Abstract
Acquired cellular immunity to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis is believed to reside in the capacity of mononuclear phagocytes of immunized animals to inhibit intracellular multiplication of the parasite. However, in macrophage tissue culture systems, it has been customary to employ streptomycin in the medium for the purpose of restricting extracellular, but not intracellular, growth of M. tuberculosis. In contrast, our data show that small amounts of streptomycin markedly inhibit intracellular as well as extracellular growth of M. tuberculosis in normal mouse peritoneal macrophages, and that the degree of this inhibition is directly proportional to the concentration of streptomycin used. In the absence of streptomycin, virulent tubercle bacilli grew as rapidly in “immune” macrophages as in normal macrophages. “Immune” macrophages, however, were slightly more resistant to destruction by the intracellularly multiplying mycobacteria. In the presence of streptomycin, however, intracellular mycobacterial growth was inhibited more in “immune” macrophages than in normal macrophages, and this effect also was directly proportional to the concentration of streptomycin used. Virulent mycobacteria grew somewhat more slowly within mouse peritoneal macrophages obtained after induction of a peritoneal exudate with glycogen than in noninduced cells. The rate of multiplication, though, was the same within normal and “immune” induced peritoneal cells except in the presence of streptomycin. As with noninduced macrophages, this drug inhibited the intracellular multiplication of virulent tubercle bacilli more effectively within “immune” induced than within normal induced cells. It would appear, therefore, that the greater inhibition of intracellular multiplication of virulent tubercle bacilli in “immune” macrophages in tissue culture noted by a number of investigators in the past may have been an artifact created by the use of streptomycin in the tissue culture medium.
Full text
PDF


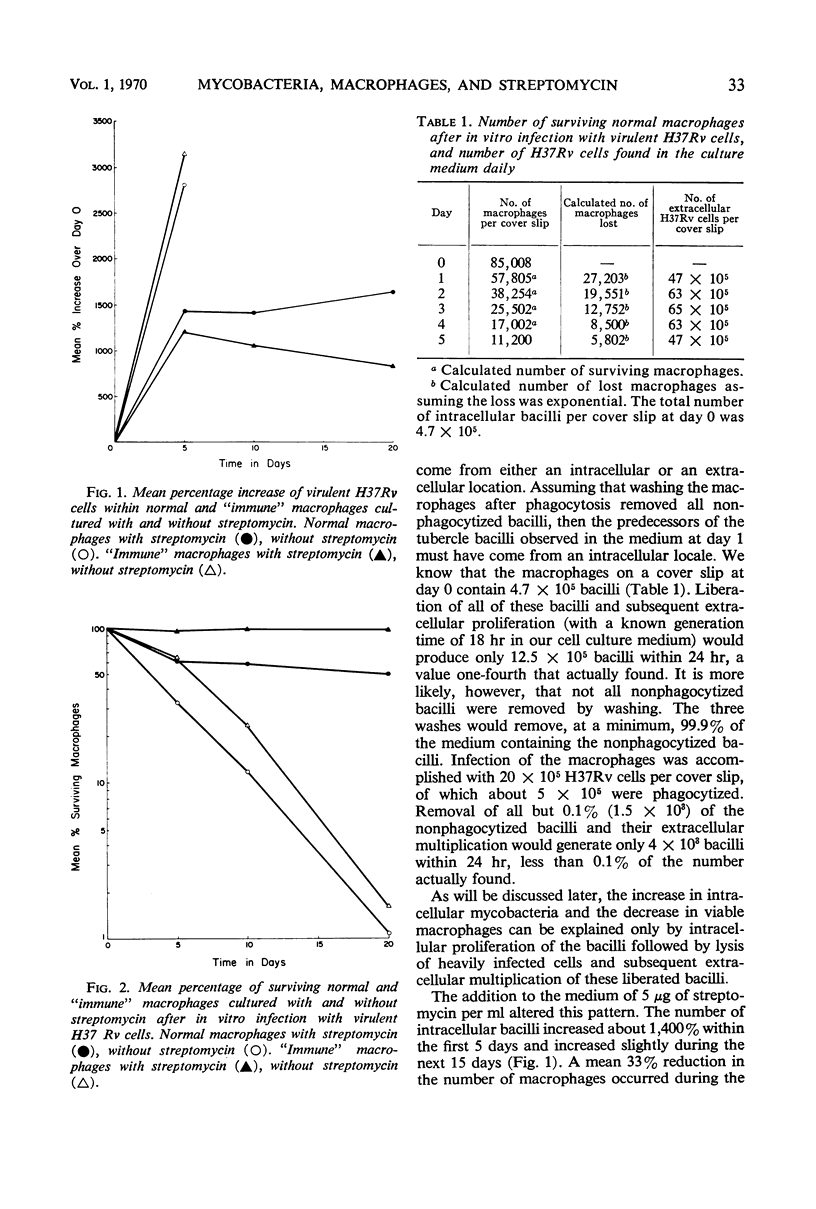
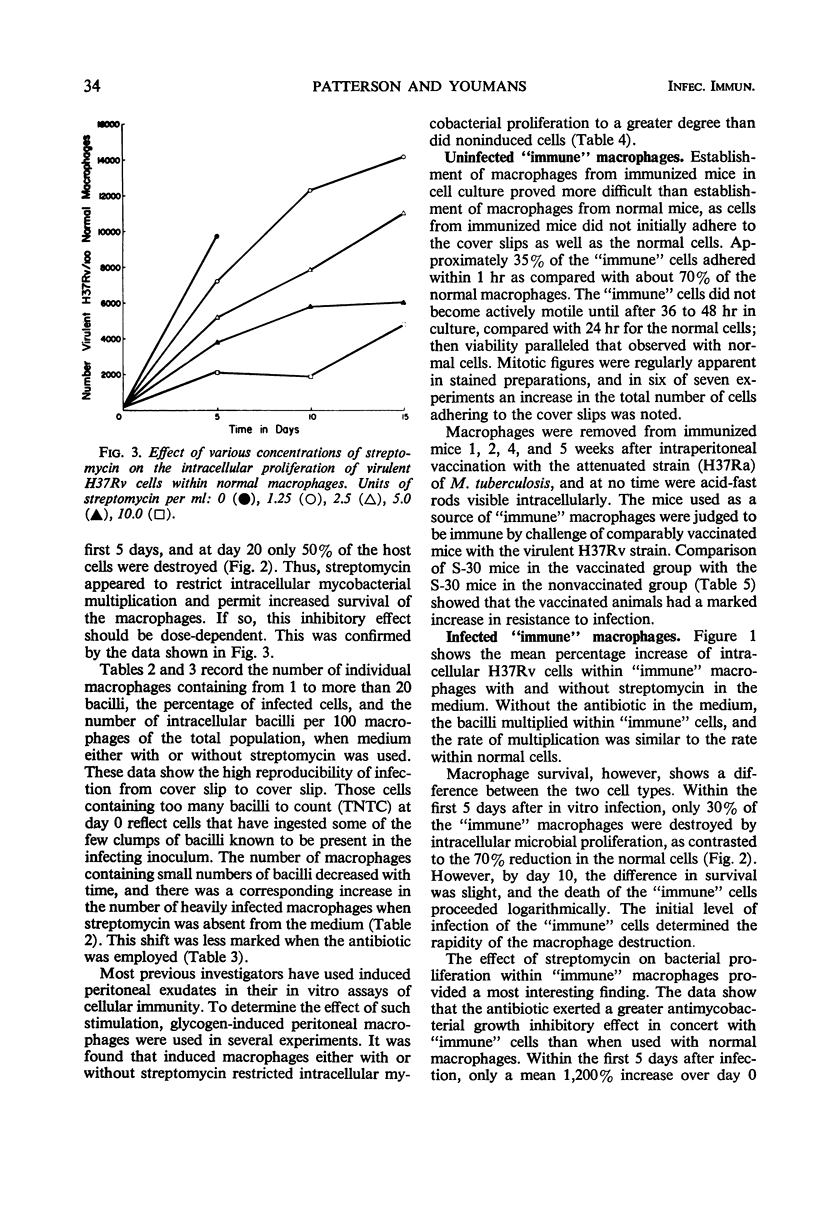
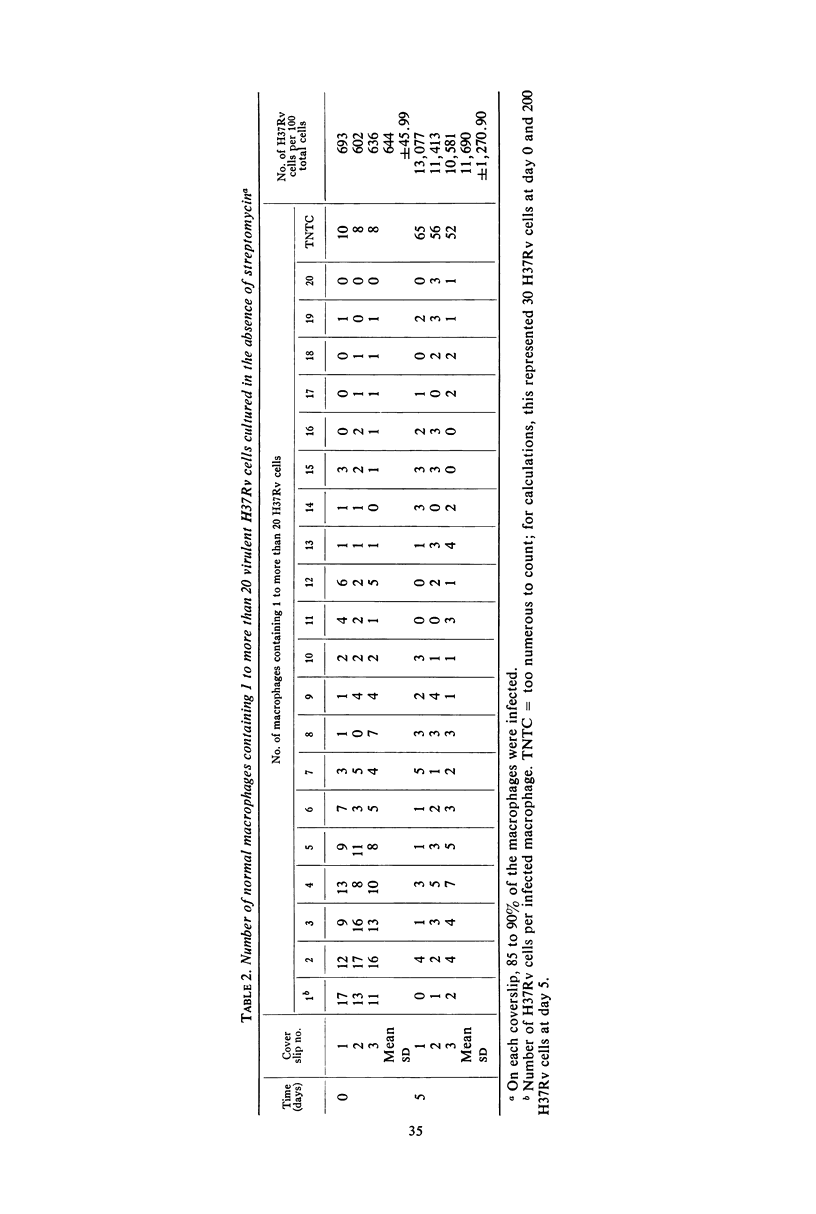



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERTHRONG M., HAMILTON M. A. Tissie culture studies on resistance in tuberculosis. I. Normal guinea pig monocytes with tubercle bacilli of different virulence. Am Rev Tuberc. 1958 Mar;77(3):436–449. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1958.77.3.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTHRONG M., HAMILTON M. A. Tissue culture studies on resistance in tuberculosis. II. Monocytes from normal and immunized guinea pigs infected with virulent human tubercle bacilli. Am Rev Tuberc. 1959 Feb;79(2):221–231. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1959.79.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUN W., POMALES-LEBRON A., STINEBRING W. R. Interactions between mononuclear phagocytes and Brucella abortus strains of different virulence. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Feb;97(2):393–397. doi: 10.3181/00379727-97-23752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRIEGER E. M. New approaches to the study of experimental infection. Bibl Tuberc. 1951;5:236–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V. Modification of macrophage function. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1968 Jun;5(3):179–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG Y. T. LONG-TERM CULTIVATION OF MOUSE PERITONEAL MACROPHAGES. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1964 Jan;32:19–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., BENSON B. THE DIFFERENTIATION OF MONONUCLEAR PHAGOCYTES. MORPHOLOGY, CYTOCHEMISTRY, AND BIOCHEMISTRY. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:153–170. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. T. Suppressive activity of streptomycin on the growth of Mycobacterium lepraemurium in macrophage cultures. Appl Microbiol. 1969 May;17(5):750–754. doi: 10.1128/am.17.5.750-754.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn Z. A., Parks E. The regulation of pinocytosis in mouse macrophages. II. Factors inducing vesicle formation. J Exp Med. 1967 Feb 1;125(2):213–232. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.2.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dannenberg A. M., Jr, Meyer O. T., Esterly J. R., Kambara T. The local nature of immunity in tuberculosis, illustrated histochemically in dermal BCG lesions. J Immunol. 1968 May;100(5):931–941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H., SAZ A. K. Antibiotics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1955;9:173–226. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.09.100155.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELBERG S. S., FONG J., SCHNEIDER P. Studies on tubercle bacillus-monocyte relationship. I. Quantitative analysis of effect of serum of animals vaccinated with BCG upon bacterium-monocyte system. J Exp Med. 1956 Oct 1;104(4):455–465. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.4.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELBERG S. S., FONG J., SCHNEIDER P. Studies on tubercle bacillus-monocyte relationship. II. Induction of monocyte degeneration by bacteria and culture filtrate: specificity of serum and monocyte effects on resistance to degeneration. J Exp Med. 1957 Jan 1;105(1):25–37. doi: 10.1084/jem.105.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekzemplyarov O. N. Penetration of tetracycline and streptomycin into macrophages cultured in vitro. Fed Proc Transl Suppl. 1966 Mar-Apr;25(2):312–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN B. A., VANA L. R. Host-parasite relationships in brucellosis. I. Infection of normal guinea pig macrophages in tissue culture. J Infect Dis. 1958 May-Jun;102(3):258–267. doi: 10.1093/infdis/102.3.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgeorge R. B., Solotorovsky M., Smith H. The behaviour of Brucella abortus within macrophages separated from the blood of normal and immune cattle by adherence to glass. Br J Exp Pathol. 1967 Oct;48(5):522–528. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaugas J., Rees R. J. Enhancing effect of antilymphocytic serum on mycobacterial infections in mice. Nature. 1968 Jul 27;219(5152):408–409. doi: 10.1038/219408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEISE E. R., MYRVIK Q. N., LEAKE E. S. EFFECT OF BACILLUS CALMETTE-GU'ERIN ON THE LEVELS OF ACID PHOSPHATASE, LYSOZYME AND CATHEPSIN IN RABBIT ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGES. J Immunol. 1965 Jul;95:125–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., PICKETT M. J. A cellular basis of immunity in experimental Brucella infection. J Exp Med. 1958 Sep 1;108(3):343–360. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.3.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HSU H. S. IN VITRO STUDIES ON THE INTERACTIONS BETWEEN MACROPHAGES OF RABBITS AND TUBERCLE BACILLI. I. CELLULAR BASIS OF NATIVE RESISTANCE. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1965 Apr;91:488–498. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1965.91.4.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HSU H. S. IN VITRO STUDIES ON THE INTERACTIONS BETWEEN MACROPHAGES OF RABBITS AND TUBERCLE BACILLI. II. CELLULAR AND HUMORAL ASPECTS OF ACQUIRED RESISTANCE. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1965 Apr;91:499–509. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1965.91.4.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCHAN I., SMITH L. ANTIMYCOBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF TUBERCULOSTATIC FACTOR ON INTRACELLULAR BACILLI. J Immunol. 1965 Feb;94:220–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. The action of drugs on intracellular tubercle bacilli. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1952 Jul;64(3):429–446. doi: 10.1002/path.1700640302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. The growth of tubercle bacilli in monocytes from normal and vaccinated rabbits. Am Rev Tuberc. 1954 Apr;69(4):495–504. doi: 10.1164/art.1954.69.4.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITSUHASHI S., SATO I., TANAKA T. Experimental salmonellosis. Intracellular growth of Salmonella enteritidis ingested in mononuclear phagocytes of mice, and cellular basis of immunity. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jun;81:863–868. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.6.863-868.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORELLO J. A., BAKER E. E. INTERACTION OF SALMONELLA WITH PHAGOCYTES IN VITRO. J Infect Dis. 1965 Apr;115:131–141. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIFFENEGGER J., YOUMANS G. P. The effect of macrocyclon on the multiplication of tubercle bacilli in the lungs and spleen of mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1960 Aug;41:403–413. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nutter J. E., Myrvik Q. N. In vitro interactions between rabbit alveolar macrophages and Pasteurella tularensis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):645–651. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.645-651.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxman E., Bonventre P. F. Facilitated uptake of streptomycin by Kupffer cells during phagocytosis. Nature. 1967 Jan 21;213(5073):294–295. doi: 10.1038/213294a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATNODE R. A., HUDGINS P. C. Sonic fragility of leukocytes from guinea pigs vaccinated with BCG. Am Rev Tuberc. 1959 Mar;79(3):323–328. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1959.79.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POMALES-LEBRON A., STINEBRING W. R. Intracellular multiplication of Brucella abortus in normal and immune mononuclear phagocytes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Jan;94(1):78–83. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-22860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO K., AKIYAMA T., NAKANO M., USHBA D. Interaction between Salmonella enteritidis and tissue cultured macrophages derived from immunized animals. Jpn J Microbiol. 1960 Oct;4:395–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1960.tb00188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L., YOUMANS G. P. Enumeration of viable tubercle bacilli from the organs of nonimmunized and immunized mice. Am Rev Tuberc. 1957 Oct;76(4):616–635. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1957.76.4.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPARD C. C. Use of HeLa cells infected with tubercle bacilli for the study of antituberculous drugs. J Bacteriol. 1957 Apr;73(4):494–498. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.4.494-498.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTER E. Multiplication of tubercle bacilli within mononuclear phagocytes in tissue cultures derived from normal animals and animals vaccinated with BCG. J Exp Med. 1953 Feb 1;97(2):235–245. doi: 10.1084/jem.97.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTER E. Multiplication of tubercle bacilli within phagocytes cultivated in vitro, and effect of streptomycin and isonicotinic acid hydrazide. Am Rev Tuberc. 1952 Jun;65(6):775–776. doi: 10.1164/art.1952.65.6.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTER E. The multiplication of tubercle bacilli within normal phagocytes in tissue culture. J Exp Med. 1952 Aug;96(2):137–150. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS G. P., YOUMANS A. S. AN ACUTE PULMONARY GRANULOMATOUS RESPONSE IN MICE PRODUCED BY MYCOBACTERIAL CELLS AND ITS RELATION TO INCREASED RESISTANCE AND INCREASED SUSCEPTIBILITY TO EXPERIMENTAL TUBERCULOUS INFECTION. J Infect Dis. 1964 Apr;114:135–151. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.2.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS G. P., YOUMANS A. S. The measurement of the response of immunized mice to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis va. hominis. J Immunol. 1957 May;78(5):318–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans G. P., Youmans A. S. A METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF THE RATE OF GROWTH OF TUBERCLE BACILLI BY THE USE OF SMALL INOCULA. J Bacteriol. 1949 Aug;58(2):247–255. doi: 10.1128/jb.58.2.247-255.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



