Abstract
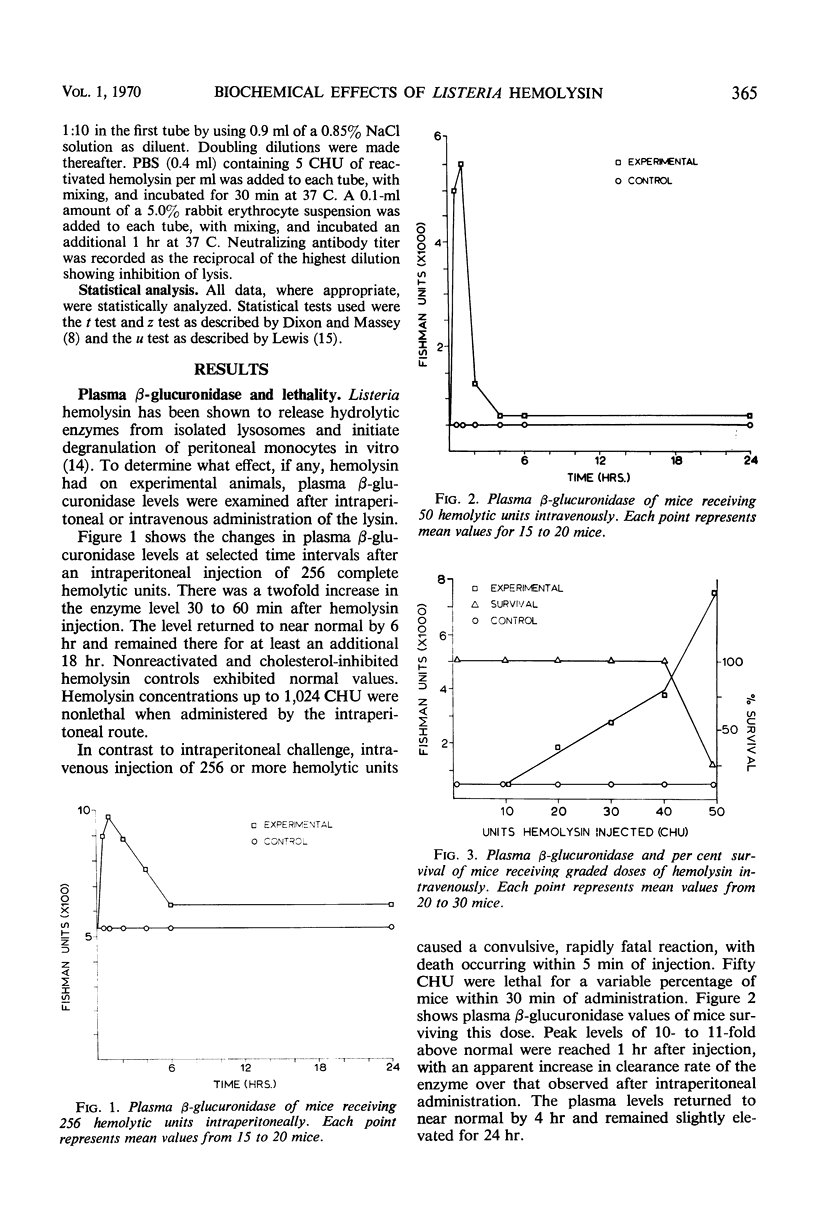
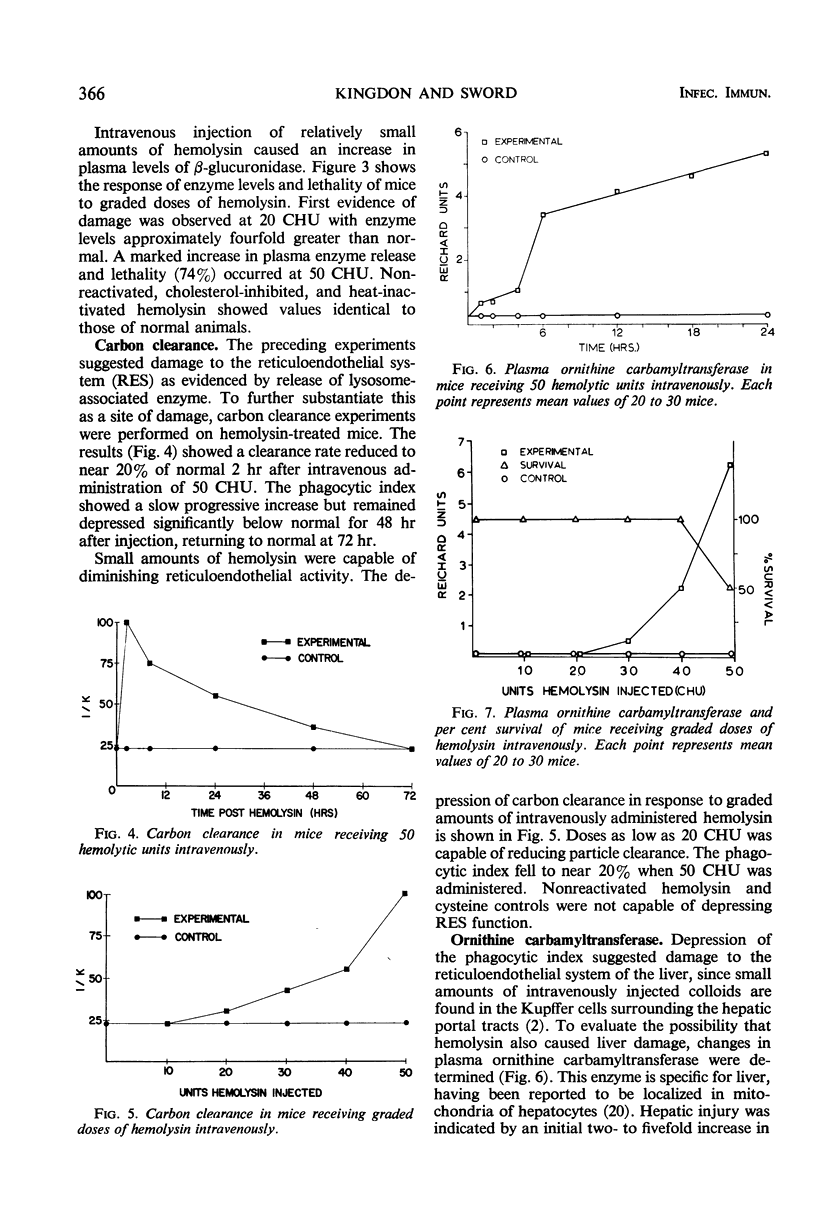
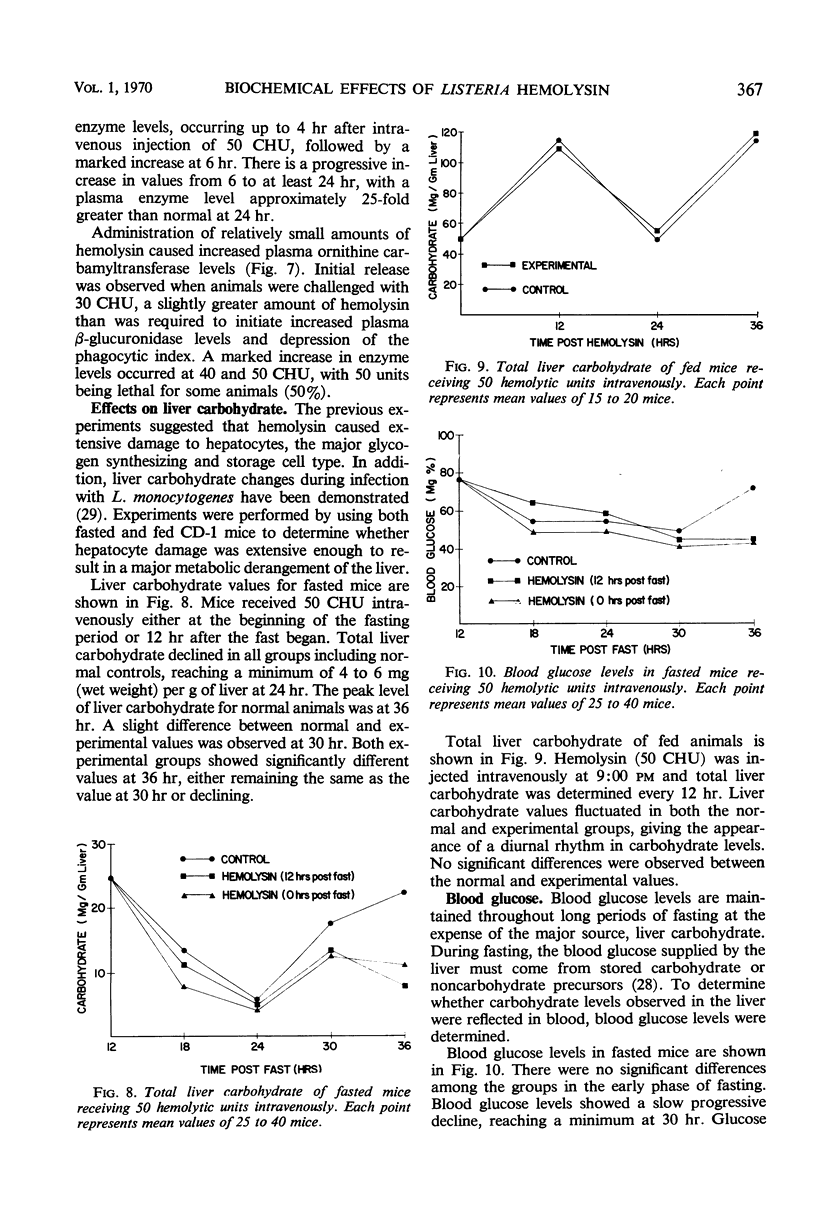
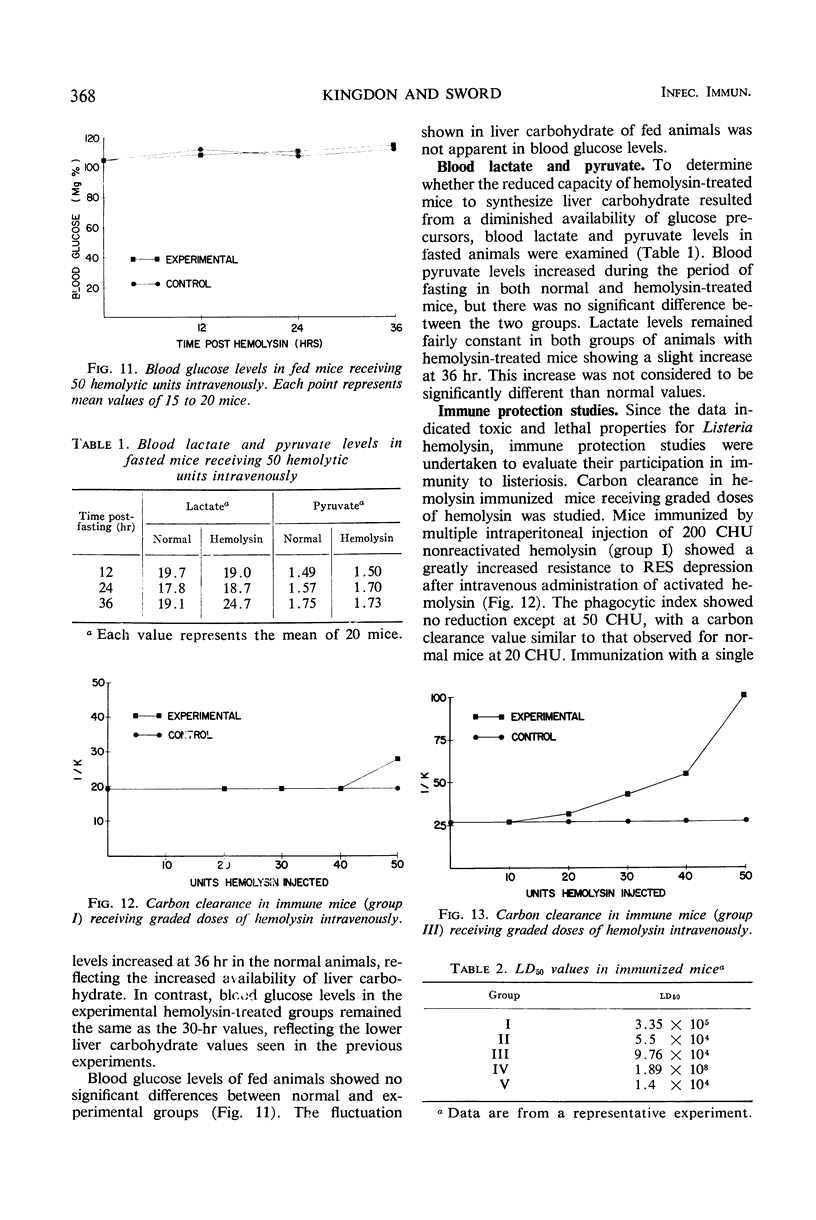
The biochemical and immunological effects of Listeria monocytogenes hemolysin in CD-1 mice were studied. Intraperitoneal injection of 256 complete hemolytic units (CHU) caused a twofold increase in plasma β-glucuronidase levels but was not lethal. In contrast, 256 or more CHU caused 100% lethality in 4 to 5 min when administered intravenously. Intravenous administration of 50 CHU caused a 10- to 11-fold increase in plasma β-glucuronidase levels and was lethal for a variable percentage of the animals. Carbon clearance experiments showed the phagocytic index to be depressed by relatively small amounts of intravenously administered hemolysin and suggested that hemolysin may function as a leucocidal agressin during listeric infection. Increased plasma levels of ornithine carbamyltransferase after intravenous injection of hemolysin indicated hepatocellular damage. Liver carbohydrate and blood glucose determinations on fasted mice showed a reduced gluconeogenic capability in hemolysin-treated animals. Mice immunized with purified hemolysin or live vaccine were more resistant to several of the toxic parameters studied. The data indicate that hemolysin is produced during listeric infection and is antigenic, but not necessarily a protective immunogen.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG A. S., SWORD C. P. CELLULAR RESISTANCE IN LISTERIOSIS. J Infect Dis. 1964 Jun;114:258–264. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.3.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENACERRAF B., SEBESTYEN M. M. Effect of bacterial endotoxins on the reticuloendothelial system. Fed Proc. 1957 Sep;16(3):860–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIOZZI G., BENACERRAF B., HALPERN B. N. Quantitative study of the granulopectic activity of the reticulo-endothelial system. II. A study of the kinetics of the R. E. S. in relation to the dose of carbon injected; relationship between the weight of the organs and their activity. Br J Exp Pathol. 1953 Aug;34(4):441–457. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINGLE J. T., LUCY J. A., FELL H. B. Studies on the mode of action of excess of vitamin A. 1. Effect of excess of vitamin A on the metabolism and composition of embryonic chick-limb cartilage grown in organ culture. Biochem J. 1961 Jun;79:497–500. doi: 10.1042/bj0790497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLAND D. M., WYNN C. H. The degradation of acidsoluble collagen by rat-liver preparations. Biochem J. 1962 Nov;85:276–282. doi: 10.1042/bj0850276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARD K. F., SBARRA A. J., BARDAWIL W. A. Serology of Listeria monocytogenes. I. Characteristics of the soluble hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1963 Feb;85:349–355. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.2.349-355.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINS E. M., NJOKU-OBI A. N., ADAMS E. W. PURIFICATION OF THE SOLUBLE HEMOLYSINS OF LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:418–424. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.418-424.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingdon G. C., Sword C. P. Effects of Listeria monocytogenes Hemolysin on Phagocytic Cells and Lysosomes. Infect Immun. 1970 Apr;1(4):356–362. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.4.356-362.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIKI K., MACKANESS G. B. THE PASSIVE TRANSFER OF ACQUIRED RESISTANCE TO LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES. J Exp Med. 1964 Jul 1;120:93–103. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLANDER D. W., WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Serum glutamic oxalacetic transaminase as an index of hepatocellular integrity. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Dec;46(6):831–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani A. Light and electron microscopic localization of ornithine carbamoyltransferase activity in liver mitochondria of rat and mouse. J Histochem Cytochem. 1967 Oct;15(10):603–604. doi: 10.1177/15.10.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NJOKU-OBI A. N., JENKINS E. M., NJOKU-OBI J. C., ADAMS J., COVINGTON V. PRODUCTION AND NATURE OF LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES HEMOLYSINS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:1–8. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.1-8.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NYDICK I., WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Evidence for increased serum glutamic oxalacetic transaminase (SGO-T) activity following graded myocardial infarcts in dogs. Circulation. 1955 Aug;12(2):161–168. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.12.2.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEIFTER S., DAYTON S. The estimation of glycogen with the anthrone reagent. Arch Biochem. 1950 Jan;25(1):191–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sword C. P., Wilder M. S. Plasma enzyme changes in Listeria monocytogenes-infected mice. J Infect Dis. 1967 Dec;117(5):387–392. doi: 10.1093/infdis/117.5.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS L., McCLUSKEY R. T., POTTER J. L., WEISSMANN G. Comparison of the effects of papain n vitamin A on cartilage. I. The effects in rabbits. J Exp Med. 1960 May 1;111:705–718. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.5.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER G., CANTERO A. Glucose-6-phosphatase studies in fasting. Science. 1954 Nov 19;120(3125):851–852. doi: 10.1126/science.120.3125.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Serum glutamic-oxalacetic-transaminase activity as an index of liver-cell injury from cancer; a preliminary report. Cancer. 1955 Nov-Dec;8(6):1155–1163. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(1955)8:6<1155::aid-cncr2820080611>3.0.co;2-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G., Singhal R. L., Stamm N. B., Fisher E. A., Mentendiek M. A. Regulation of enzymes involved in gluconeogenesis. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1964;2:1–38. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2571(64)80003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder M. S., Sword C. P. Mechanisms of pathogenesis in Listeria monocytogenes infection. 3. Carbohydrate metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):538–543. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.538-543.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


