Abstract
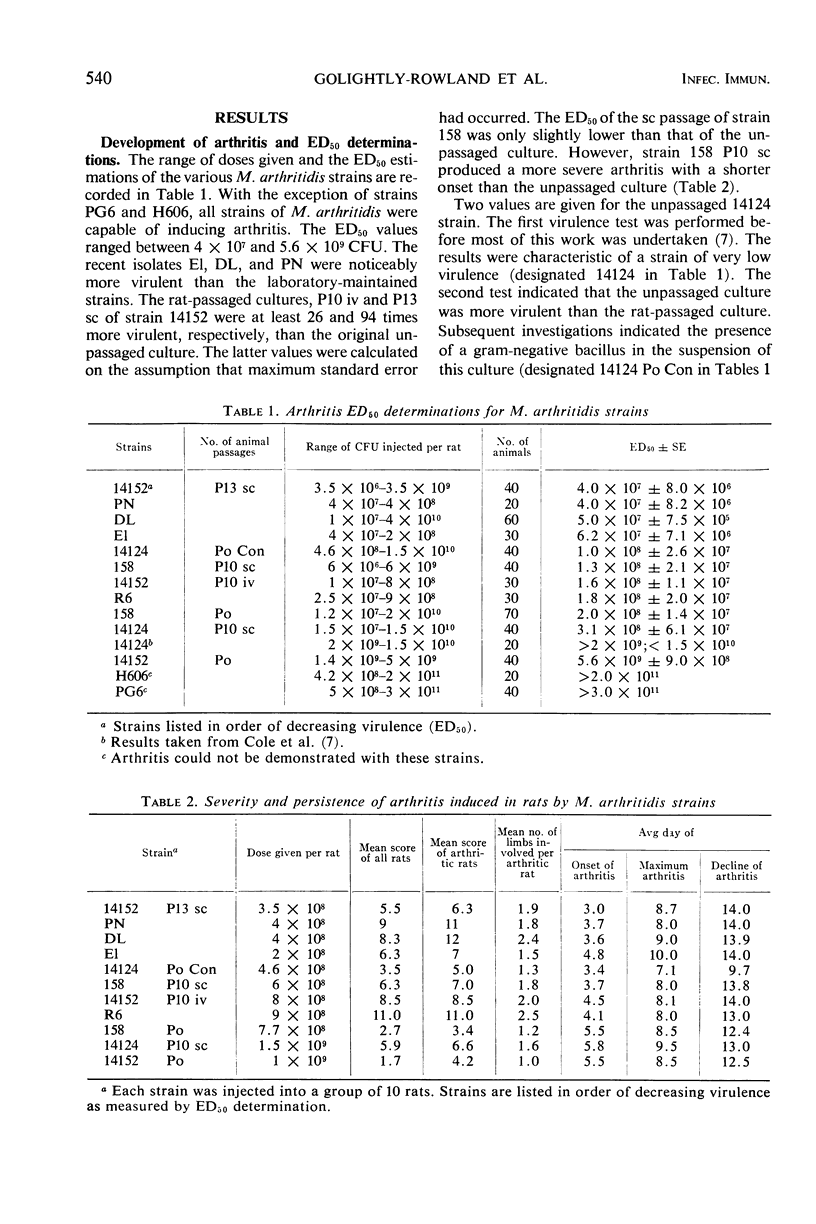
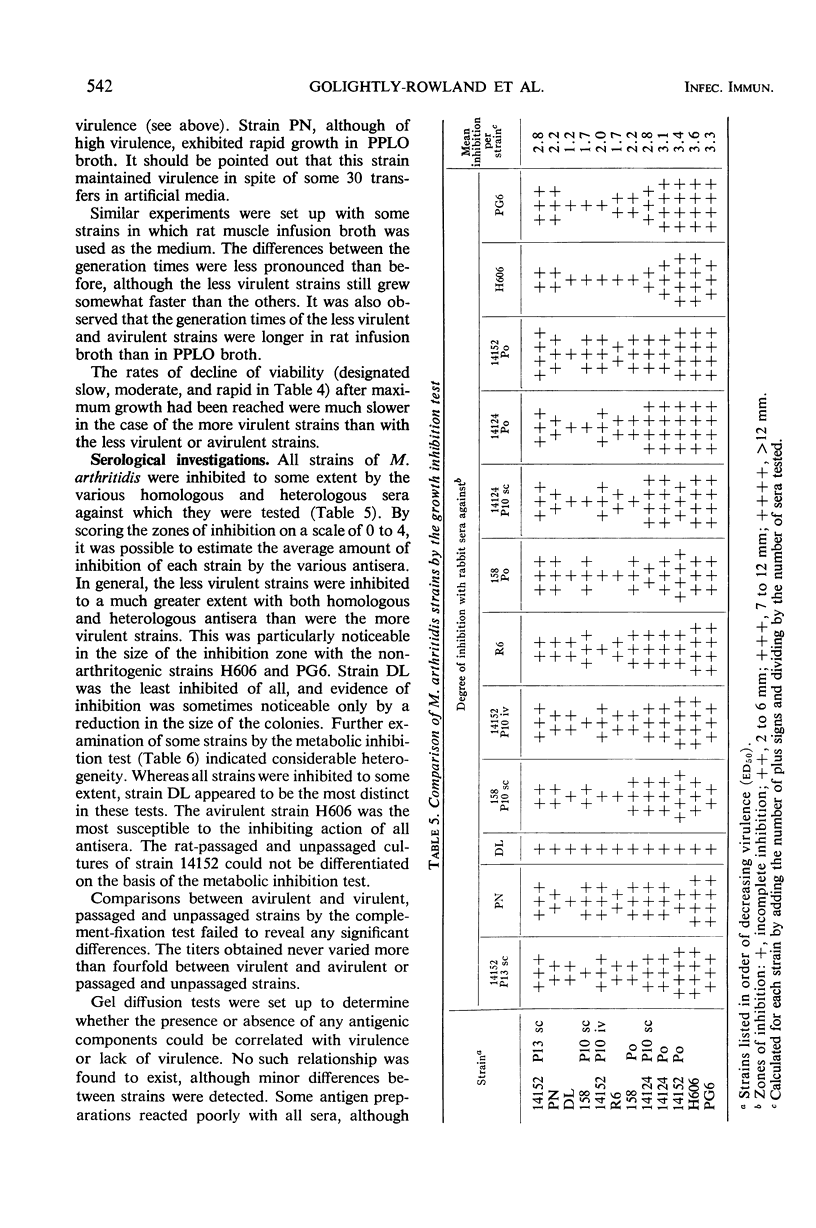
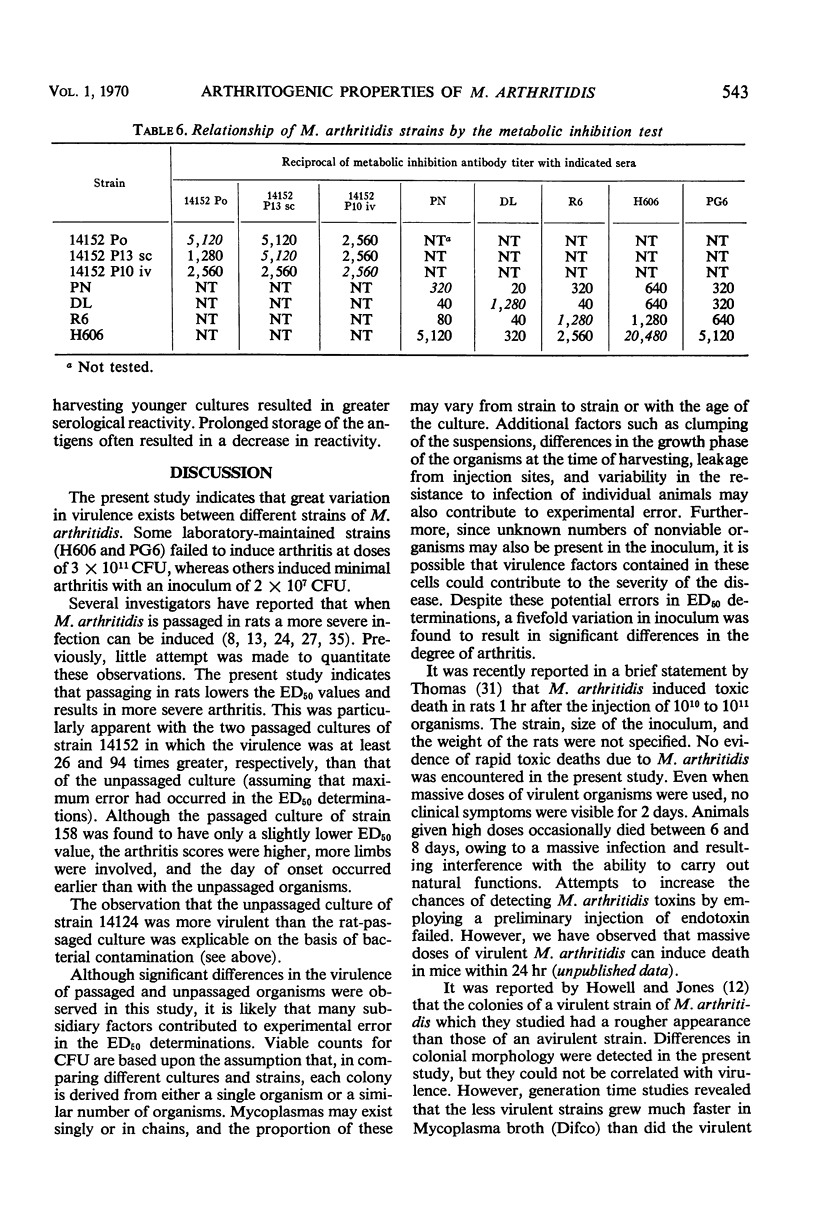
Determinations of the ED50 of cultures of Mycoplasma arthritidis disclosed the existence of great diversity in the arthritogenic properties of the various strains. In most cases, the ED50 values were lowered after passaging in rats, and a more severe arthritis with a shorter period of onset was observed. Heavy suspensions of arthritogenic M. arthritidis did not appear to induce any toxic symptoms. Prior injections of endotoxin did not enhance the toxicity of M. arthritidis suspensions. The more arthritogenic strains grew more slowly in the basal medium and remained viable for longer periods of time than those with lower arthritogenic properties. All strains were identical on the basis of complement-fixation tests. Minor differences observed between strains during gel-diffusion studies could not be correlated with arthritogenic properties. Arthritogenic strains appeared to be less susceptible to the inhibiting action of rabbit antisera than were the nonarthritogenic strains.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brennan P. C., Fritz T. E., Flynn R. J. Role of Pasteurella pneumotropica and Mycoplasma pulmonis in murine pneumonia. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):337–349. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.337-349.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R. M., HAYFLICK L., BARILE M. F. Growth on artificial medium of an agent associated with atypical pneumonia and its identification as a PPLO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:41–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYDE W. A., Jr MYCOPLASMA SPECIES IDENTIFICATION BASED UPON GROWTH INHIBITION BY SPECIFIC ANTISERA. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:958–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Cahill J. F., Wiley B. B., Ward J. R. Immunological responses of the rat to Mycoplasma arthritidis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):930–937. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.930-937.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Golightly L., Ward J. R. Characterization of mycoplasma strains from cats. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1451–1458. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1451-1458.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Miller M. L., Ward J. R. A comparative study on the virulence of Mycoplasma arthritidis and "Mycoplasma hominis, type 2" strains in rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jan;124(1):103–107. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARD D. G. The pleuropneumonia group of organisms: a review, together with some new observations. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Feb;10(1):27–64. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-1-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL E. V., JONES R. S. Factors influencing pathogenicity of Mycoplasma arthritidis (PPLO). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Jan;112:69–72. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-27952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. Tissue cultures and mycoplasmas. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Jun;23(Suppl):285+–285+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLIENEBERGER-NOBEL E. Pathogenicity and immunology of organisms of the pleuropneumonia group. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 15;79:615–625. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42731.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEMCKE R. M. A SEROLOGICAL COMPARISON OF VARIOUS SPECIES OF MYCOPLASMA BY AN AGAR GEL DOUBLE-DIFFUSION TECHNIQUE. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Jan;38:91–100. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman R. P., Clyde W. A., Jr, Denny F. W. Characteristics of virulent, attenuated, and avirulent Mycoplasma pneumoniae strains. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1037–1043. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1037-1043.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton H. E., Roberts R. J. Production of anti-Mycoplasma (PPLO) antibodies in rabbits. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jun;125(2):538–543. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKES M. W., WRIGLEY F., O'BRIEN B. Arthritis in rats produced by pleuro-pneumonia-like organisms. Ann Rheum Dis. 1951 Jun;10(2):177–181. doi: 10.1136/ard.10.2.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pease P. The antigenic structure of PPLO (Mycoplasma hominis) and related bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Dec;41(3):299–308. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-3-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. D., Somerson N. L., Senterfit L. B. Effect of pH on the immunogenicity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):612–619. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.612-619.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Taylor-Robinson D., Wong D. C., Chanock R. M. A color test for the measurement of antibody to the non-acid-forming human Mycoplasma species. Am J Epidemiol. 1966 Jul;84(1):51–66. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMKE R. T., BARILE M. F. Arginine breakdown in mammalian cell culture contaminated with pleuropneumonia-like organisms (PPLO). Exp Cell Res. 1963 May;30:593–596. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR-ROBINSON D., SOMERSON N. L., TURNER H. C., CHANOCK R. M. SEROLOGICAL RELATIONSHIPS AMONG HUMAN MYCOPLASMAS AS SHOWN BY COMPLEMENT-FIXATION AND GEL DIFFUSION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1261–1273. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1261-1273.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L. Mycoplasmas as pathogens. Yale J Biol Med. 1968 Apr-Jun;40(5-6):444–448. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Rask-Nielsen R. Mycoplasma in leukemic and nonleukemic mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):345–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD J. R., JONES R. S. The pathogenesis of mycoplasma (PPLO) arthritis in rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1962 Apr;5:163–175. doi: 10.1002/art.1780050205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. Observations on Some Biological Characteristics of Organisms of the Pleuropneumonia Group. J Bacteriol. 1942 Feb;43(2):211–228. doi: 10.1128/jb.43.2.211-228.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



