Grabe HJ, Kessler C, Freyberger HJ. Individual characteristics, familial experience, and psychopathology in children of mothers with borderline personality disorder. J Am Acad Child Psychiatry. 2006;45:965–972. doi: 10.1097/01.chi.0000222790.41853.b9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sandahl C, Lindberg S, Bergman H. The relation between drinking habits and neuroticism and weak ego among male and female alcoholic patients. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1987;75:500–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1987.tb02825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cervera S, Lahortiga F, Martínez-González MA, Gual P, de Irala-Estévez J, Alonso Y. Neuroticism and low self-esteem as risk factors for incident eating disorders in a prospective cohort study. Int J Eat Disord. 2003;33:271–280. doi: 10.1002/eat.10147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Eysenck HJ, Eysenck MW. Personality and individual differences. New York: Plenum Press; 1985. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dunkley DM, Sanislow CA, Grilo CM, McGlashan TH. Self-criticism versus neuroticism in predicting depression and psychosocial impairment for 4 years in a clinical sample. Compr Psychiatry. 2009;50:335–346. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2008.09.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kendler KS, Gatz M, Gardner CO, Pedersen NL. Personality and major depression: a Swedish longitudinal, population-based twin study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63:1113–1120. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.63.10.1113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jylhä P, Isometsä E. The relationship of neuroticism and extraversion to symptoms of anxiety and depression in the general population. Depress Anxiety. 2006;23:281–289. doi: 10.1002/da.20167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Uliaszek AA, Hauner KK, Zinbarg RE, Craske MG, Mineka S, Griffith JW, Rose RD. An examination of content overlap and disorder-specific predictions in the Associations of Neuroticism with Anxiety and Depression. J Res Pers. 2009;43:785–794. doi: 10.1016/j.jrp.2009.05.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Eysenck HJ. The Structure of Human Personality. London: Methuen; 1953. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cloninger CR, Svrakic DM, Przybeck TR. A psychobiological model of temperament and character. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993;50:975–990. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1993.01820240059008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Roberts BW, DelVecchio WF. The rank-order consistency of personality traits from childhood to old age: a quantitative review of longitudinal studies. Psychol Bull. 2000;126:3–25. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.126.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Caspi A, Roberts BW, Shiner RL. Personality development: stability and change. Annu Rev Psychol. 2005;56:453–484. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.55.090902.141913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Roberts BW, Walton KE, Viechtbauer W. Patterns of mean-level change in personality traits across the life course: a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Psychol Bull. 2006;132:1–25. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.132.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Terracciano A, McCrae RR, Costa PT., Jr Intra-individual change in personality stability and age. J Res Pers. 2010;44:31–37. doi: 10.1016/j.jrp.2009.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Specht J, Egloff B, Schmukle SC. Stability and change of personality across the life course: the impact of age and major life events on mean-level and rank-order stability of the big five. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2011;101:862–882. doi: 10.1037/a0024950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Littlefield AK, Sher KJ, Wood PK. Is “maturing out” of problematic alcohol involvement related to personality change? J Abnorm Psychol. 2009;118:360–374. doi: 10.1037/a0015125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Roberts BW, Robins RW, Caspi A, Trzesniewski KH. Personality Trait Development in Adulthood. In: Mortimer J, Shanahan M, editors. Handbook of the Life Course. New York: Kluwer; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Roberts BW, Wood D. Personality Development in the Context of the neo-Socioanalytical Model of Personality. In: Mroczek D, Little TD, editors. Handbook of Personality Development. Mahwah, New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Roberts BW, Mroczek D. Personality trait change in adulthood. Curr Dir Psychol Sci. 2008;17:31–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8721.2008.00543.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Klimstra TA, Luyckx K, Hale WW, III, Goossens L, Meeus WHJ. Longitudinal associations between personality profile stability and adjustment in college students: distinguishing among overall stability, distinctive stability, and within-time normativeness. J Pers. 2010;78:1163–1184. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6494.2010.00646.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.De Bolle M, Beyers W, De Clercq B, De Fruyt F. General personality and psychopathology in referred and nonreferred children and adolescents: an investigation of continuity, pathoplasty, and complication models. J Abnorm Psychol. 2012;121:958–970. doi: 10.1037/a0027742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Robins RW, Fraley RC, Roberts BW, Trzesniewski KH. A longitudinal study of personality change in young adulthood. J Pers. 2001;69:617–640. doi: 10.1111/1467-6494.694157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Johnson W, Hicks BM, McGue M, Iacono WG. Most of the girls are alright, but some aren’t: personality trajectory groups from ages 14 to 24 and some associations with outcomes. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2007;93:266–284. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.93.2.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Aluja A, Blanch A. The five and seven factors personality models: differences and similitude between the TCI-R, NEO-FFI-R and ZKPQ-50-CC. Span J Psychol. 2011;14:659–666. doi: 10.5209/rev_SJOP.2011.v14.n2.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mroczek DK, Spiro A., 3rd Personality change influences mortality in older men. Psychol Sci. 2007;18:371–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2007.01907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ben-Zeev D, Young MA, Madsen JW. Retrospective recall of affect in clinically depressed individuals and controls. Cognition Emotion. 2009;23:1021–1040. doi: 10.1080/02699930802607937. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Stone AA, Shiffman S. Ecological momentary assessment (EMA) in behavorial medicine. Ann Behav Med. 1994;16:199–202. [Google Scholar]
- 29.W: International Classification of Disorders, ICD-10. 1991, Huber, Bern
- 30.Trull TJ, Ebner-Priemer UW. Using experience sampling methods/ecological momentary assessment (ESM/EMA) in clinical assessment and clinical research: introduction to the special section. Psychol Assess. 2009;21:457–462. doi: 10.1037/a0017653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Koval P, Pe ML, Meers K, Kuppens P. Affect dynamics in relation to depressive symptoms: variable, unstable or inert? Emotion. 2013;13:1132–1141. doi: 10.1037/a0033579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Thompson RJ, Mata J, Jaeggi SM, Buschkuehl M, Jonides J, Gotlib IH. The everyday emotional experience of adults with major depressive disorder: examining emotional instability, inertia, and reactivity. J Abnorm Psychol. 2012;121:819–829. doi: 10.1037/a0027978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ebner-Priemer UW, Trull TJ. Ecological momentary assessment of mood disorders and mood dysregulation. Psychol Assess. 2009;21:463–475. doi: 10.1037/a0017075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Telford C, McCarthy-Jones S, Corcoran R, Rowse G. Experience sampling methodology studies of depression: the state of the art. Psychol Med. 2012;42:1119–1129. doi: 10.1017/S0033291711002200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tong EM. Personality influences in appraisal-emotion relationships: the role of neuroticism. J Pers. 2010;78:393–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6494.2010.00620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ilies R, Judge TA. Understanding the dynamic relationships among personality, mood and job satisfaction: a field experience sampling study. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process. 2002;89:1119–1139. doi: 10.1016/S0749-5978(02)00018-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Bolger N, Schilling EA. Personality and the problems of everyday life: the role of neuroticism in exposure and reactivity to daily stressors. J Pers. 1991;59:355–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6494.1991.tb00253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wichers M, Peeters F, Geschwind N, Jacobs N, Simons CJP, Derom C, Thiery E, Delespaul PH, van Os J. Unveiling patterns of affective responses in daily life may improve outcome prediction in depression: a momentary assessment study. J Affect Disord. 2010;124:191–195. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2009.11.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wichers M, Peeters F, Rutten BPF, Jacobs N, Derom C, Thiery E, Delespaul P, van Os J. A time-lagged momentary assessment study on daily life physical activity and affect. Health Psychol. 2012;31:135–144. doi: 10.1037/a0025688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zautra AJ, Affleck GG, Tennen H, Reich JW, Davis MC. Dynamic approaches to emotions and stress in everyday life: Bolger and Zuckerman reloaded with positive as well as negative affects. J Pers. 2005;73:1511–1538. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-3506.2005.00357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Miller DJ, Vachon DD, Lynam DR. Neuroticism, negative affect, and negative affect instability: establishing convergent and discriminant validity using ecological momentary assessment. Pers Individ Differ. 2009;47:873–877. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2009.07.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Schimmack U. Affect measurement in experience sampling research. J Happiness. 2003;4:79–106. doi: 10.1023/A:1023661322862. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Howell RT, Rodzon KS. An exploration of personality–affect relations in daily life: determining the support for the affect-level and affect-reactivity views. Pers Individ Differ. 2011;51:797–801. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2011.06.020. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.David JP, Green PJ, Martin R, Suls J. Differential roles of neuroticism, extraversion, and event desirability for mood in daily life: an integrative model of top-down and bottom-up influences. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1997;73:149–159. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.73.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Suls J, Martin R. The daily life of the garden-variety neurotic: reactivity, stressor exposure, mood spillover, and maladaptive coping. J Pers. 2005;73:1485–1510. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6494.2005.00356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Jacobs N, van Os J, Derom C, Thiery E, Delespaul P, Wichers M. Neuroticism explained? From a non-informative vulnerability marker to informative person-context interactions in the realm of daily life. Br J Clin Psychol. 2011;50:19–32. doi: 10.1348/014466510X491397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Barnow S, Aldinger M, Arens EA, Ulrich I, Spitzer C, Grabe HJ, Stopsack M. Maternal transmission of borderline personality disorder symptoms in the community-based Greifswald family study. J Pers Disord. 2012;27:806–819. doi: 10.1521/pedi_2012_26_058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Barnow S, Ulrich I, Grabe HJ, Freyberger HJ, Spitzer C. The influence of parental drinking behaviour and antisocial personality disorder on adolescent behavioural problems: results of the Greifswalder family study. Alcohol Alcohol. 2007;42:623–628. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agm051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Costa PTJ, McCrae RR. Revised NEO Personality Inventory (NEO-PI-R) and NEO-Five-Factor-Inventory (NEO-FFI): professional manual. Odessa: Psychological Assessment Ressources; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Borkenau P, Ostendorf F. NEO-Fünf-Faktoren Inventar (NEO-FFI) Göttingen: Hogrefe Verlag; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ostendorf F, Angleitner A. NEO-Persönlichkeitsinventar nach Costa und McCrae, Revidierte Fassung (NEO-PI-R). Manual. Göttingen: Hogrefe; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lüdtke O, Trautwein U, Nagy G, Köller O. Eine Validierungsstudie zum NEO-FFI in einer Stichprobe junger Erwachsener: effekte des Itemformats, faktorielle Validität und Zusammenhänge mit Schulleistungsindikatoren. Diagnostica. 2004;50:134–144. doi: 10.1026/0012-1924.50.3.134. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Roth M. Überprüfung der Anwendbarkeit des NEO-Fünf-Faktoren Inventars (NEO-FFI) bei Jugendlichen im Alter zwischen 14 und 16 Jahren. Diagnostica. 2002;48:59–67. doi: 10.1026//0012-1924.48.2.59. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Luby JL, Svrakic DM, McCallum K, Przybeck TR, Cloninger CR. The junior temperament and character inventory: preliminary validation of a child self-report measure. Psychol Rep. 1999;84:1127–1138. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1999.84.3c.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Cloninger CR, Przybeck TR, Svrakic DM, Wetzel RD. The Temperament and Character Inventory (TCI): A Guide to its Development and use. St. Louis: Washington University; 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Widiger TA, Simonsen E. Alternative dimensional models of personality disorder: finding a common ground. J Pers Disord. 2005;19:110–130. doi: 10.1521/pedi.19.2.110.62628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Stepp SD, Yu L, Miller JD, Hallquist MN, Trull TJ, Pilkonis PA. Integrating competing dimensional models of personality: linking the SNAP, TCI, and NEO using item response theory. Pers Disord. 2012;3:107–126. doi: 10.1037/a0025905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Wittchen HU, Lachner G, Wunderlich U, Pfister H. Test-retest reliability of the computerized DSM-IV version of the Munich-Composite International Diagnostic Interview (M-CIDI) Soc Psych Psych Epid. 1998;33:568–578. doi: 10.1007/s001270050095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Wittchen HU, Semmler G. Composite International Diagnostic Interview (CIDI) Beltz: Weinheim; 1990. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Unnewehr S, Schneider S, Margraf J. Kinder-DIPS: Diagnostisches Interview bei Psychischen Störungen im Kindes- und Jugendalter. Berlin: Springer; 1995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Döpfner M, Berner W, Lehmkuhl G. Handbuch: Fragebogen für Jugendliche. Forschungsergebnisse zur Deutschen Fassung des Youth Self Report (YSR) der Child Behavior Checklist. Köln: Arbeitsgruppe Kinder-, Jugend- und Familiendiagnostik (KJFD); 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Achenbach TM. Child Behaviour Checklist and Related Instruments. In: Maruish ME, editor. The use of Psychological Testing for Treatment Planning and Outcome Assessment. Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 1994. pp. 517–549. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Derogatis LR. SCL-90-R, Administration, Scoring & Procedures Manual-I for the R(Evised) Version. Baltimore: John Hopkins University School of Medicine; 1977. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Franke GH. SCL-90-R: Die Symptom-Checkliste von Derogatis: Deutsche Version. Göttingen: Beltz Test; 1995. [Google Scholar]
- 65.Derogatis LR, Melisaratos N. The brief symptom inventory: an introductory report. Psychol Med. 1983;13:595–605. doi: 10.1017/S0033291700048017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Prinz U, Nutzinger DO, Schulz H, Petermann F, Braukhaus C, Andreas D. The symptom-check-list-90-R (SCL-90-R) and the short versions of the SCL-90-R: psychometric analyses of inpatients with mental disorders. Phys Rehab Kur Med. 2008;18:337–343. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093323. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Hessel A, Schumacher J, Geyer M, Brähler E. Symptom-checklist SCL-90-R: validation and standardization based on a representative sample of the German population. Diagnostica. 2001;47:27–39. doi: 10.1026//0012-1924.47.1.27. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Geisheim C, Hahlweg K, Fiegenbaum W, Frank M, Schröder B, von Witzleben I. Das Brief Symptom Inventory (BSI) als Instrument zur Qualitätssicherung in der Psychotherapie. Diagnostica. 2002;48:28–36. doi: 10.1026//0012-1924.48.1.28. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Moskowitz DS, Young SN. Ecological momentary assessment: what it is and why it is a method of the future in clinical psychopharmacology. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2006;31:13–20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Csikszentmihalyi M, Larson R. Validity and reliability of the experience-sampling method. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1987;175:526–536. doi: 10.1097/00005053-198709000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Feldman BJ, Masyn KE, Conger RD. New approaches to studying problem behaviors: a comparison of methods for modeling longitudinal, categorical adolescent drinking data. Dev Psychol. 2009;45:652–676. doi: 10.1037/a0014851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Muthén L, Muthén B. Mplus user’s Guide. Los Angeles: Muthén & Muthén; 1998-2010. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Jung T, Wickrama KAS. An introduction to latent class growth analysis and growth mixture modeling. Soc Pers Psychol Compass. 2008;2:302–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-9004.2007.00054.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Nylund KL, Asparouhov T, Muthén BO. Deciding on the number of classes in latent class analysis and growth mixture modeling: a Monte Carlo simulation study. Struct Equ Model. 2007;14:535–569. doi: 10.1080/10705510701575396. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Lo Y, Mendell NR, Rubin DB. Testing the number of components in a normal mixture. Biometrika. 2001;88:767–778. doi: 10.1093/biomet/88.3.767. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 76.McLachlan G. On bootstrapping the likelihood ratio test statistic for the number of components in a normal mixture. Appl Stat. 1987;36:318–324. doi: 10.2307/2347790. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Clark SL. Mixture Modeling With Behavioral Data. Los Angeles: University of California; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 78.Ebner-Priemer UW, Eid M, Kleindienst N, Stabenow S, Trull TJ. Analytic strategies for understanding affective (in) stability and other dynamic processes in psychopathology. J Abnorm Psychol. 2009;118:195–202. doi: 10.1037/a0014868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Jahng S, Wood PK, Trull TJ. Analysis of affective instability in ecological momentary assessment: indices using successive difference and group comparison via multilevel modeling. Psychol Metod. 2008;13:354–375. doi: 10.1037/a0014173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Schimmack U, Oishi S, Furr RM, Funder DC. Personality and life satisfaction: a facet-level analysis. Pers Soc Psychol Bull. 2004;30:1062–1075. doi: 10.1177/0146167204264292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Vitterso J, Nilsen F. The conceptual and relational structure of subjective well-being, neuroticism, and extraversion: once again, neuroticism is the important predictor of happiness. Soc Ind Res. 2002;57:89–118. doi: 10.1023/A:1013831602280. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Ormel J, Riese H, Rosmalen JGM. Interpreting neuroticism scores across the adult life course: immutable or experience-dependent set points of negative affect? Clin Psychol Rev. 2012;32:71–79. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2011.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Roberts BW, Caspi A, Moffitt TE. The kids are alright: growth and stability in personality development from adolescence to adulthood. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2001;81:670–683. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.81.4.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Twenge JM, Nolen-Hoeksema S. Age, gender, race, socioeconomic status, and birth cohort differences on the children’s depression inventory: a meta-analysis. J Abnorm Psychol. 2002;111:578–588. doi: 10.1037/0021-843X.111.4.578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Garber J, Keiley MK, Martin C. Developmental trajectories of adolescents’ depressive symptoms: predictors of change. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2002;70:79–95. doi: 10.1037/0022-006X.70.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Ormel J, Rosmalen J, Farmer A. Neuroticism: a non-informative marker of vulnerability to psychopathology. Soc Psych Psych Epid. 2004;39:906–912. doi: 10.1007/s00127-004-0873-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Nicholls JG, Licht BG, Pearl RA. Some dangers of using personality questionnaires to study personality. Psychol Bull. 1982;92:572–580. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.92.3.572. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Howe ML, Malone C. Mood-congruent true and false memory: effects of depression. Memory. 2011;19:192–201. doi: 10.1080/09658211.2010.544073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Koster EHW, De Raedt R, Leyman L, De Lissnyder E. Mood-congruent attention and memory bias in dysphoria: exploring the coherence among information-processing biases. Behav ResTher. 2010;48:219–225. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2009.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Wichers M, Myin-Germeys I, Jacobs N, Peeters F, Kenis G, Derom C, Vlietinck R, Delespaul P, Van Os J. Genetic risk of depression and stress-induced negative affect in daily life. Br J Psych. 2007;191:218–223. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.106.032201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Shiffman S, Balabanis MH, Gwaltney CJ, Paty JA, Gnys M, Kassel JD, Hickcox M, Paton SM. Prediction of lapse from associations between smoking and situational antecedents assessed by ecological momentary assessment. Drug Alcohol Depen. 2007;91:159–168. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2007.05.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Wegner KE, Smyth JM, Crosby RD, Wittrock D, Wonderlich SA, Mitchell JE. An evaluation of the relationship between mood and binge eating in the natural environment using ecological momentary assessment. Int J Eat Disord. 2002;32:352–361. doi: 10.1002/eat.10086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Wichers MC, Myin-Germeys I, Jacobs N, Peeters F, Kenis G, Derom C, Vlietinck R, Delespaul P, van Os J. Evidence that moment-to-moment variation in positive emotions buffer genetic risk for depression: a momentary assessment twin study. Acta Psych Scand. 2007;115:451–457. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.2006.00924.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Murray G, Allen NB, Trinder J. Longitudinal investigation of mood variability and the ffm: neuroticism predicts variability in extended states of positive and negative affect. Pers Individ Differ. 2002;33:1217–1228. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8869(01)00217-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Klein DN, Kotov R, Bufferd SJ. Personality and depression: explanatory models and review of the evidence. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2011;7:269–295. doi: 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032210-104540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Cloninger CR, Svrakic DM, Przybeck TR. Can personality assessment predict future depression? A twelve-month follow-up of 631 subjects. J Affect Disord. 2006;92:35–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2005.12.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Weber K, Giannakopoulos P, Bacchetta J-P, Quast S, Herrmann F, Delaloye C, Ghisletta P, De Ribaupierre A, Canuto A. Personality traits are associated with acute major depression across the age spectrum. Aging Ment Health. 2012;16:472–480. doi: 10.1080/13607863.2011.630375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Akiskal HS, Hirschfeld RM, Yerevanian BI. The relationship of personality to affective disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1983;40:801–810. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1983.01790060099013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Ulrich I, Stopsack M, Spitzer C, Grabe HJ, Freyberger HJ, Barnow S. [Familial transmission of depression: the importance of harm avoidance] Nervenarzt. 2011;82:1169–1177. doi: 10.1007/s00115-010-3209-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Jain U, Blais MA, Otto MW, Hirshfeld DR, Sachs GS. Five-factor personality traits in patients with seasonal depression: treatment effects and comparisons with bipolar patients. J Affect Disord. 1999;55:51–54. doi: 10.1016/S0165-0327(98)00206-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Kendler KS, Kuhn J, Prescott CA. The interrelationship of neuroticism, sex, and stressful life events in the prediction of episodes of major depression. Am J Psychiatry. 2004;161:631–636. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.161.4.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Roy A. Childhood trauma and neuroticism as an adult: possible implication for the development of the common psychiatric disorders and suicidal behaviour. Psychol Med. 2002;32:1471–1474. doi: 10.1017/S0033291702006566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Blaney PH. Affect and memory: a review. Psychol Bull. 1986;99:229–246. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.99.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Coifman KG, Bonanno GA. When distress does not become depression: emotion context sensitivity and adjustment to bereavement. J Abnorm Psychol. 2010;119:479–490. doi: 10.1037/a0020113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Aldao A. The future of emotion regulation research: capturing context. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2013;8:155–172. doi: 10.1177/1745691612459518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Clark LA, Watson D, Mineka S. Temperament, personality, and the mood and anxiety disorders. J Abnorm Psychol. 1994;103:103–116. doi: 10.1037/0021-843X.103.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Farmer A, Redman K, Harris T, Mahmood A, Sadler S, Pickering A, McGuffin P. Neuroticism, extraversion, life events and depression. The Cardiff depression study. Brit J Psych. 2002;181:118–122. doi: 10.1017/s0007125000161823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Lejuez CW, Magidson JF, Mitchell SH, Sinha R, Stevens MC, De Wit H. Behavioral and biological indicators of impulsivity in the development of alcohol use, problems, and disorders. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010;34:1334–1345. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01217.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


