Abstract
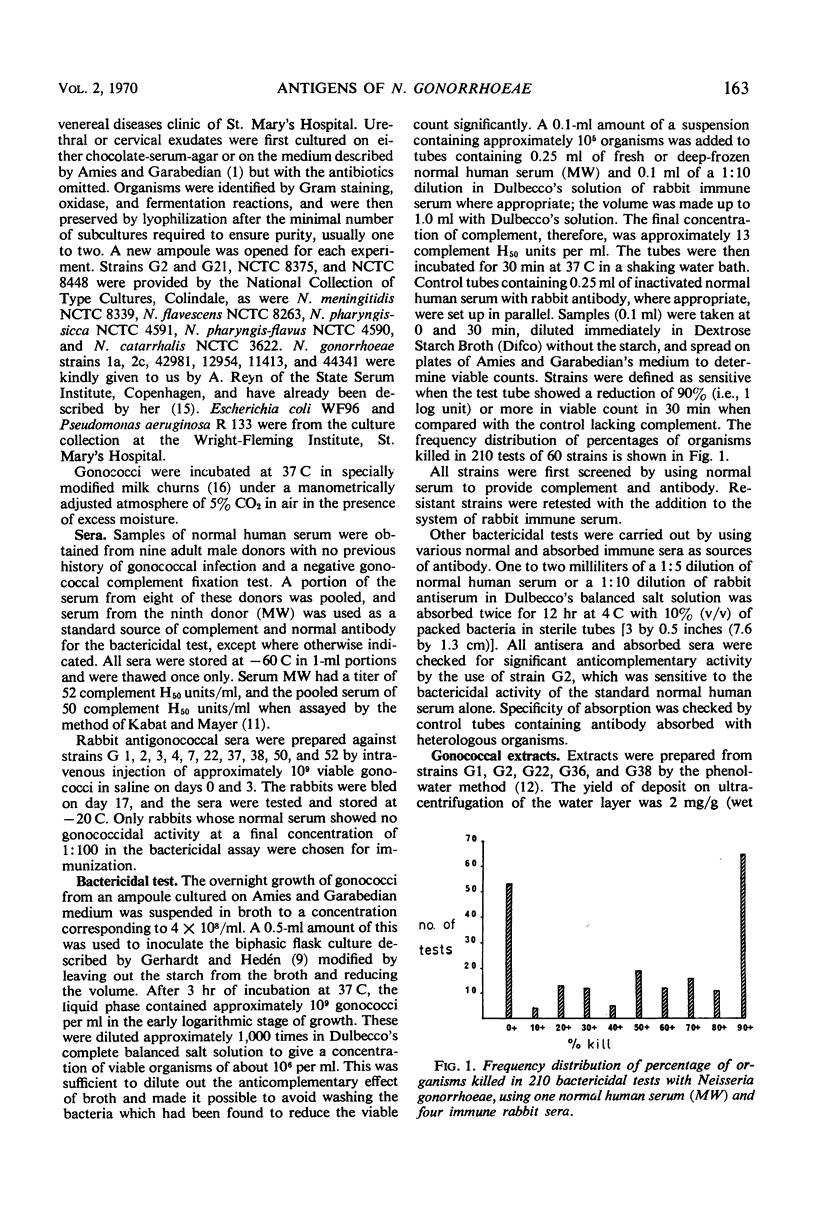
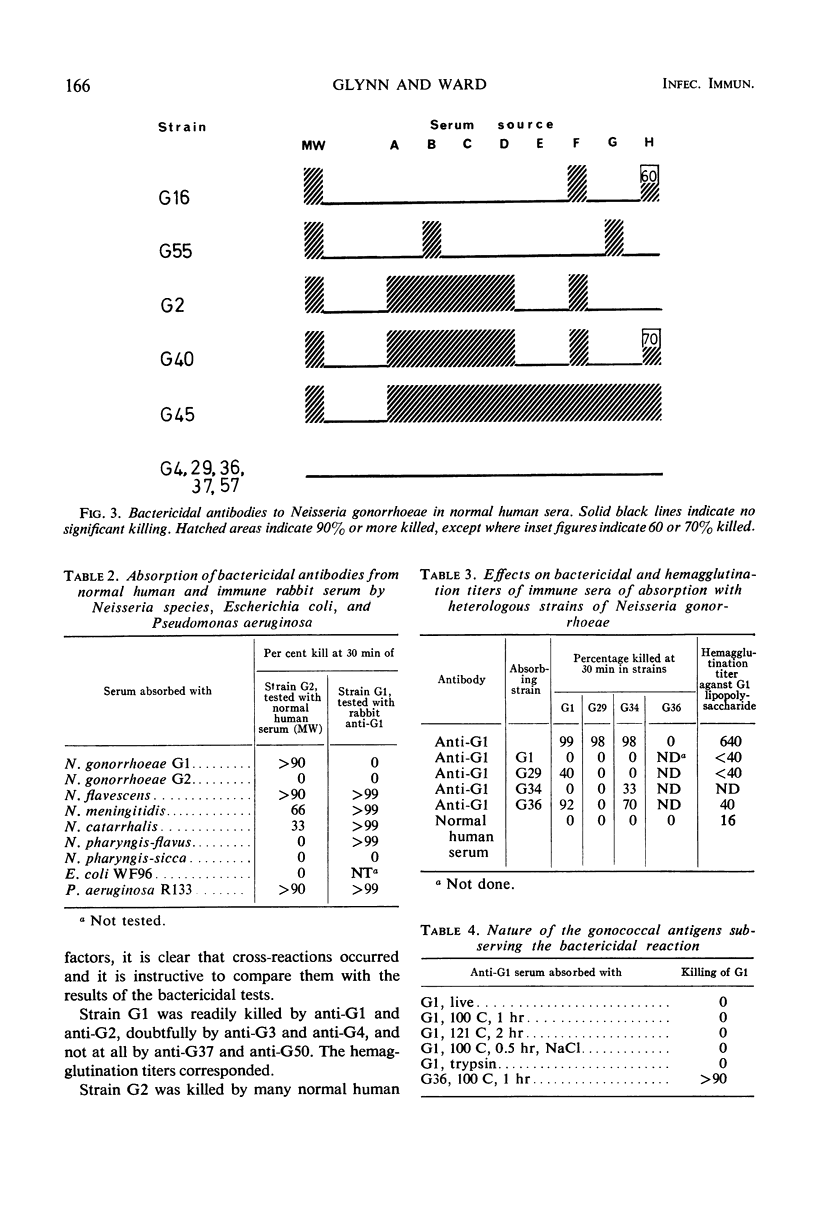
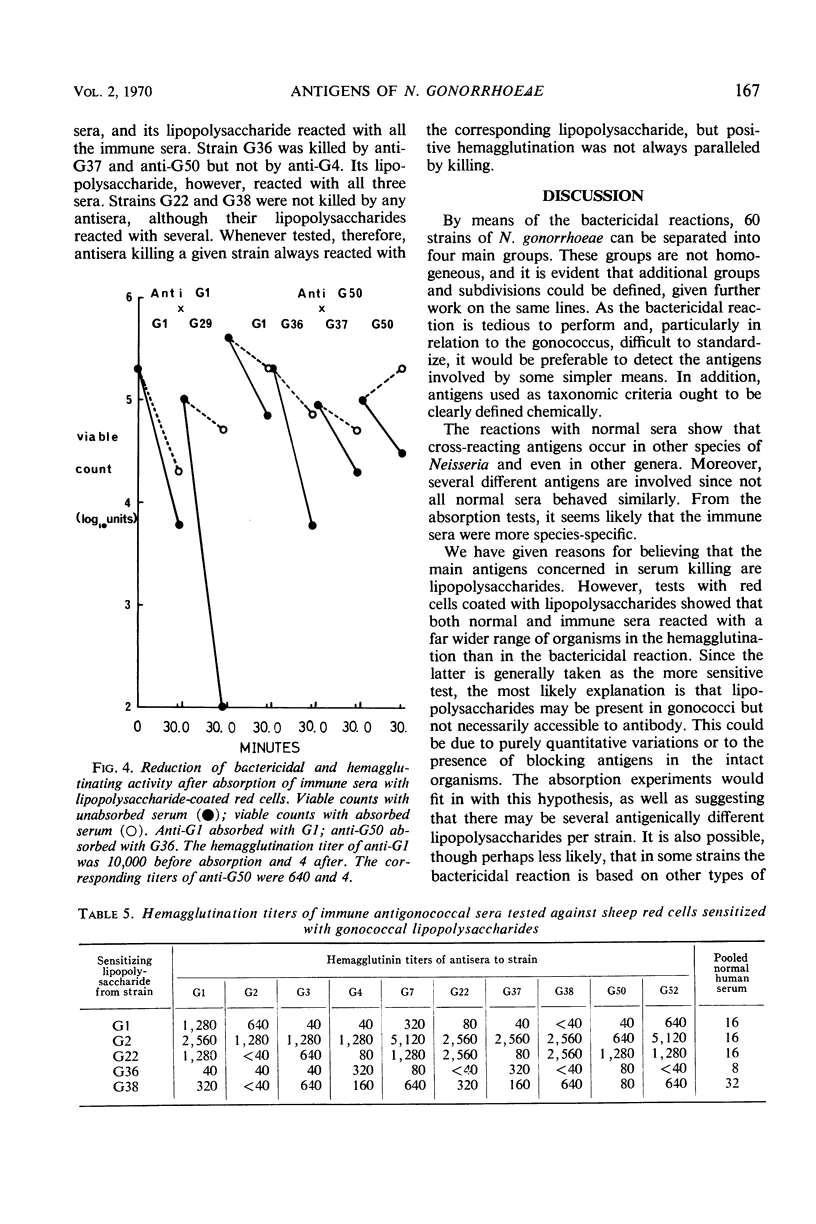
Sixty strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae have been classified into four main groups according to their resistance to killing by human complement together with either normal human or immune rabbit antibodies. The rabbit antisera had been raised against 10 of the strains tested. The normal human antibodies had probably been formed against cross-reacting organisms since they could be removed by absorption with N. pharyngis sicca, N. pharyngis flavus, N. catarrhalis, or Escherichia coli. Bactericidal antibodies could be absorbed from both normal and immune sera by N. gonorrhoeae which had been autoclaved or trypsinized, and by red cells coated with gonococcal lipopolysaccharides. The results suggest that the antigens involved in the bactericidal reaction are lipopolysaccharides of several distinct specificities. Since individual sera always reacted more widely in hemagglutination than in bactericidal tests, it is postulated that surface-blocking antigens may restrict access to the lipopolysaccharides in the intact organisms.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amies C. R., Garabedian M. An easily prepared selective medium for the cultivation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Br J Vener Dis. 1967 Jun;43(2):137–139. doi: 10.1136/sti.43.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANARIN I. An investigation of neisseria gonorrhoeae by a red cell sensitization technique. J Hyg (Lond) 1954 Dec;52(4):425–443. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400036901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chacko C. W., Nair G. M. Sero-diagnosis of gonorrhoea with a microprecipitin test using a lipopolysaccharide antigen from N. gonorrhoeae. Br J Vener Dis. 1969 Mar;45(1):33–39. doi: 10.1136/sti.45.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R. Natural and immune human antibodies reactive with antigens of virulent Neisseria gonorrhoeae: immunoglobulins G, M, And A. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):141–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.141-148.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIELSSON D. THE DEMONSTRATION OF N. GONORRHOEAE WITH THE AID OF FLUORESCENT ANTIBODIES. 4. STUDIES BY IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE AND DOUBLE DIFFUSION-IN-GEL TECHNIQUE ON THE ANTIGENIC RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN N. GONORRHOEAE AND OTHER NEISSERIA STRAINS. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64:267–276. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.64.2.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES D. A., CRUMPTON M. J., MACPHERSON I. A., HUTCHISON A. M. The adsorption of bacterial polysaccharides by erythrocytes. Immunology. 1958 Apr;1(2):157–171. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEACON W. E., PEACOCK W. L., Jr, FREEMAN E. M., HARRIS A. Identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by means of fluorescent antibodies. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Jun;101(2):322–325. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-24925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson D. G., Schmale J. D., Peacock W. L., Jr, Thayer J. D. Antigens of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: characterization by gel filtration, complement fixation, and agar-gel diffusion of antigens of gonococcal protoplasm. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1012–1017. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1012-1017.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERHARDT P., HEDEN C. G. Concentrated culture of gonococci in clear liquid medium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Oct;105:49–51. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-26005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A., Howard C. J. The sensitivity to complement of strains of Escherichia coli related to their K antigens. Immunology. 1970 Mar;18(3):331–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeland J. A. Antigenic properties of various preparations of Neisseria gonorrhoeae endotoxin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;73(3):413–422. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1968.tb04610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeland J. A. Immunochemical characterization of aqueous ether extracted endotoxin from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1969;76(3):484–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1969.tb03278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. E., Jr, Peacock W. L., Jr, Reising G., Kellogg D. S., Jr, Ribi E., Thayer J. D. Preparation of cell walls and protoplasm of Neisseria with the Ribi cell fractionator. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1009–1011. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1009-1011.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAEDLER R. W., DUBOS R., COSTELLO R. THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE BACTERIAL FLORA IN THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT OF MICE. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:59–66. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmale J. D., Danielsson D. G., Smith J. F., Lee L., Peacock W. L., Jr Isolation of an antigen of Neisseria gonorrhoeae involved in the human immune response to gonococcal infection. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):469–471. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.469-471.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUBER H., RUSSELL H. Biochemistry of Neisseria gonorhoea endotoxin. Bull World Health Organ. 1961;24:385–386. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



