Abstract
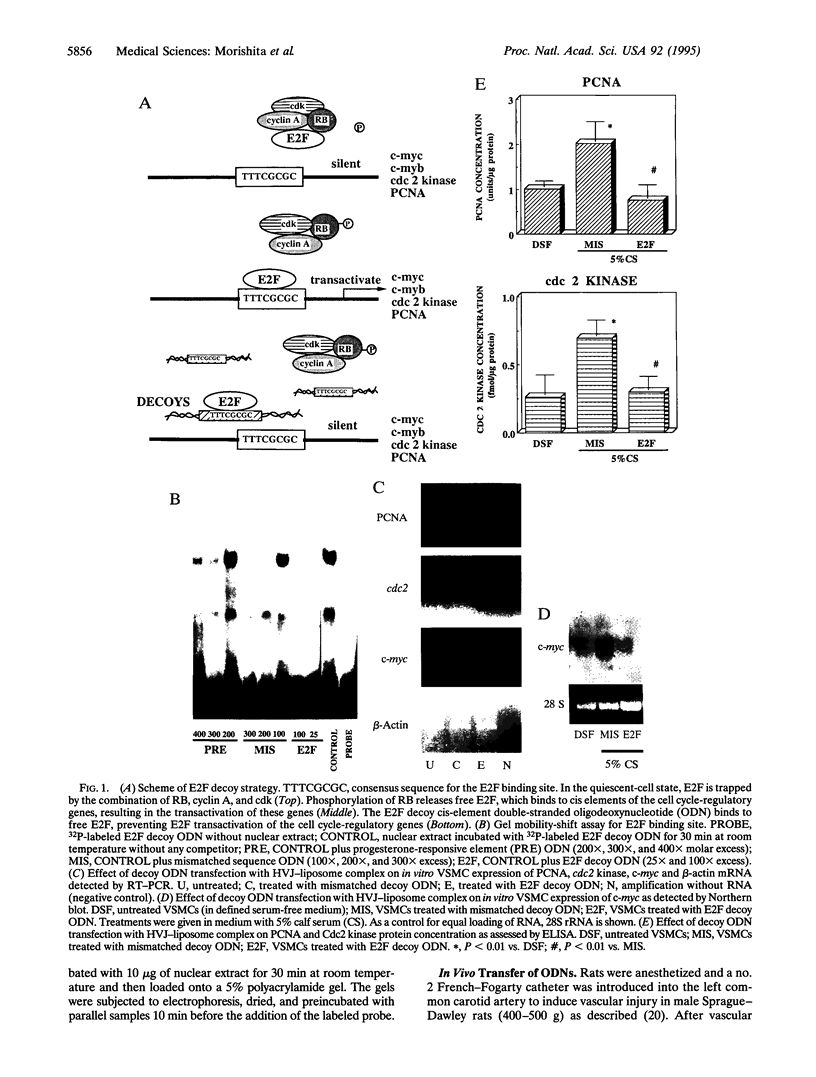
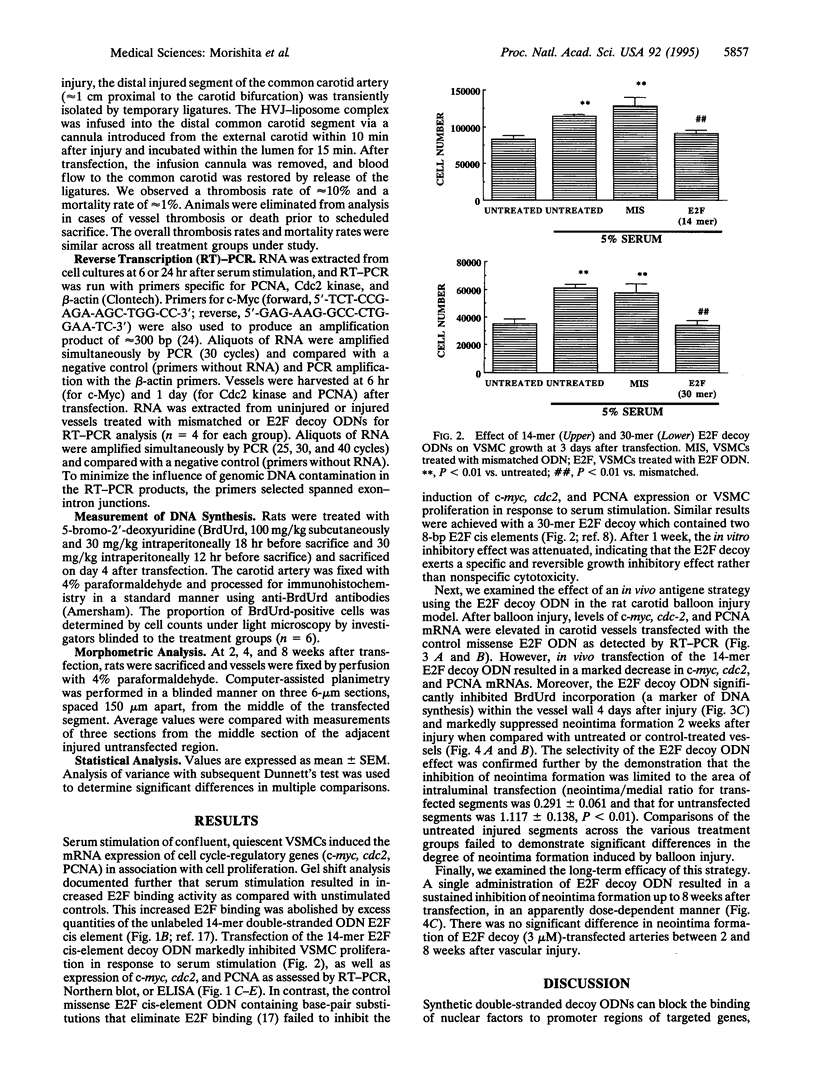
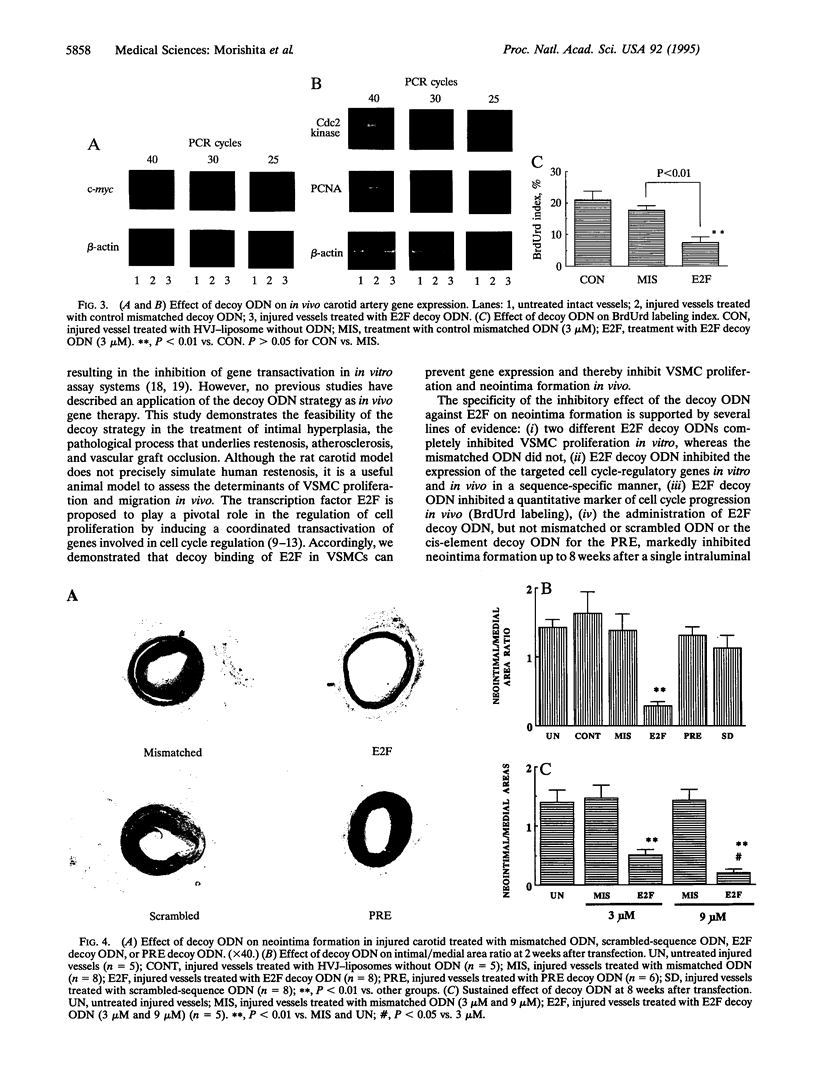
The application of DNA technology to regulate the transcription of disease-related genes in vivo has important therapeutic potentials. The transcription factor E2F plays a pivotal role in the coordinated transactivation of cell cycle-regulatory genes such as c-myc, cdc2, and the gene encoding proliferating-cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) that are involved in lesion formation after vascular injury. We hypothesized that double-stranded DNA with high affinity for E2F may be introduced in vivo as a decoy to bind E2F and block the activation of genes mediating cell cycle progression and intimal hyperplasia after vascular injury. Gel mobility-shift assays showed complete competition for E2F binding protein by the E2F decoy. Transfection with E2F decoy inhibited expression of c-myc, cdc2, and the PCNA gene as well as vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation both in vitro and in the in vivo model of rat carotid injury. Furthermore, 2 weeks after in vivo transfection, neointimal formation was significantly prevented by the E2F decoy, and this inhibition continued up to 8 weeks after a single transfection in a dose-dependent manner. Transfer of an E2F decoy can therefore modulate gene expression and inhibit smooth muscle proliferation and vascular lesion formation in vivo.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bielinska A., Shivdasani R. A., Zhang L. Q., Nabel G. J. Regulation of gene expression with double-stranded phosphorothioate oligonucleotides. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):997–1000. doi: 10.1126/science.2237444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casscells W. Migration of smooth muscle and endothelial cells. Critical events in restenosis. Circulation. 1992 Sep;86(3):723–729. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.86.3.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chittenden T., Livingston D. M., Kaelin W. G., Jr The T/E1A-binding domain of the retinoblastoma product can interact selectively with a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1073–1082. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90559-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S. Cell cycle regulation of the human cdc2 gene. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1797–1804. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05231.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons G. H., Dzau V. J. The emerging concept of vascular remodeling. N Engl J Med. 1994 May 19;330(20):1431–1438. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199405193302008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K., Makino R., Kawamura H., Arisawa A., Yoneda K. Characterization of rat c-myc and adjacent regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6419–6436. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Lees J. A., Vidal M., Dyson N., Harlow E., Fattaey A. A cDNA encoding a pRB-binding protein with properties of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90107-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans W. R., Rensing B. J., Strauss B. H., Serruys P. W. Prevention of restenosis after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty: the search for a "magic bullet". Am Heart J. 1991 Jul;122(1 Pt 1):171–187. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(91)90775-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Lipp M., Nevins J. R. E1A-dependent trans-activation of the human MYC promoter is mediated by the E2F factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3594–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi M., Nakamura N., Tang S. S., Barrett G., Dzau V. J. Molecular mechanism of tissue-specific regulation of mouse renin gene expression by cAMP. Identification of an inhibitory protein that binds nuclear transcriptional factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16247–16254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Krek W., Sellers W. R., DeCaprio J. A., Ajchenbaum F., Fuchs C. S., Chittenden T., Li Y., Farnham P. J., Blanar M. A. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a retinoblastoma-binding protein with E2F-like properties. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90108-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. K., Lee A. S. Identification of a 70-base-pair cell cycle regulatory unit within the promoter of the human thymidine kinase gene and its interaction with cellular factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2296–2302. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Tsai S. Y., Weigel N. L., Allan G. F., Riley D., Rodriguez R., Schrader W. T., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. The progesterone receptor stimulates cell-free transcription by enhancing the formation of a stable preinitiation complex. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):247–257. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90740-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Identification of a cellular transcription factor involved in E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90386-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montalescot G., Faraggi M., Drobinski G., Messian O., Evans J., Grosgogeat Y., Thomas D. Myocardial viability in patients with Q wave myocardial infarction and no residual ischemia. Circulation. 1992 Jul;86(1):47–55. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.86.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita R., Gibbons G. H., Ellison K. E., Nakajima M., Zhang L., Kaneda Y., Ogihara T., Dzau V. J. Single intraluminal delivery of antisense cdc2 kinase and proliferating-cell nuclear antigen oligonucleotides results in chronic inhibition of neointimal hyperplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8474–8478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita R., Gibbons G. H., Kaneda Y., Ogihara T., Dzau V. J. Novel and effective gene transfer technique for study of vascular renin angiotensin system. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2580–2585. doi: 10.1172/JCI116496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. E2F: a link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):424–429. doi: 10.1126/science.1411535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popma J. J., Califf R. M., Topol E. J. Clinical trials of restenosis after coronary angioplasty. Circulation. 1991 Sep;84(3):1426–1436. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.3.1426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullenger B. A., Gallardo H. F., Ungers G. E., Gilboa E. Overexpression of TAR sequences renders cells resistant to human immunodeficiency virus replication. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):601–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90455-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thalmeier K., Synovzik H., Mertz R., Winnacker E. L., Lipp M. Nuclear factor E2F mediates basic transcription and trans-activation by E1a of the human MYC promoter. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):527–536. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner S., Green M. R. Retinoblastoma. A transcriptional tryst. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):189–190. doi: 10.1038/352189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Dyson P. J., McMahon J. Multiple c-myb transcript cap sites are variously utilized in cells of mouse haemopoietic origin. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1643–1651. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02413.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub S. J., Prater C. A., Dean D. C. Retinoblastoma protein switches the E2F site from positive to negative element. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):259–261. doi: 10.1038/358259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Hayashi Y., Hirose F., Matsuoka S., Shiroki K., Matsukage A. Activation of the mouse proliferating cell nuclear antigen gene promoter by adenovirus type 12 E1A proteins. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1992 Jun;83(6):609–617. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1992.tb00133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee A. S., Reichel R., Kovesdi I., Nevins J. R. Promoter interaction of the E1A-inducible factor E2F and its potential role in the formation of a multi-component complex. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2061–2068. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02471.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]