Abstract
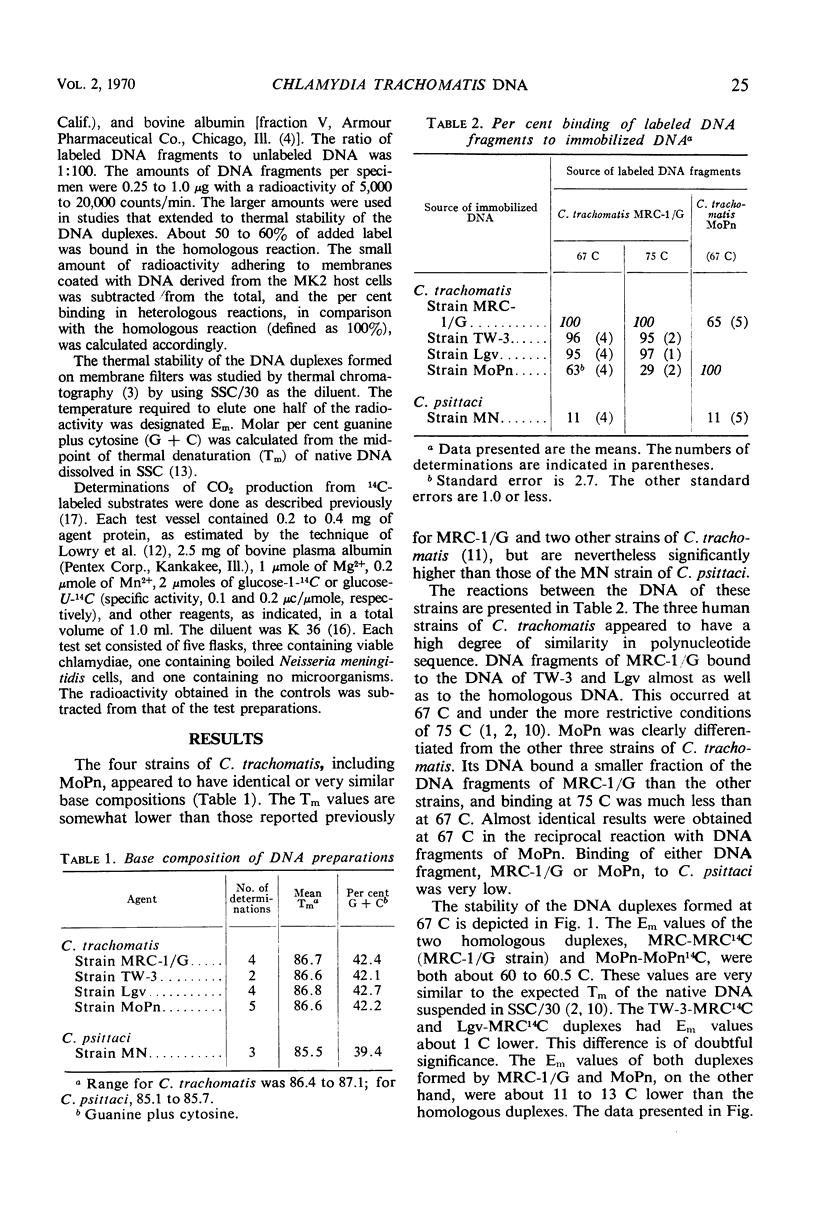
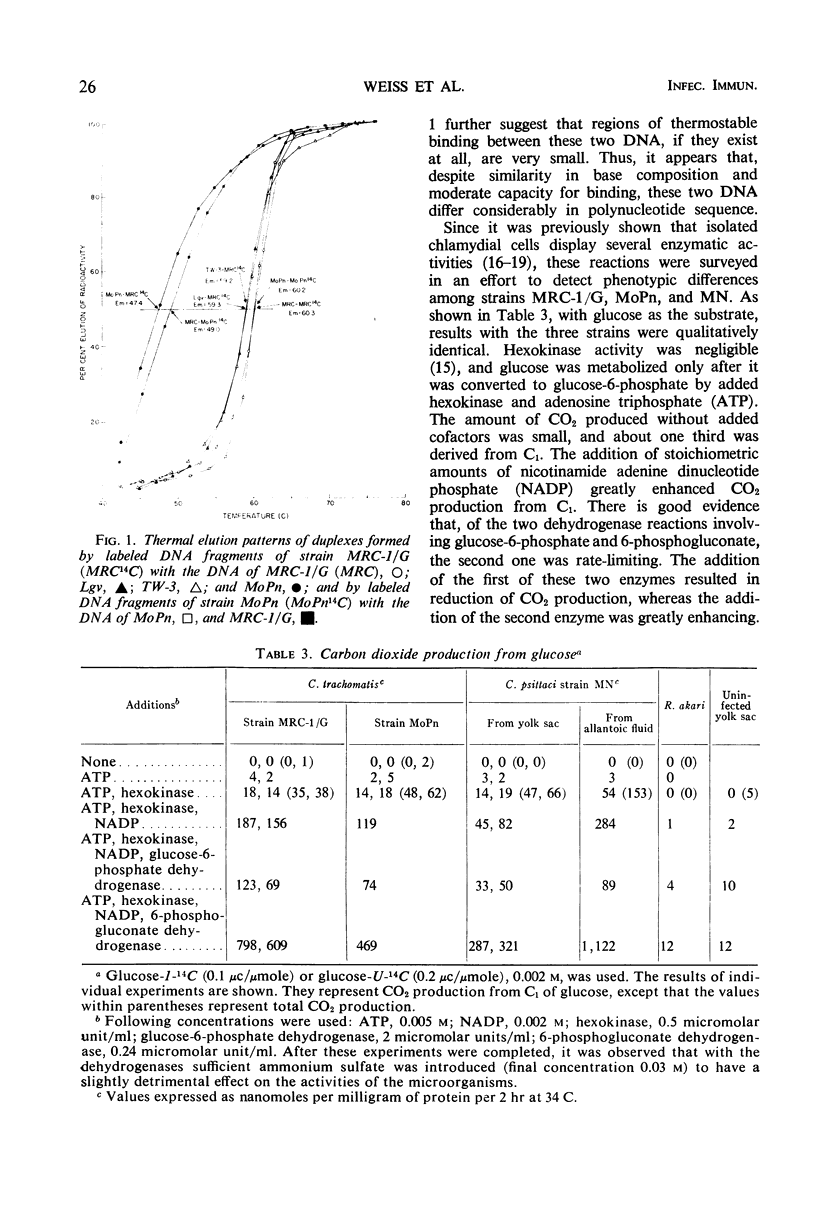
We compared the polynucleotide sequence relationships of three strains of Chlamydia trachomatis of human origin (MRC-1/G, TW-3, and Lgv), one of murine origin (MoPn), and the MN strain of C. psittaci. The four strains of C. trachomatis have the same base ratio, about 42.5 moles per cent guanine plus cytosine, which is significantly higher than the base ratio of MN (39.5). Single strands of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) fragments of MRC-1/G reassociated with immobilized DNA of TW-3 and Lgv almost as well as with the homologous DNA. The duplexes produced in these reactions were about equally thermostable. On the other hand, reassociations between MRC-1/G and MoPn involved 60 or 30% of the DNA, depending on the stringency of the conditions for reassociation, and the duplexes were thermolabile. MoPn reassociated only to a very small degree with MN. We also compared glucose catabolism of MRC-1/G, MoPn, and MN under several sets of conditions. These tests failed to reveal any qualitative phenotypic differences among the three strains. It can be concluded that, judging by polynucleotide sequence, the three human strains of C. trachomatis are closely related but appreciably different from a murine strain.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner D. J., Cowie D. B. Thermal stability of Escherichia coli-Salmonella typhimurium deoxyribocleic acid duplexes. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2258–2262. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2258-2262.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Fanning G. R., Johnson K. E., Citarella R. V., Falkow S. Polynucleotide sequence relationships among members of Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):637–650. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.637-650.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie D. B., Szafranski P. Thermal chromatography of DNA-DNA reactions. Biophys J. 1967 Sep;7(5):567–584. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86607-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerloff R. K., Ritter D. B., Watson R. O. Studies on thermal denaturation of DNA from various chlamydiae. J Infect Dis. 1970 Jan;121(1):65–69. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haapala D. K., Rogul M., Evans L. B., Alexander A. D. Deoxyribonucleic acid base composition and homology studies of Leptospira. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):421–428. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.421-428.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. T. Deoxyribonucleic acid homologies among species of the genus Neisseria. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):870–874. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.870-874.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. T., Fanning G. R., Johnson K. E., Brenner D. J. Thermal stability of interspecies Neisseria DNA duplexes. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Feb;55(2):201–208. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. T., Weiss E. Lack of deoxyribonucleic acid homology between species of the genus Chlamydia. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1421–1423. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1421-1423.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Public Health Weekly Reports for NOVEMBER 8, 1946. Public Health Rep. 1946 Nov 8;61(45):1605–1640. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J., Meyer K. F. Lymphogranuloma venereum. II. Characterization of some recently isolated strains. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):636–638. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.636-638.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vender J., Moulder J. W. Initial step in catabolism of glucose by the meningopneumonitis agent. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):867–869. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.867-869.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS E., MYERS W. F., DRESSLER H. R., CHUN-HOON H. GLUCOSE METABOLISM BY AGENTS OF THE PSITTACOSIS-TRACHOMA GROUP. Virology. 1964 Apr;22:551–562. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90076-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. Adenosine Triphosphate and Other Requirements for the Utilization of Glucose by Agents of the Psittacosis-Trachoma Group. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):243–253. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.243-253.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Neptune E. M., Jr, Gaugler R. W. Influence of gas environment on catabolic activities and on reoxidation of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate in Chlamydia. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1567–1573. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1567-1573.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. Transaminase activity and other enzymatic reactions involving pyruvate and glutamate in Chlamydia (psittacosis-trachoma group). J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):177–184. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.177-184.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



