Abstract
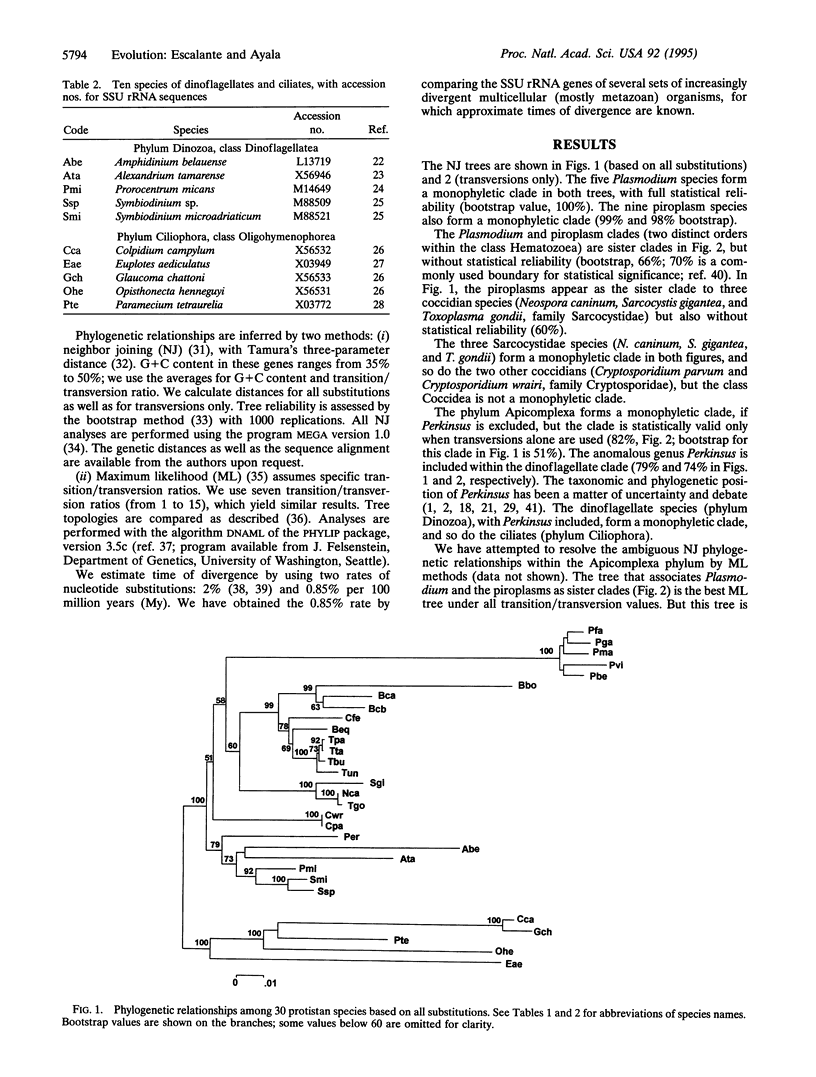
We have explored the evolutionary history of the Apicomplexa and two related protistan phyla, Dinozoa and Ciliophora, by comparing the nucleotide sequences of small subunit ribosomal RNA genes. We conclude that the Plasmodium lineage, to which the malarial parasites belong, diverged from other apicomplexan lineages (piroplasmids and coccidians) several hundred million years ago, perhaps even before the Cambrian. The Plasmodium radiation, which gave rise to several species parasitic to humans, occurred approximately 129 million years ago; Plasmodium parasitism of humans has independently arisen several times. The origin of apicomplexans (Plasmodium), dinoflagellates, and ciliates may be > 1 billion years old, perhaps older than the three multicellular kingdoms of animals, plants, and fungi. Digenetic parasitism independently evolved several times in the Apicomplexa.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allsopp B. A., Baylis H. A., Allsopp M. T., Cavalier-Smith T., Bishop R. P., Carrington D. M., Sohanpal B., Spooner P. Discrimination between six species of Theileria using oligonucleotide probes which detect small subunit ribosomal RNA sequences. Parasitology. 1993 Aug;107(Pt 2):157–165. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000067263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allsopp M. T., Cavalier-Smith T., De Waal D. T., Allsopp B. A. Phylogeny and evolution of the piroplasms. Parasitology. 1994 Feb;108(Pt 2):147–152. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000068232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barta J. R. Phylogenetic analysis of the class Sporozoea (phylum Apicomplexa Levine, 1970): evidence for the independent evolution of heteroxenous life cycles. J Parasitol. 1989 Apr;75(2):195–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalier-Smith T. Kingdom protozoa and its 18 phyla. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Dec;57(4):953–994. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.4.953-994.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corliss J. O. The kingdom Protista and its 45 phyla. Biosystems. 1984;17(2):87–126. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(84)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J., Luton K., Baverstock P. R., Brindley P. J., Nimmo K. A., Johnson A. M. The phylogeny of Neospora caninum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1994 Apr;64(2):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(94)00033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escalante A. A., Ayala F. J. Phylogeny of the malarial genus Plasmodium, derived from rRNA gene sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 22;91(24):11373–11377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.24.11373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol. 1981;17(6):368–376. doi: 10.1007/BF01734359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goggin C. L., Barker S. C. Phylogenetic position of the genus Perkinsus (Protista, Apicomplexa) based on small subunit ribosomal RNA. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Jul;60(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90029-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goman M., Mons B., Scaife J. The complete sequence of a Plasmodium malariae SSUrRNA gene and its comparison to other plasmodial SSUrRNA genes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Apr;45(2):281–288. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90096-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood S. J., Sogin M. L., Lynn D. H. Phylogenetic relationships within the class Oligohymenophorea, phylum Ciliophora, inferred from the complete small subunit rRNA gene sequences of Colpidium campylum, Glaucoma chattoni, and Opisthonecta henneguyi. J Mol Evol. 1991 Aug;33(2):163–174. doi: 10.1007/BF02193631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunderson J. H., McCutchan T. F., Sogin M. L. Sequence of the small subunit ribosomal RNA gene expressed in the bloodstream stages of Plasmodium berghei: evolutionary implications. J Protozool. 1986 Nov;33(4):525–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1986.tb05656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog M., Maroteaux L. Dinoflagellate 17S rRNA sequence inferred from the gene sequence: Evolutionary implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8644–8648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Bleasby A. J., Fuchs R. CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992 Apr;8(2):189–191. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. M., Murray P. J., Illana S., Baverstock P. J. Rapid nucleotide sequence analysis of the small subunit ribosomal RNA of Toxoplasma gondii: evolutionary implications for the Apicomplexa. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Oct;25(3):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishino H., Hasegawa M. Evaluation of the maximum likelihood estimate of the evolutionary tree topologies from DNA sequence data, and the branching order in hominoidea. J Mol Evol. 1989 Aug;29(2):170–179. doi: 10.1007/BF02100115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll A. H. Proterozoic and early Cambrian protists: evidence for accelerating evolutionary tempo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):6743–6750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.6743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll A. H. The early evolution of eukaryotes: a geological perspective. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):622–627. doi: 10.1126/science.1585174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labandeira C. C., Sepkoski J. J., Jr Insect diversity in the fossil record. Science. 1993 Jul 16;261(5119):310–315. doi: 10.1126/science.11536548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANWELL R. D. Some evolutionary possibilities in the history of the malaria parasites. Indian J Malariol. 1955 Dec;9(4):247–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T. F., de la Cruz V. F., Lal A. A., Gunderson J. H., Elwood H. J., Sogin M. L. Primary sequences of two small subunit ribosomal RNA genes from Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Feb;28(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Wilson A. C. Evolution in bacteria: evidence for a universal substitution rate in cellular genomes. J Mol Evol. 1987;26(1-2):74–86. doi: 10.1007/BF02111283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowan R., Powers D. A. Ribosomal RNA sequences and the diversity of symbiotic dinoflagellates (zooxanthellae). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3639–3643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Elwood H. J. Primary structure of the Paramecium tetraurelia small-subunit rRNA coding region: phylogenetic relationships within the Ciliophora. J Mol Evol. 1986;23(1):53–60. doi: 10.1007/BF02100998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Swanton M. T., Gunderson J. H., Elwood H. J. Sequence of the small subunit ribosomal RNA gene from the hypotrichous ciliate Euplotes aediculatus. J Protozool. 1986 Feb;33(1):26–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1986.tb05550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions when there are strong transition-transversion and G+C-content biases. Mol Biol Evol. 1992 Jul;9(4):678–687. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters A. P., Higgins D. G., McCutchan T. F. Plasmodium falciparum appears to have arisen as a result of lateral transfer between avian and human hosts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3140–3144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters A. P., McCutchan T. F. Partial sequence of the asexually expressed SU rRNA gene of Plasmodium vivax. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2135–2135. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



