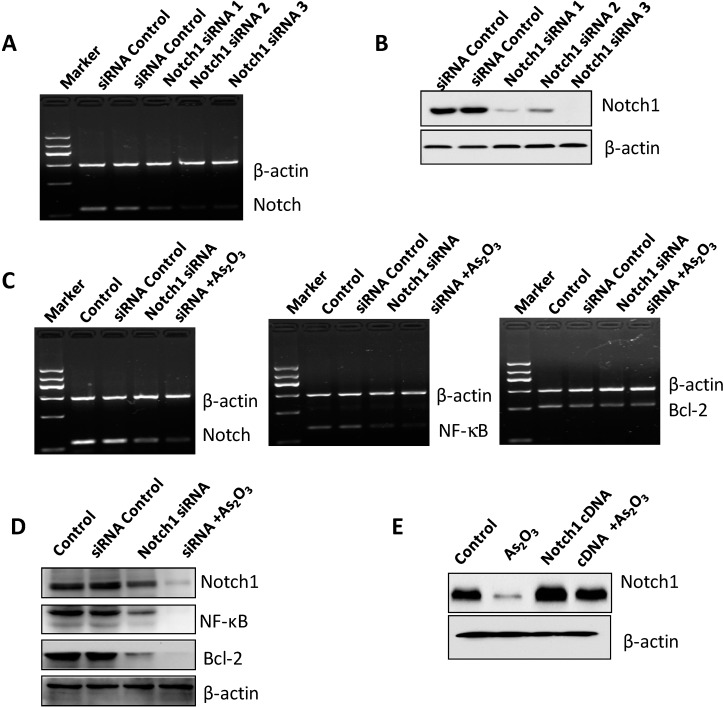
The authors wish to change Figure 5D of the paper published in IJMS [1]. In Figure 5D, the bands for NF-κB and Bcl-2 are similar with Notch-1 bands. The authors have carefully checked the original files and found that it is an inadvertent mistake in the published version of Figure 5D. Figure 5 is revised as follows. The authors would like to apologize for any inconvenience caused to the readers by these changes.
Figure 5.
The efficacy of transfection by Notch-1 siRNA and Notch-1 cDNA in SKBR-3 cells. A-D: The expression of Notch-1 was detected by RT-PCR and Western blotting, respectively, to check the Notch-1 siRNA transfection efficacy; E: The expression of Notch-1 was detected by Western blotting for assessing the Notch-1 cDNA plasmid transfection efficacy.
Reference
- 1.Xia J., Li Y., Yang Q., Mei C., Chen Z., Bao B., Ahmad A., Miele L., Sarkar F., Wang Z. Arsenic trioxide inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis through inactivation of Notch signaling pathway in breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012;13:9627–9641. doi: 10.3390/ijms13089627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]