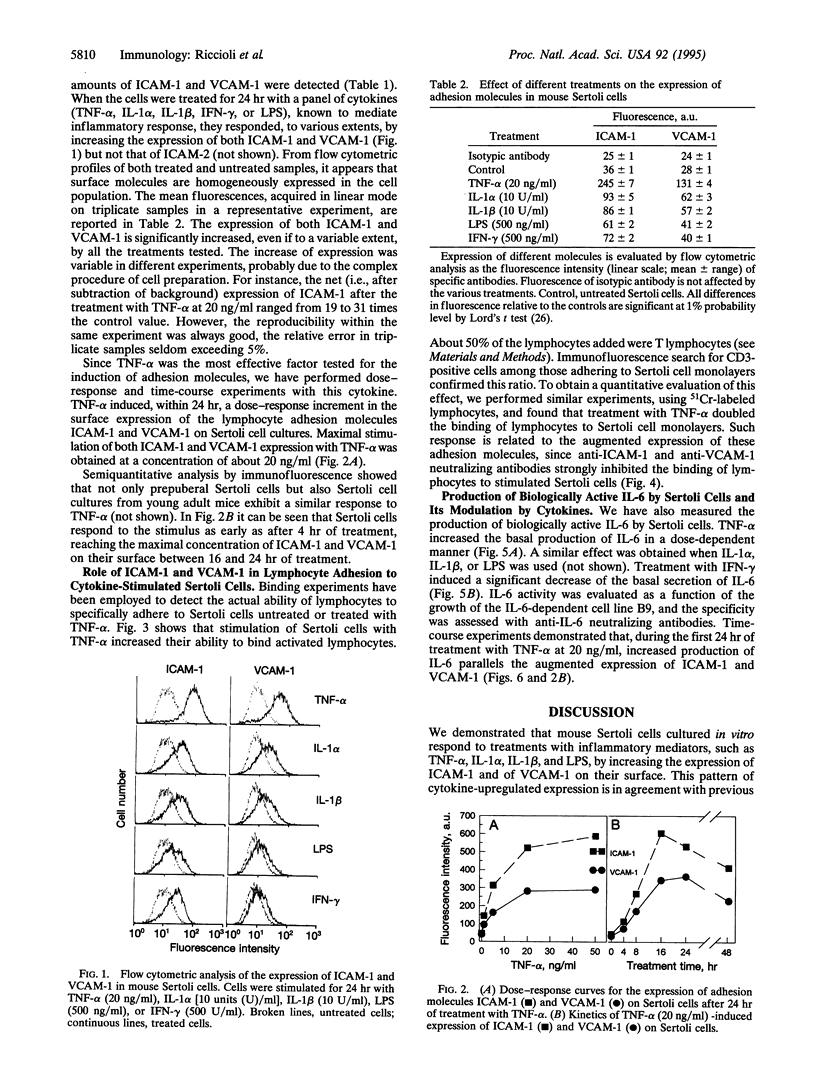
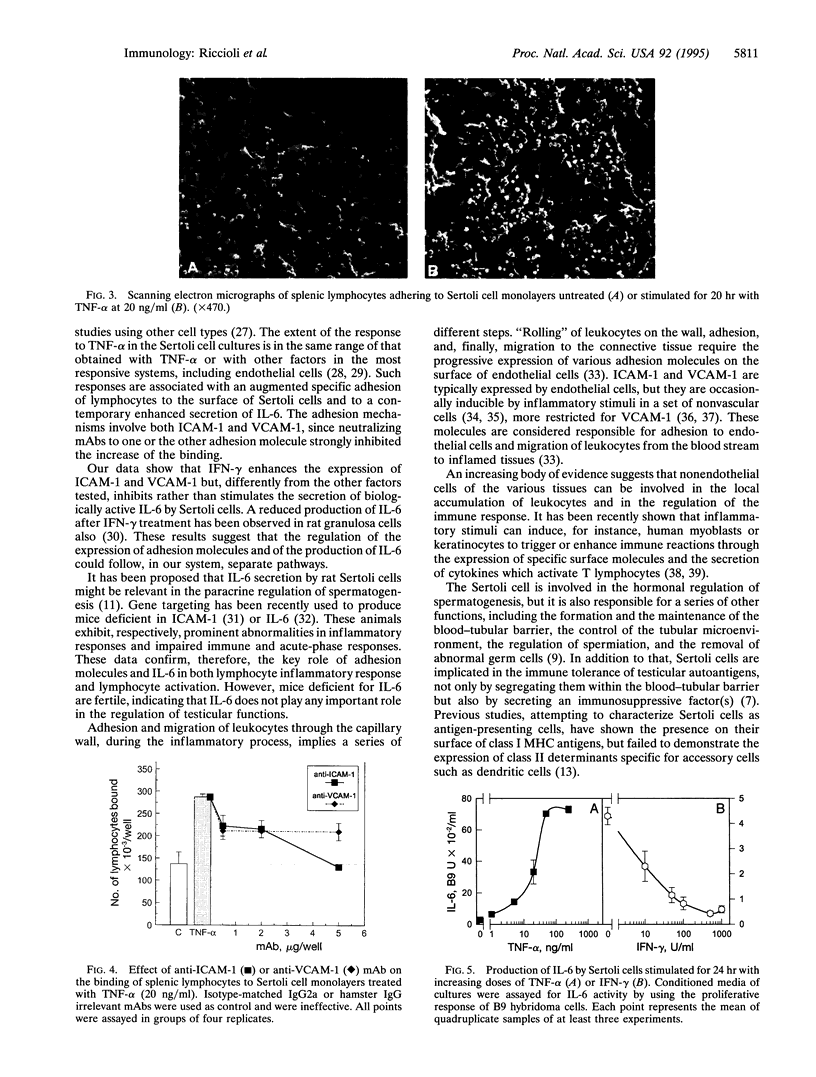
Abstract
The expression of the cell adhesion molecules ICAM-1, ICAM-2, and VCAM-1 and the secretion of the cytokine interleukin 6 have been measured in mouse Sertoli cells cultured in vitro. Cytometric analysis revealed that, in basal conditions, low levels of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 were present on the surface of the cells, whereas treatment with interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor alpha, lipopolysaccharide, or interferon gamma induced, with different kinetics, increases in their expression. ICAM-2 was not detectable in basal conditions, nor was it inducible. Electron microscopic analysis and binding experiments using 51Cr-labeled lymphocytes demonstrated that increased expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 on the surface of Sertoli cells, induced by inflammatory mediators, determines an augmented adhesion between the two cell types. The same stimuli, with the exception of interferon gamma, produced a rapid and remarkable increment of interleukin 6 production by Sertoli cells. These results suggest the presence of both direct and paracrine mechanisms of interaction between Sertoli and immune-competent cells, possibly involved in the control of immune reactions in the testis. Such mechanisms are of interest for the understanding of autoimmune pathologies of the testis and, if confirmed in humans, they could be involved in the sexual transmission of human immunodeficiency virus infection.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker J. N., Mitra R. S., Griffiths C. E., Dixit V. M., Nickoloff B. J. Keratinocytes as initiators of inflammation. Lancet. 1991 Jan 26;337(8735):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92168-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P. Endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecules. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:767–804. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.004003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Cesaris P., Filippini A., Cervelli C., Riccioli A., Muci S., Starace G., Stefanini M., Ziparo E. Immunosuppressive molecules produced by Sertoli cells cultured in vitro: biological effects on lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Aug 14;186(3):1639–1646. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81596-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Rothlein R., Bhan A. K., Dinarello C. A., Springer T. A. Induction by IL 1 and interferon-gamma: tissue distribution, biochemistry, and function of a natural adherence molecule (ICAM-1). J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):245–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. T-cell receptor cross-linking transiently stimulates adhesiveness through LFA-1. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):619–624. doi: 10.1038/341619a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dym M., Fawcett D. W. The blood-testis barrier in the rat and the physiological compartmentation of the seminiferous epithelium. Biol Reprod. 1970 Dec;3(3):308–326. doi: 10.1093/biolreprod/3.3.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippini A., Russo M. A., Palombi F., Bertalot G., De Cesaris P., Stefanini M., Ziparo E. Modulation of phagocytic activity in cultured Sertoli cells. Gamete Res. 1989 Aug;23(4):367–375. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1120230402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garman R. D., Jacobs K. A., Clark S. C., Raulet D. H. B-cell-stimulatory factor 2 (beta 2 interferon) functions as a second signal for interleukin 2 production by mature murine T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7629–7633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garza M. M., Schwarz L. K., Bonner J. M., Boockfor F. R. Sertoli cell function varies along the seminiferous tubule: the proportion and response of transferrin secretors differ between stage-associated tubule segments. Endocrinology. 1991 Apr;128(4):1869–1874. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-4-1869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebels N., Michaelis D., Wekerle H., Hohlfeld R. Human myoblasts as antigen-presenting cells. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 15;149(2):661–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorospe W. C., Hughes F. M., Jr, Spangelo B. L. Interleukin-6: effects on and production by rat granulosa cells in vitro. Endocrinology. 1992 Mar;130(3):1750–1752. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.3.1537322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gérard N., Syed V., Jégou B. Lipopolysaccharide, latex beads and residual bodies are potent activators of Sertoli cell interleukin-1 alpha production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 29;185(1):154–161. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80969-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head J. R., Billingham R. E. Immune privilege in the testis. II. Evaluation of potential local factors. Transplantation. 1985 Sep;40(3):269–275. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198509000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head J. R., Neaves W. B., Billingham R. E. Immune privilege in the testis. I. Basic parameters of allograft survival. Transplantation. 1983 Oct;36(4):423–431. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198310000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Matsuda T., Turner M., Miyasaka N., Buchan G., Tang B., Sato K., Shimizu M., Maini R., Feldmann M. Excessive production of interleukin 6/B cell stimulatory factor-2 in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Nov;18(11):1797–1801. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Taga T., Yasukawa K., Nakajima K., Nakano N., Takatsuki F., Shimizu M., Murashima A., Tsunasawa S., Sakiyama F. Human B-cell differentiation factor defined by an anti-peptide antibody and its possible role in autoantibody production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):228–231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Yasukawa K., Harada H., Taga T., Watanabe Y., Matsuda T., Kashiwamura S., Nakajima K., Koyama K., Iwamatsu A. Complementary DNA for a novel human interleukin (BSF-2) that induces B lymphocytes to produce immunoglobulin. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):73–76. doi: 10.1038/324073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno S., Munoz J. A., Williams T. M., Teuscher C., Bernard C. C., Tung K. S. Immunopathology of murine experimental allergic orchitis. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2675–2682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno S., Ziparo E., Marek L. F., Tung K. S. Murine Sertoli cells: major histocompatibility antigens and glycoconjugates. J Reprod Immunol. 1983 Nov;5(6):339–350. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(83)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopf M., Baumann H., Freer G., Freudenberg M., Lamers M., Kishimoto T., Zinkernagel R., Bluethmann H., Köhler G. Impaired immune and acute-phase responses in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Nature. 1994 Mar 24;368(6469):339–342. doi: 10.1038/368339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lansdorp P. M., Aarden L. A., Calafat J., Zeiljemaker W. P. A growth-factor dependent B-cell hybridoma. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;132:105–113. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71562-4_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzavecchia A. Identifying strategies for immune intervention. Science. 1993 May 14;260(5110):937–944. doi: 10.1126/science.8493532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luscinskas F. W., Cybulsky M. I., Kiely J. M., Peckins C. S., Davis V. M., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Cytokine-activated human endothelial monolayers support enhanced neutrophil transmigration via a mechanism involving both endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 1;146(5):1617–1625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makgoba M. W., Sanders M. E., Ginther Luce G. E., Dustin M. L., Springer T. A., Clark E. A., Mannoni P., Shaw S. ICAM-1 a ligand for LFA-1-dependent adhesion of B, T and myeloid cells. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):86–88. doi: 10.1038/331086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlor C. W., Webb D. L., Bombara M. P., Greve J. M., Blue M. L. Expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in fibroblastlike synoviocytes after stimulation with tumor necrosis factor. Am J Pathol. 1992 May;140(5):1055–1060. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A., Huber G. K., Davies T. F. Induction of human thyroid cell ICAM-1 (CD54) antigen expression and ICAM-1-mediated lymphocyte binding. Endocrinology. 1990 Aug;127(2):651–657. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-2-651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin J. M., Snock K. V. Effect of tumor necrosis factor on epithelial tight junctions and transepithelial permeability. Cancer Res. 1990 Apr 1;50(7):2172–2176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuovo G. J., Gallery F., MacConnell P., Braun A. In situ detection of polymerase chain reaction-amplified HIV-1 nucleic acids and tumor necrosis factor-alpha RNA in the central nervous system. Am J Pathol. 1994 Apr;144(4):659–666. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palombi F., Di Carlo C. Alkaline phosphatase is a marker for myoid cells in cultures of rat peritubular and tubular tissue. Biol Reprod. 1988 Dec;39(5):1101–1109. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod39.5.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Lapierre L. A., Mendrick D. L., Fiers W., Rothlein R., Springer T. A. Overlapping patterns of activation of human endothelial cells by interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor, and immune interferon. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1893–1896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sligh J. E., Jr, Ballantyne C. M., Rich S. S., Hawkins H. K., Smith C. W., Bradley A., Beaudet A. L. Inflammatory and immune responses are impaired in mice deficient in intercellular adhesion molecule 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8529–8533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the multistep paradigm. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suematsu S., Matsuda T., Aozasa K., Akira S., Nakano N., Ohno S., Miyazaki J., Yamamura K., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. IgG1 plasmacytosis in interleukin 6 transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7547–7551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syed V., Gérard N., Kaipia A., Bardin C. W., Parvinen M., Jégou B. Identification, ontogeny, and regulation of an interleukin-6-like factor in the rat seminiferous tubule. Endocrinology. 1993 Jan;132(1):293–299. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.1.8380379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung K. S., Ellis L., Teuscher C., Meng A., Blaustein J. C., Kohno S., Howell R. The black mink (Mustela vison). A natural model of immunologic male infertility. J Exp Med. 1981 Oct 1;154(4):1016–1032. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.4.1016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yule T. D., Mahi-Brown C. A., Tung K. S. Role of testicular autoantigens and influence of lymphokines in testicular autoimmune disease. J Reprod Immunol. 1990 Aug;18(1):89–103. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(90)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yule T. D., Montoya G. D., Russell L. D., Williams T. M., Tung K. S. Autoantigenic germ cells exist outside the blood testis barrier. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 15;141(4):1161–1167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yule T. D., Tung K. S. Experimental autoimmune orchitis induced by testis and sperm antigen-specific T cell clones: an important pathogenic cytokine is tumor necrosis factor. Endocrinology. 1993 Sep;133(3):1098–1107. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.3.8103448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]