Abstract
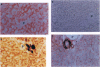
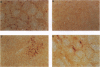
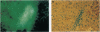
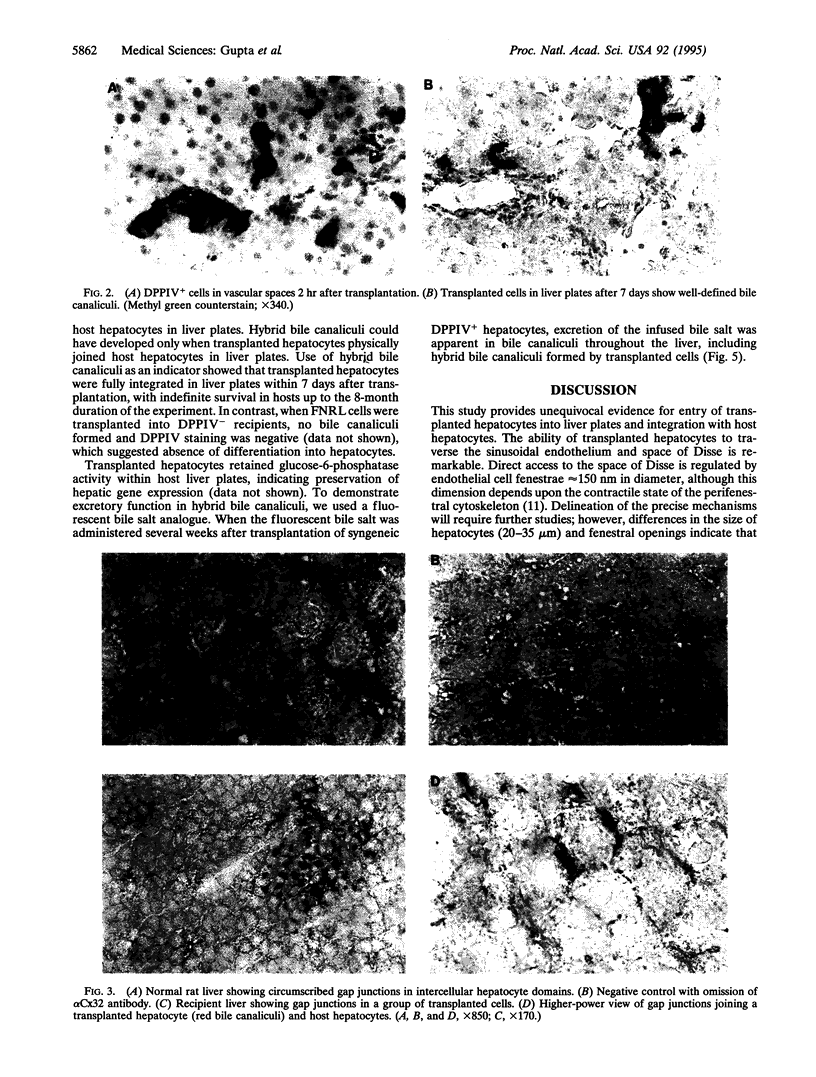
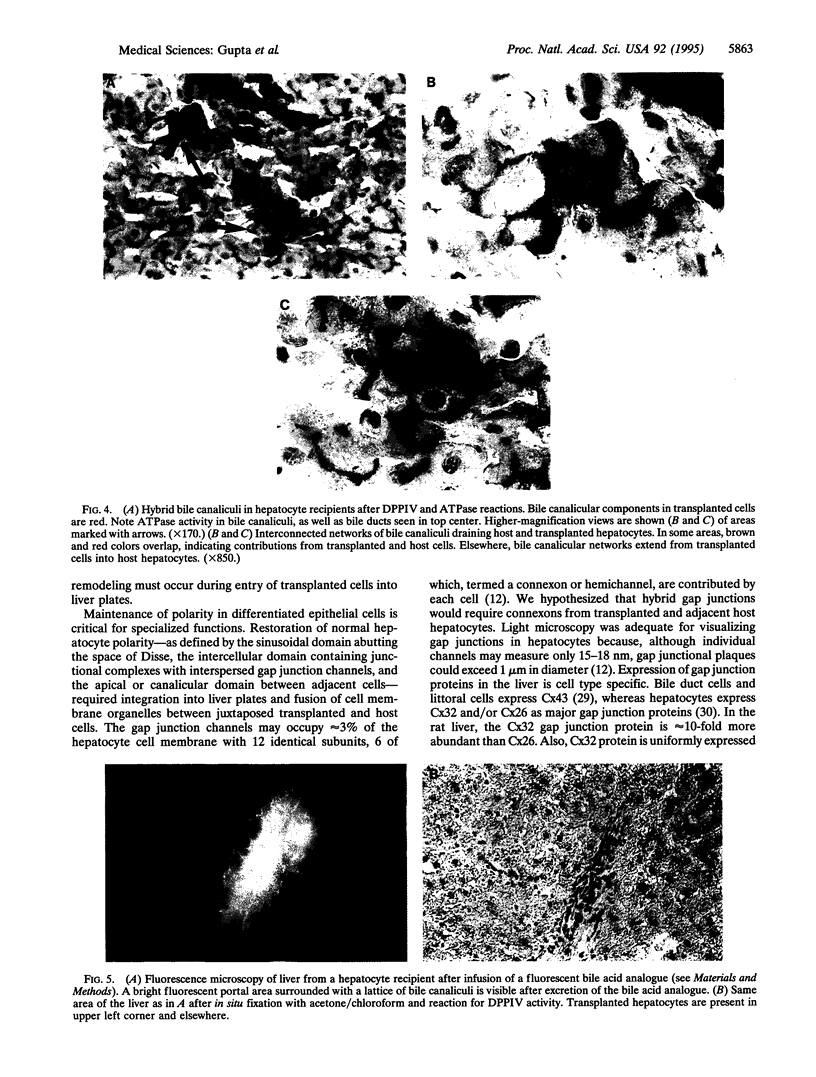
To analyze mechanisms of liver repopulation, we transplanted normal hepatocytes into syngeneic rats deficient in dipeptidyl peptidase IV activity. When isolated hepatocytes were injected into splenic pulp, cells promptly migrated into hepatic sinusoids. To examine whether transplanted hepatocytes entered liver plates and integrated with host hepatocytes, we analyzed sharing of hepatocyte-specific gap junctions and bile canaliculi. Colocalization studies showed gap junctions uniting adjacent transplanted and host hepatocytes in liver plates. Visualization of bile canalicular domains in transplanted and host hepatocytes with dipeptidyl peptidase IV and ATPase activities, respectively, demonstrated hybrid bile canaliculi, which excreted a fluorescent conjugated bile acid analogue. These results indicate that transplanted hepatocytes swiftly overcome mechanical barriers in hepatic sinusoids to enter liver plates and join host cells. Integration into liver parenchyma should physiologically regulate the function or disposition of transplanted hepatocytes and benefit applications such as gene therapy.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arias I. M., Che M., Gatmaitan Z., Leveille C., Nishida T., St Pierre M. The biology of the bile canaliculus, 1993. Hepatology. 1993 Feb;17(2):318–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartles J. R., Zhang L. Q., Verheyen E. M., Hospodar K. S., Nehme C. L., Fayos B. E. Decreases in the relative concentrations of specific hepatocyte plasma membrane proteins during liver regeneration: down-regulation or dilution? Dev Biol. 1991 Feb;143(2):258–270. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90076-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthoud V. M., Iwanij V., Garcia A. M., Sáez J. C. Connexins and glucagon receptors during development of rat hepatic acinus. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 1):G650–G658. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.263.5.G650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury J. R., Grossman M., Gupta S., Chowdhury N. R., Baker J. R., Jr, Wilson J. M. Long-term improvement of hypercholesterolemia after ex vivo gene therapy in LDLR-deficient rabbits. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1802–1805. doi: 10.1126/science.1722351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunsford H. A., Sell S. Production of monoclonal antibodies to preneoplastic liver cell populations induced by chemical carcinogens in rats and to transplantable Morris hepatomas. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 1;49(17):4887–4893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fini A., Roda A. Chemical properties of bile acids. IV. Acidity constants of glycine-conjugated bile acids. J Lipid Res. 1987 Jul;28(7):755–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Yamamoto A., Kyoden T., Kato K., Tashiro Y. Quantitative immunogold localization of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP IV) in rat liver cells. Cell Struct Funct. 1990 Apr;15(2):117–125. doi: 10.1247/csf.15.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfield S., Huber B. E., Nagy P., Cordingley M. G., Thorgeirsson S. S. Neoplastic transformation and lineage switching of rat liver epithelial cells by retrovirus-associated oncogenes. Mol Carcinog. 1988;1(3):189–195. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman M., Raper S. E., Kozarsky K., Stein E. A., Engelhardt J. F., Muller D., Lupien P. J., Wilson J. M. Successful ex vivo gene therapy directed to liver in a patient with familial hypercholesterolaemia. Nat Genet. 1994 Apr;6(4):335–341. doi: 10.1038/ng0494-335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Aragona E., Vemuru R. P., Bhargava K. K., Burk R. D., Chowdhury J. R. Permanent engraftment and function of hepatocytes delivered to the liver: implications for gene therapy and liver repopulation. Hepatology. 1991 Jul;14(1):144–149. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840140124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Chowdhury N. R., Jagtiani R., Gustin K., Aragona E., Shafritz D. A., Chowdhury J. R., Burk R. D. A novel system for transplantation of isolated hepatocytes utilizing HBsAg-producing transgenic donor cells. Transplantation. 1990 Sep;50(3):472–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. Hepatocyte transplantation: new strategies for hepatic reconstitution and gene therapy. Indian J Gastroenterol. 1994 Jan;13(1):13–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., LaBrecque D. R., Shafritz D. A. Mitogenic effects of hepatic stimulator substance on cultured nonparenchymal liver epithelial cells. Hepatology. 1992 Mar;15(3):485–491. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Lee C. D., Vemuru R. P., Bhargava K. K. 111Indium labeling of hepatocytes for analysis of short-term biodistribution of transplanted cells. Hepatology. 1994 Mar;19(3):750–757. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840190330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Vemuru R. P., Lee C. D., Yerneni P. R., Aragona E., Burk R. D. Hepatocytes exhibit superior transgene expression after transplantation into liver and spleen compared with peritoneal cavity or dorsal fat pad: implications for hepatic gene therapy. Hum Gene Ther. 1994 Aug;5(8):959–967. doi: 10.1089/hum.1994.5.8-959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Yerneni P. R., Vemuru R. P., Lee C. D., Yellin E. L., Bhargava K. K. Studies on the safety of intrasplenic hepatocyte transplantation: relevance to ex vivo gene therapy and liver repopulation in acute hepatic failure. Hum Gene Ther. 1993 Jun;4(3):249–257. doi: 10.1089/hum.1993.4.3-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbuch B., Stieger B., Foguet M., Lübbert H., Meier P. J. Functional expression cloning and characterization of the hepatocyte Na+/bile acid cotransport system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10629–10633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrinig A. S., Raychaudhuri R., Kelley S. P., Iype P. T. Repeated establishment of diploid epithelial cell cultures from normal and partially hepatectomized rats. In Vitro. 1983 Jul;19(7):576–588. doi: 10.1007/BF02619606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg E. L., Spray D. C., Bennett M. V. Reduction of gap junctional conductance by microinjection of antibodies against the 27-kDa liver gap junction polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2412–2416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lack L., Weiner I. M. Intestinal bile salt transport: structure-activity relationships and other properties. Am J Physiol. 1966 May;210(5):1142–1152. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.5.1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lojda Z. Studies on dipeptidyl(amino)peptidase IV (glycyl-proline naphthylamidase). II. Blood vessels. Histochemistry. 1979 Jan 22;59(3):153–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00495663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponder K. P., Gupta S., Leland F., Darlington G., Finegold M., DeMayo J., Ledley F. D., Chowdhury J. R., Woo S. L. Mouse hepatocytes migrate to liver parenchyma and function indefinitely after intrasplenic transplantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1217–1221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teutsch H. F. Improved method for the histochemical demonstration of glucose-6-phosphatase activity. Histochemistry. 1978 Aug 25;57(2):107–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00496675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub O., Look J., Dermietzel R., Brümmer F., Hülser D., Willecke K. Comparative characterization of the 21-kD and 26-kD gap junction proteins in murine liver and cultured hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):1039–1051. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vemuru R. P., Davidson A., Aragona E., Chowdhury J. R., Burk R. D., Gupta S. Immune tolerance to a defined heterologous antigen after intrasplenic hepatocyte transplantation: implications for gene therapy. FASEB J. 1992 Jul;6(10):2836–2842. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.10.1634046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WACHSTEIN M., MEISEL E. Histochemistry of hepatic phosphatases of a physiologic pH; with special reference to the demonstration of bile canaliculi. Am J Clin Pathol. 1957 Jan;27(1):13–23. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/27.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe N., Tsukada N., Smith C. R., Phillips M. J. Motility of bile canaliculi in the living animal: implications for bile flow. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1069–1080. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]