Abstract
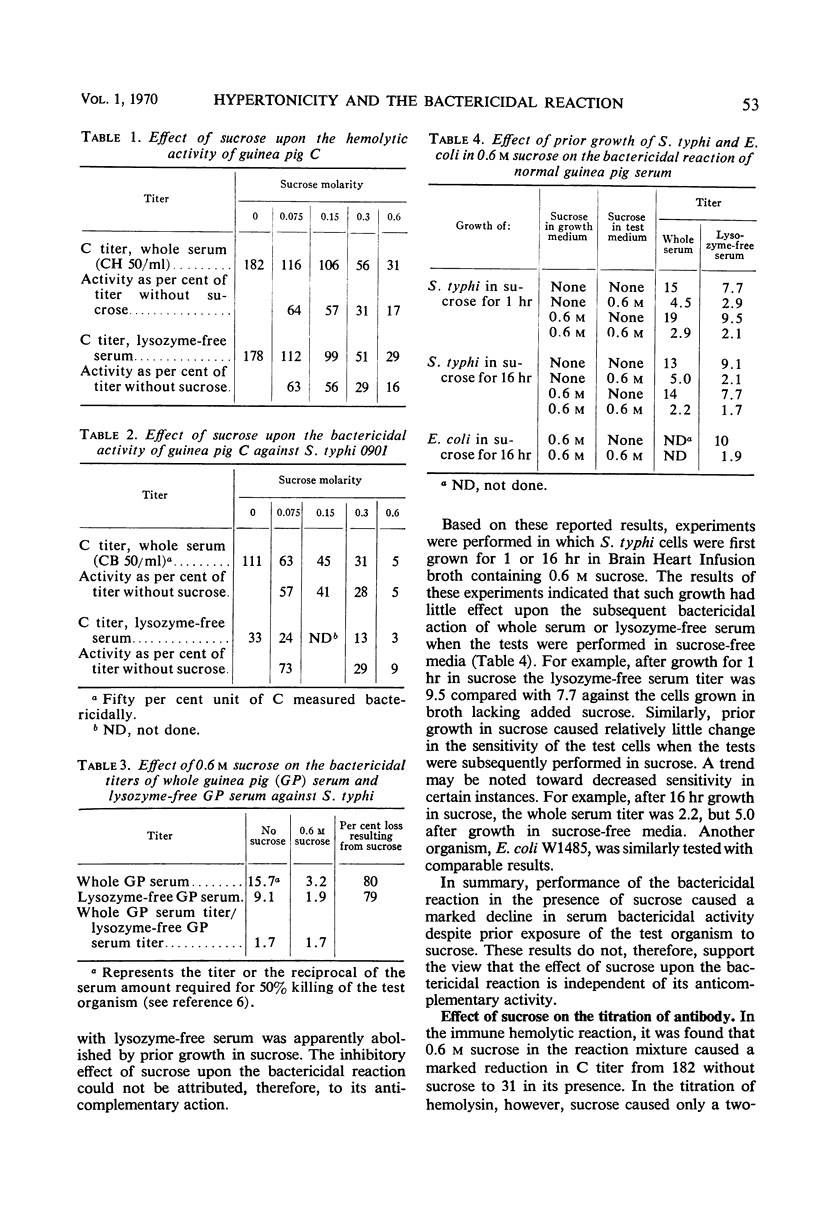
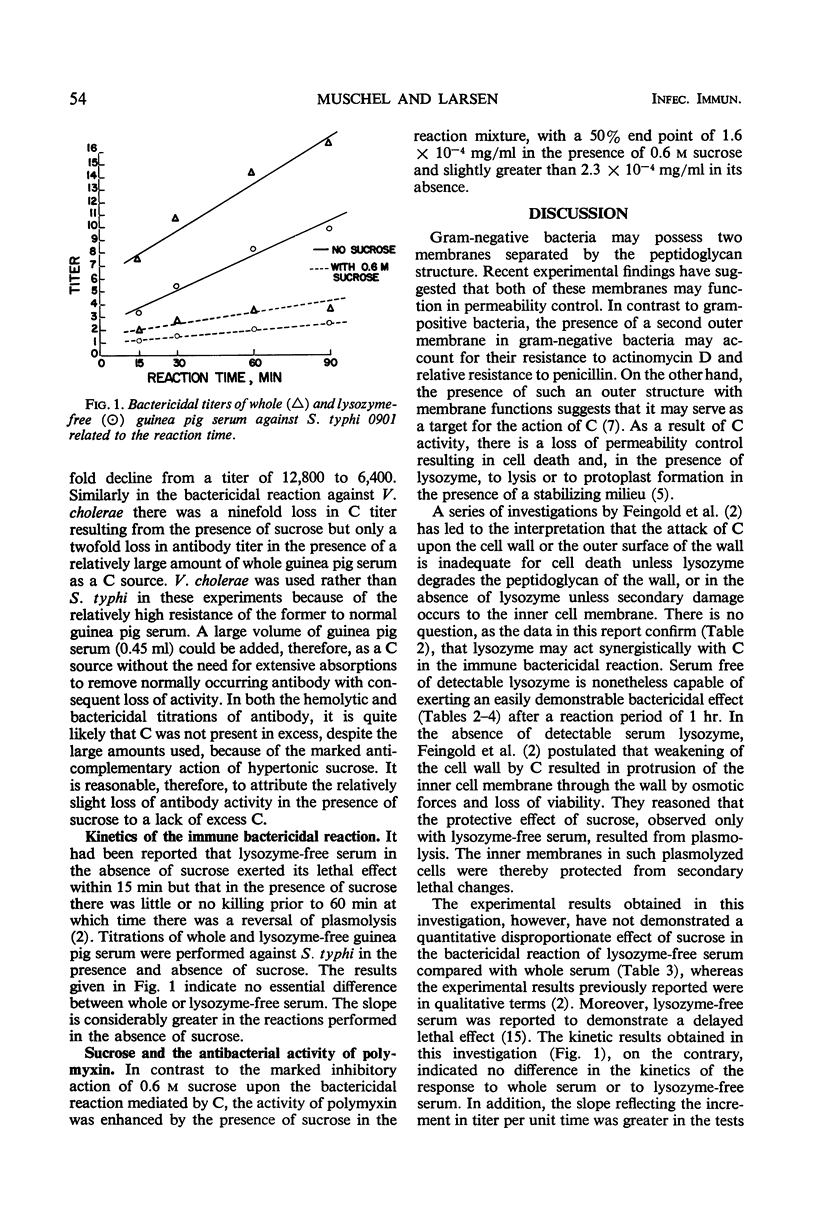
This study was performed to determine the mechanism whereby hypertonic sucrose inhibits the immune bactericidal reaction. Other investigators had postulated that the initial attack of complement (C) on the cell wall was followed with lysozyme-containing whole serum by an enzymatic reaction upon the peptidoglycan substrate resulting in cell death. In the absence of serum lysozyme, secondary lethal changes might occur from damage to the cell's inner membrane as a result of osmotic forces in the presence of a defective cell wall. Hypertonic sucrose giving rise to plasmolysis and protection of the inner membrane was presumed to differentially inhibit the immune response mediated by lysozyme-free serum. The experimental results observed in this investigation have indicated, however, that the inhibitory effect of sucrose upon the bactericidal reaction may be explained simply by its anticomplementary effect and not by any effect on the bacterial cell. This view was supported by the following observations: (i) the comparability of the inhibitory effect of sucrose upon the immune hemolytic and bactericidal reactions, (ii) the comparable percentage loss in bactericidal activity of whole serum and lysozyme-free serum resulting from hypertonic sucrose, (iii) bactericidal antibody titrations were relatively unaffected and C titrations markedly inhibited by sucrose, (iv) the inhibitory effect of sucrose on the bactericidal reaction was unaffected by prior growth of the organism in the presence of sucrose, (v) the kinetics of the bactericidal reactivity of lysozyme-free serum in hypertonic sucrose, compared with whole serum, did not reveal a prolonged lag phase with lysozyme-free serum, but simply diminished reactivity at all times. These observations are compatible with the view that the C attack upon the outer surface of gram-negative bacteria, which plays a part in the cell's permeability control, may account for cell death. In this regard, the immune bactericidal reaction is quite comparable to the lysis of red cells or nucleated cells by C despite the lack of overt lysis in bacteria, probably because of their underlying supporting structures.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECKER E. L., WIRTZ G. H. The salt-sensitive step in immune hemolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Sep;35:291–292. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90377-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S., Goldman J. N., Kuritz H. M. Locus of the action of serum and the role of lysozyme in the serum bactericidal reaction. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2118–2126. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2118-2126.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A. The complement lysozyme sequence in immune bacteriolysis. Immunology. 1969 Apr;16(4):463–471. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHEL L. H., CAREY W. F., BARON L. S. Formation of bacterial protoplasts by serum components. J Immunol. 1959 Jan;82(1):38–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHEL L. H., CHAMBERLIN R. H., OSAWA E. Bactericidal activity of normal serum against bacterial cultures. I. Activity against Salmonella typhi strains. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Feb;97(2):376–382. doi: 10.3181/00379727-97-23748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHEL L. H., LOWE K. M. A new complement fixation test for syphilis. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Jul;46(1):147–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHEL L. H. Serum bactericidal actions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Nov 21;88:1265–1272. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb20117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHEL L. H., TREFFERS H. P. Quantitative studies on the bactericidal actions of serum and complement. I. A rapid photometric growth assay for bactericidal activity. J Immunol. 1956 Jan;76(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muschel L. H., Gustafson L. Antibiotic, detergent, and complement sensitivity of Salmonella typhi after ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid treatment. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2010–2013. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2010-2013.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muschel L. H., Jackson J. E. The reactivity of serum against protoplasts and spheroplasts. J Immunol. 1966 Jul;97(1):46–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D., Turner K. J. Passive sensitization of Salmonella adelaide to the bactericidal action of antibody and complement. Nature. 1968 Feb 17;217(5129):657–658. doi: 10.1038/217657a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMOLELIS A. N., HARTSELL S. E. The determination of lysozyme. J Bacteriol. 1949 Dec;58(6):731–736. doi: 10.1128/jb.58.6.731-736.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREFFERS H. P., MUSCHEL L. H. The combined actions of chloramphenicol and of bactericidal antibody plus complement on Salmonella typhosa. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):155–165. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



