Abstract
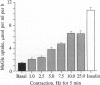
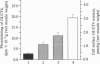
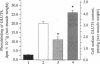
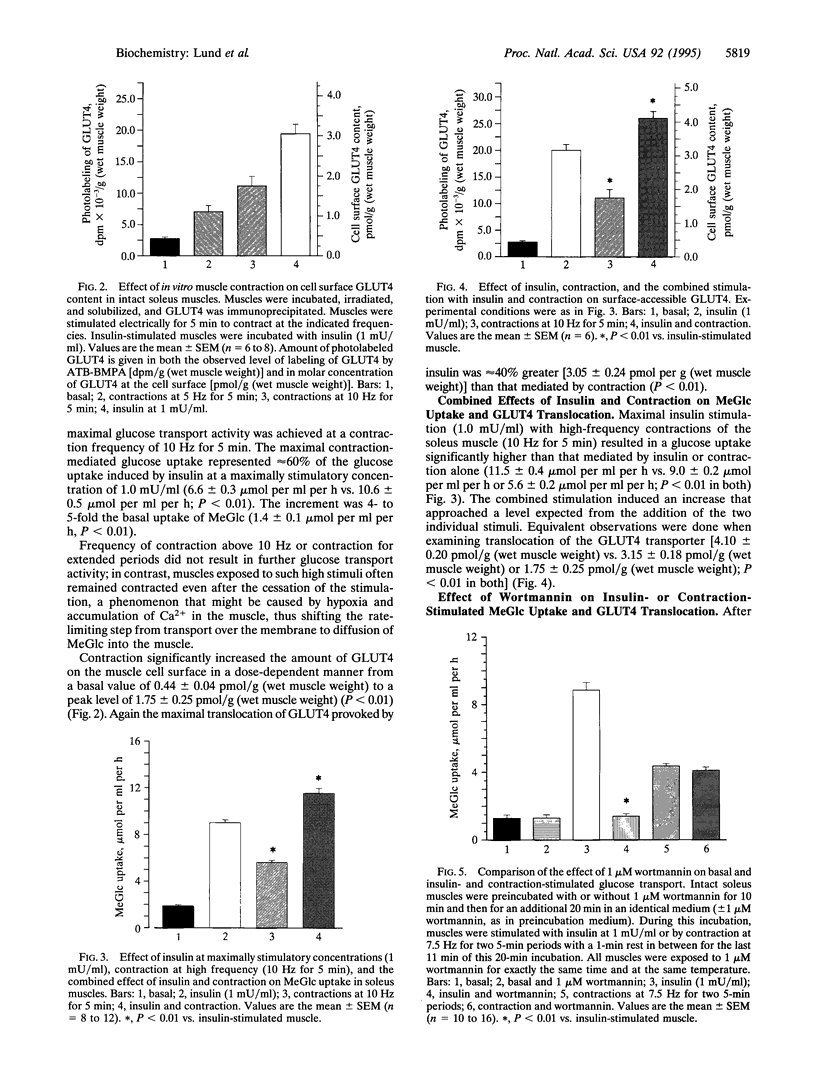
The acute effects of contraction and insulin on the glucose transport and GLUT4 glucose transporter translocation were investigated in rat soleus muscles by using a 3-O-methylglucose transport assay and the sensitive exofacial labeling technique with the impermeant photoaffinity reagent 2-N-4-(1-azi-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)benzoyl-1,3-bis(D-mannose-4-y loxy)-2- propylamine (ATB-BMPA), respectively. Addition of wortmannin, which inhibits phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, reduced insulin-stimulated glucose transport (8.8 +/- 0.5 mumol per ml per h vs. 1.4 +/- 0.1 mumol per ml per h) and GLUT4 translocation [2.79 +/- 0.20 pmol/g (wet muscle weight) vs. 0.49 +/- 0.05 pmol/g (wet muscle weight)]. In contrast, even at a high concentration (1 microM), wortmannin had no effect on contraction-mediated glucose uptake (4.4 +/- 0.1 mumol per ml per h vs. 4.1 +/- 0.2 mumol per ml per h) and GLUT4 cell surface content [1.75 +/- 0.16 pmol/g (wet muscle weight) vs. 1.52 +/- 0.16 pmol/g (wet muscle weight)]. Contraction-mediated translocation of the GLUT4 transporters to the cell surface was closely correlated with the glucose transport activity and could account fully for the increment in glucose uptake after contraction. The combined effects of contraction and maximal insulin stimulation were greater than either stimulation alone on glucose transport activity (11.5 +/- 0.4 mumol per ml per h vs. 5.6 +/- 0.2 mumol per ml per h and 9.0 +/- 0.2 mumol per ml per h) and on GLUT4 translocation [4.10 +/- 0.20 pmol/g (wet muscle weight) vs. 1.75 +/- 0.25 pmol/g (wet muscle weight) and 3.15 +/- 0.18 pmol/g (wet muscle weight)]. The results provide evidence that contraction stimulates translocation of GLUT4 in skeletal muscle through a mechanism distinct from that of insulin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brozinick J. T., Jr, Etgen G. J., Jr, Yaspelkis B. B., 3rd, Ivy J. L. The effects of muscle contraction and insulin on glucose-transporter translocation in rat skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1994 Feb 1;297(Pt 3):539–545. doi: 10.1042/bj2970539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheatham B., Vlahos C. J., Cheatham L., Wang L., Blenis J., Kahn C. R. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation is required for insulin stimulation of pp70 S6 kinase, DNA synthesis, and glucose transporter translocation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4902–4911. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. E., Holman G. D. Exofacial photolabelling of the human erythrocyte glucose transporter with an azitrifluoroethylbenzoyl-substituted bismannose. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 1;269(3):615–622. doi: 10.1042/bj2690615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke J. F., Young P. W., Yonezawa K., Kasuga M., Holman G. D. Inhibition of the translocation of GLUT1 and GLUT4 in 3T3-L1 cells by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor, wortmannin. Biochem J. 1994 Jun 15;300(Pt 3):631–635. doi: 10.1042/bj3000631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Buxton J. M. Insulin action on the internalization of the GLUT4 glucose transporter in isolated rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9187–9190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douen A. G., Ramlal T., Cartee G. D., Klip A. Exercise modulates the insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters in rat skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 26;261(2):256–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80566-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douen A. G., Ramlal T., Klip A., Young D. A., Cartee G. D., Holloszy J. O. Exercise-induced increase in glucose transporters in plasma membranes of rat skeletal muscle. Endocrinology. 1989 Jan;124(1):449–454. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-1-449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douen A. G., Ramlal T., Rastogi S., Bilan P. J., Cartee G. D., Vranic M., Holloszy J. O., Klip A. Exercise induces recruitment of the "insulin-responsive glucose transporter". Evidence for distinct intracellular insulin- and exercise-recruitable transporter pools in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13427–13430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J. Signal transduction. Regulating S6 kinase. Nature. 1994 Sep 29;371(6496):378–379. doi: 10.1038/371378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enrich C., Gahmberg C. G. Characterization of plasma-membrane glycoproteins from functional domains of the rat hepatocyte. Biochem J. 1985 Apr 15;227(2):565–572. doi: 10.1042/bj2270565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fushiki T., Wells J. A., Tapscott E. B., Dohm G. L. Changes in glucose transporters in muscle in response to exercise. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 1):E580–E587. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.256.5.E580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao J., Ren J., Gulve E. A., Holloszy J. O. Additive effect of contractions and insulin on GLUT-4 translocation into the sarcolemma. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1994 Oct;77(4):1597–1601. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1994.77.4.1597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodyear L. J., King P. A., Hirshman M. F., Thompson C. M., Horton E. D., Horton E. S. Contractile activity increases plasma membrane glucose transporters in absence of insulin. Am J Physiol. 1990 Apr;258(4 Pt 1):E667–E672. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.258.4.E667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen P. A., Gulve E. A., Holloszy J. O. Suitability of 2-deoxyglucose for in vitro measurement of glucose transport activity in skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1994 Feb;76(2):979–985. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1994.76.2.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara K., Yonezawa K., Sakaue H., Ando A., Kotani K., Kitamura T., Kitamura Y., Ueda H., Stephens L., Jackson T. R. 1-Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity is required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport but not for RAS activation in CHO cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 2;91(16):7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.16.7415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen E. J., Bourey R. E., Rodnick K. J., Koranyi L., Permutt M. A., Holloszy J. O. Glucose transporter protein content and glucose transport capacity in rat skeletal muscles. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 1):E593–E598. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.259.4.E593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirshman M. F., Goodyear L. J., Wardzala L. J., Horton E. D., Horton E. S. Identification of an intracellular pool of glucose transporters from basal and insulin-stimulated rat skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):987–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirshman M. F., Wallberg-Henriksson H., Wardzala L. J., Horton E. D., Horton E. S. Acute exercise increases the number of plasma membrane glucose transporters in rat skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1988 Oct 10;238(2):235–239. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80486-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman G. D., Kozka I. J., Clark A. E., Flower C. J., Saltis J., Habberfield A. D., Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Cell surface labeling of glucose transporter isoform GLUT4 by bis-mannose photolabel. Correlation with stimulation of glucose transport in rat adipose cells by insulin and phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18172–18179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman G. D., Lo Leggio L., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated GLUT4 glucose transporter recycling. A problem in membrane protein subcellular trafficking through multiple pools. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 1;269(26):17516–17524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhun B. H., Rampal A. L., Liu H., Lachaal M., Jung C. Y. Effects of insulin on steady state kinetics of GLUT4 subcellular distribution in rat adipocytes. Evidence of constitutive GLUT4 recycling. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17710–17715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King P. A., Hirshman M. F., Horton E. D., Horton E. S. Glucose transport in skeletal muscle membrane vesicles from control and exercised rats. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 1):C1128–C1134. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.6.C1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund S., Flyvbjerg A., Holman G. D., Larsen F. S., Pedersen O., Schmitz O. Comparative effects of IGF-I and insulin on the glucose transporter system in rat muscle. Am J Physiol. 1994 Sep;267(3 Pt 1):E461–E466. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1994.267.3.E461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund S., Holman G. D., Schmitz O., Pedersen O. Glut 4 content in the plasma membrane of rat skeletal muscle: comparative studies of the subcellular fractionation method and the exofacial photolabelling technique using ATB-BMPA. FEBS Lett. 1993 Sep 20;330(3):312–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80895-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesher R., Karl I. E., Kipnis D. M. Dissociation of effects of insulin and contraction on glucose transport in rat epitrochlearis muscle. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 1):C226–C232. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.3.C226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada T., Kawano Y., Sakakibara T., Hazeki O., Ui M. Essential role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in insulin-induced glucose transport and antilipolysis in rat adipocytes. Studies with a selective inhibitor wortmannin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3568–3573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploug T., Galbo H., Richter E. A. Increased muscle glucose uptake during contractions: no need for insulin. Am J Physiol. 1984 Dec;247(6 Pt 1):E726–E731. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.6.E726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploug T., Galbo H., Vinten J., Jørgensen M., Richter E. A. Kinetics of glucose transport in rat muscle: effects of insulin and contractions. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 1):E12–E20. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.253.1.E12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploug T., Wojtaszewski J., Kristiansen S., Hespel P., Galbo H., Richter E. A. Glucose transport and transporters in muscle giant vesicles: differential effects of insulin and contractions. Am J Physiol. 1993 Feb;264(2 Pt 1):E270–E278. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1993.264.2.E270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh S., Nishimura H., Clark A. E., Kozka I. J., Vannucci S. J., Simpson I. A., Quon M. J., Cushman S. W., Holman G. D. Use of bismannose photolabel to elucidate insulin-regulated GLUT4 subcellular trafficking kinetics in rat adipose cells. Evidence that exocytosis is a critical site of hormone action. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):17820–17829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternlicht E., Barnard R. J., Grimditch G. K. Exercise and insulin stimulate skeletal muscle glucose transport through different mechanisms. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 1):E227–E230. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.256.2.E227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallberg-Henriksson H., Constable S. H., Young D. A., Holloszy J. O. Glucose transport into rat skeletal muscle: interaction between exercise and insulin. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Aug;65(2):909–913. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.2.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallberg-Henriksson H., Holloszy J. O. Activation of glucose transport in diabetic muscle: responses to contraction and insulin. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 1):C233–C237. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.3.C233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallberg-Henriksson H., Holloszy J. O. Contractile activity increases glucose uptake by muscle in severely diabetic rats. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Oct;57(4):1045–1049. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.4.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. M., Cushman S. W. Insulin stimulation of glucose transport activity in rat skeletal muscle: increase in cell surface GLUT4 as assessed by photolabelling. Biochem J. 1994 May 1;299(Pt 3):755–759. doi: 10.1042/bj2990755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzano A., Balon T. W., Goodman M. N., Ruderman N. B. Additive effects of prior exercise and insulin on glucose and AIB uptake by rat muscle. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jul;251(1 Pt 1):E21–E26. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.251.1.E21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]