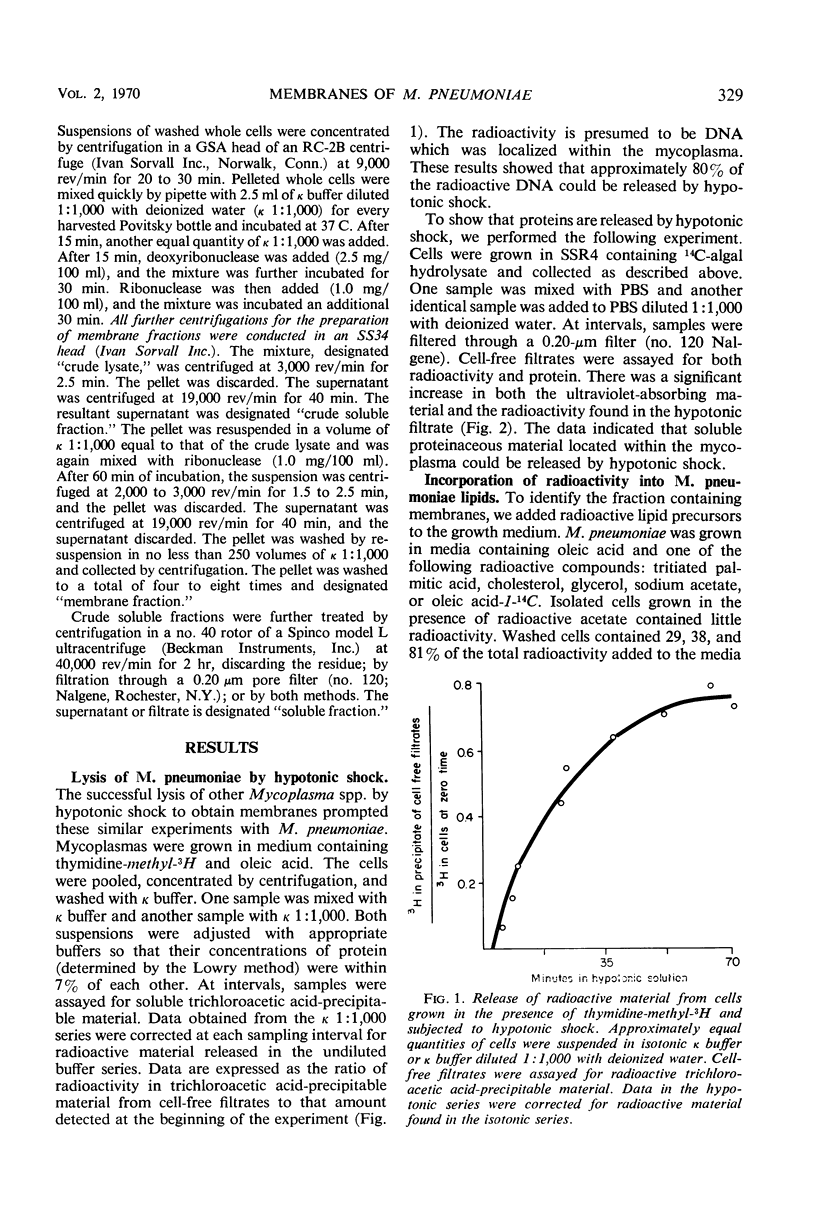
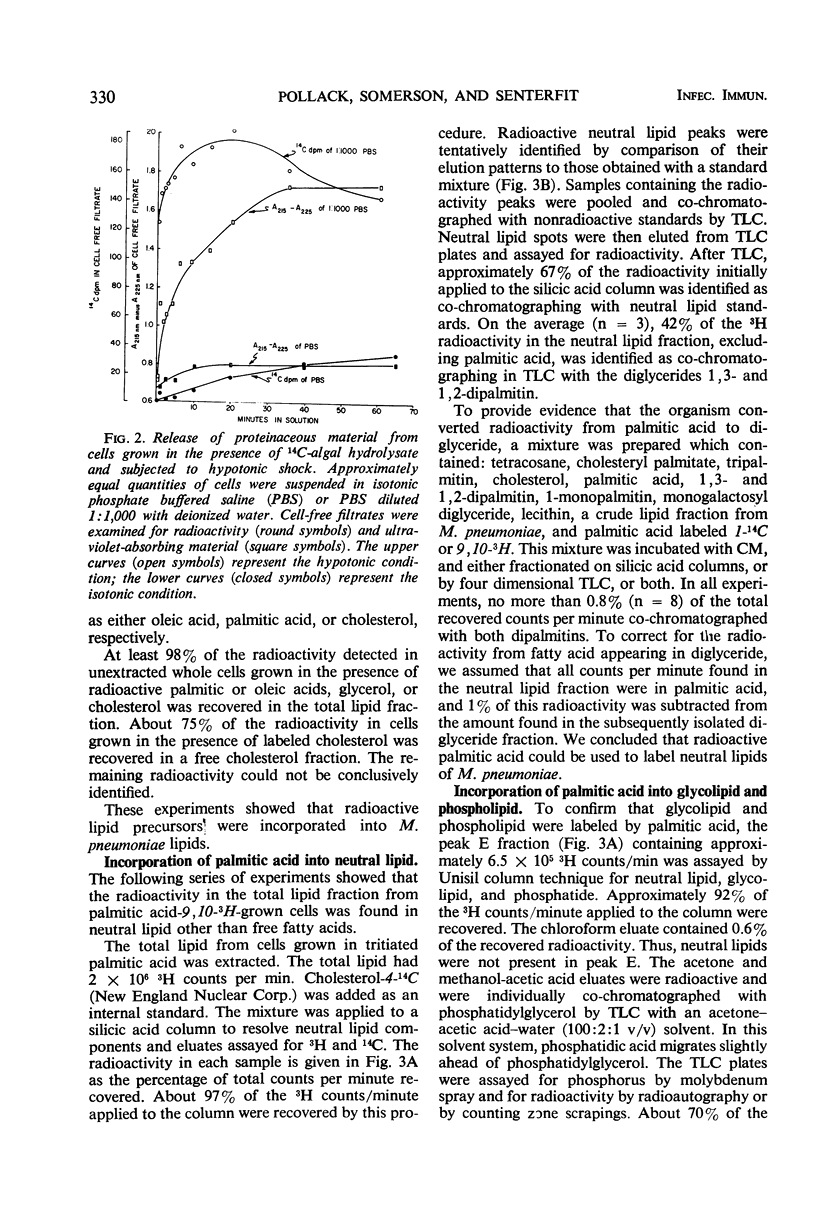
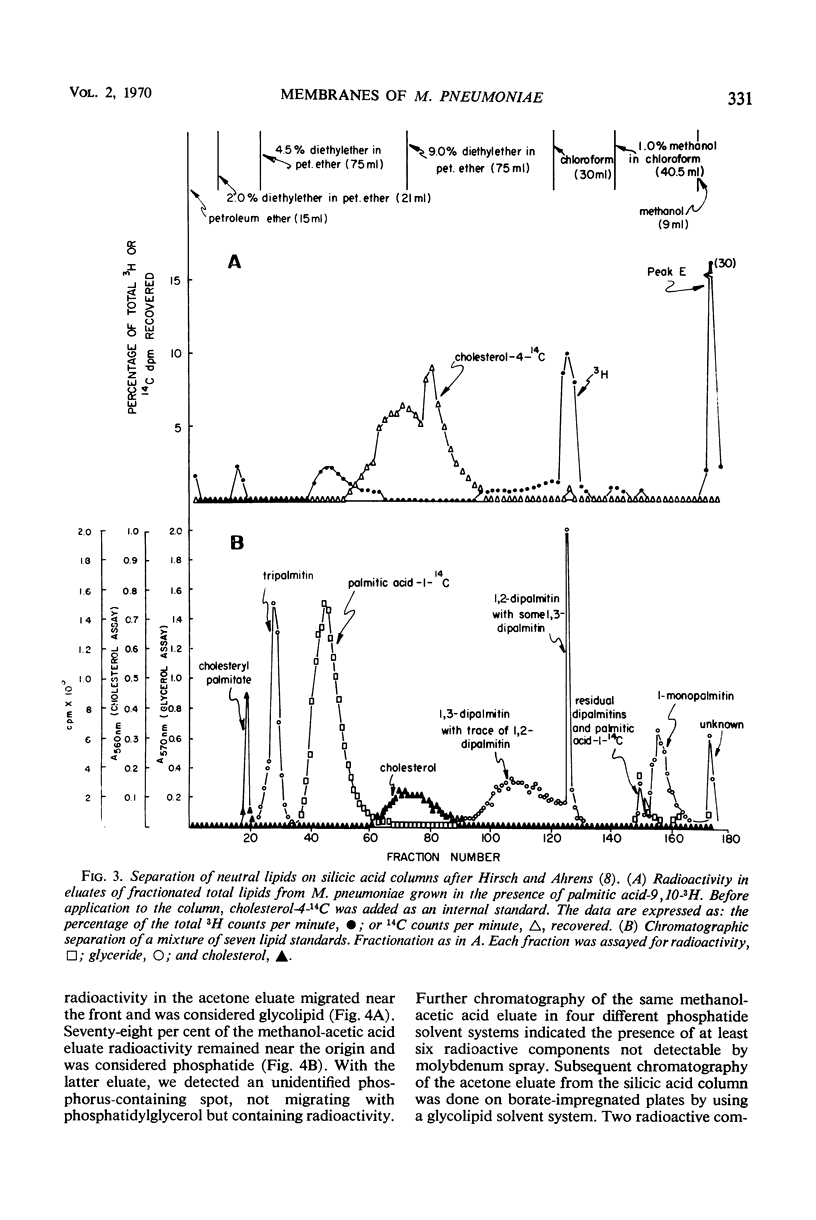
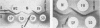Abstract
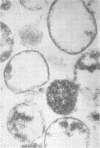
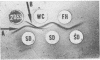
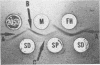
Membrane and soluble fractions of Mycoplasma pneumoniae, M. pulmonis, and M. laidlawii B were prepared by hypotonic lysis of whole cells. The membranes of M. pneumoniae and M. laidlawii B contained, as percentage of dry weight: 34 to 37% protein, 59 to 61% lipid, 3 to 4% carbohydrate as hexose, and 0.2% ribonucleic acid as ribose. NADH2 and NADPH2 oxidase activities were localized in the soluble fractions of M. pneumoniae and in the membrane fraction of M. laidlawii B. NADH2 oxidase activity was localized in the soluble fraction of M. pulmonis. The lipids of M. pneumoniae were labeled when the organism was grown in the presence of either radioactive palmitic acid, oleic acid, cholesterol, or glycerol. The lipids were not labeled when grown in the presence of radioactive acetate. Palmitic acid radio-activity was found in neutral lipid, glycolipid, and phosphatide fractions. Immunodiffusion analyses of whole cells and membrane fractions demonstrated three reactive antigens. Two immunodiffusion antigens were localized in the membrane fraction. One of these apparently contains lipid. A third antigen, also considered lipoidal, was found in whole cells. Membrane and soluble fractions of M. pneumoniae were immunogenic. The immunogens eliciting metabolic-inhibiting antibodies were localized in the membrane. The membrane preparation also induced the formation of antibodies which fixed complement with an antigen extracted with lipid solvent. The soluble fraction contained a distinct immunogen which induces antibodies reactive in complement fixation with an antigen prepared by phenol extraction.
Full text
PDF


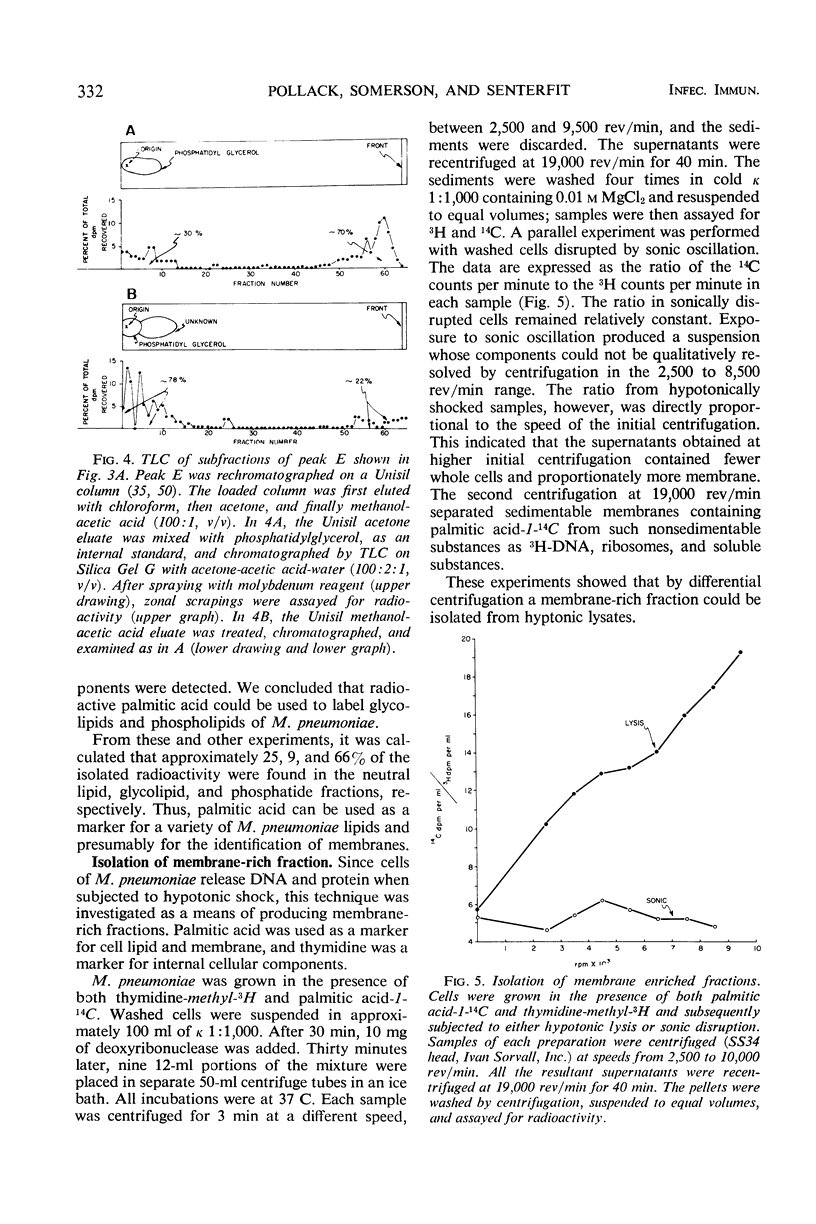
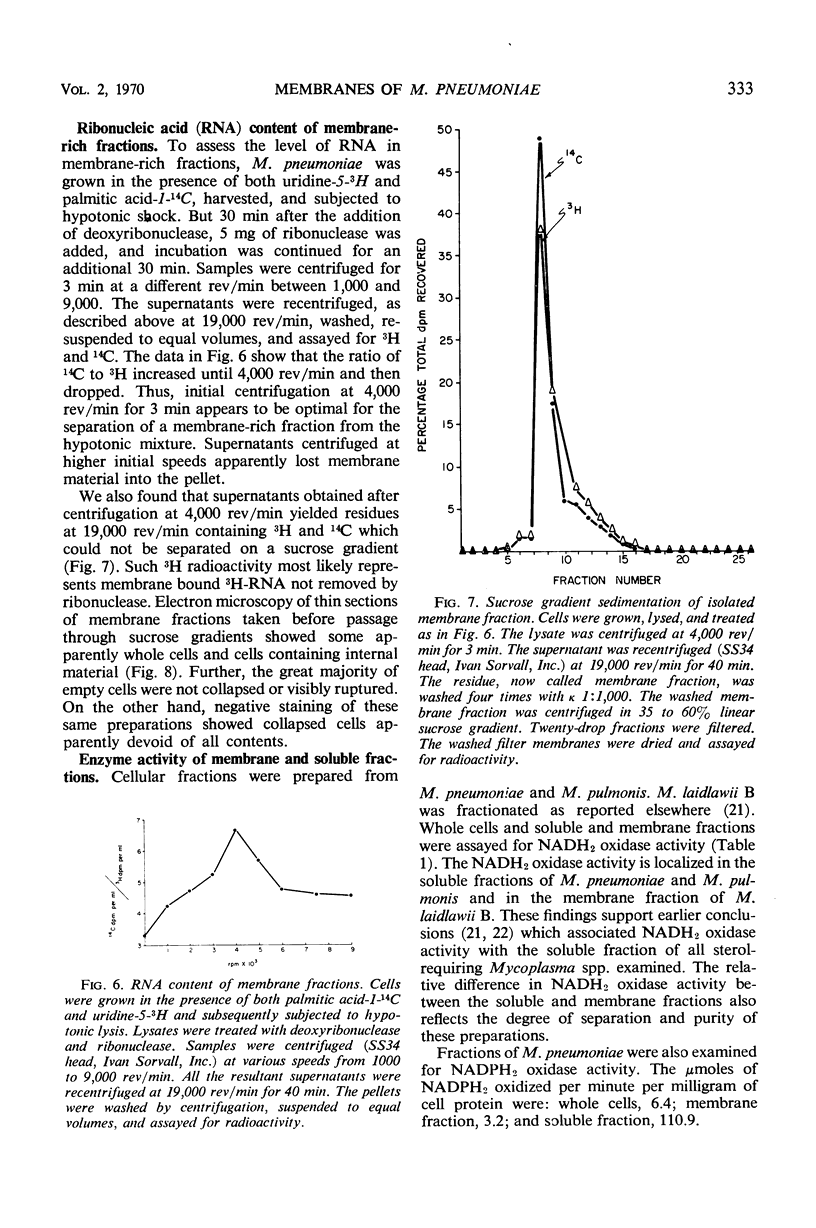
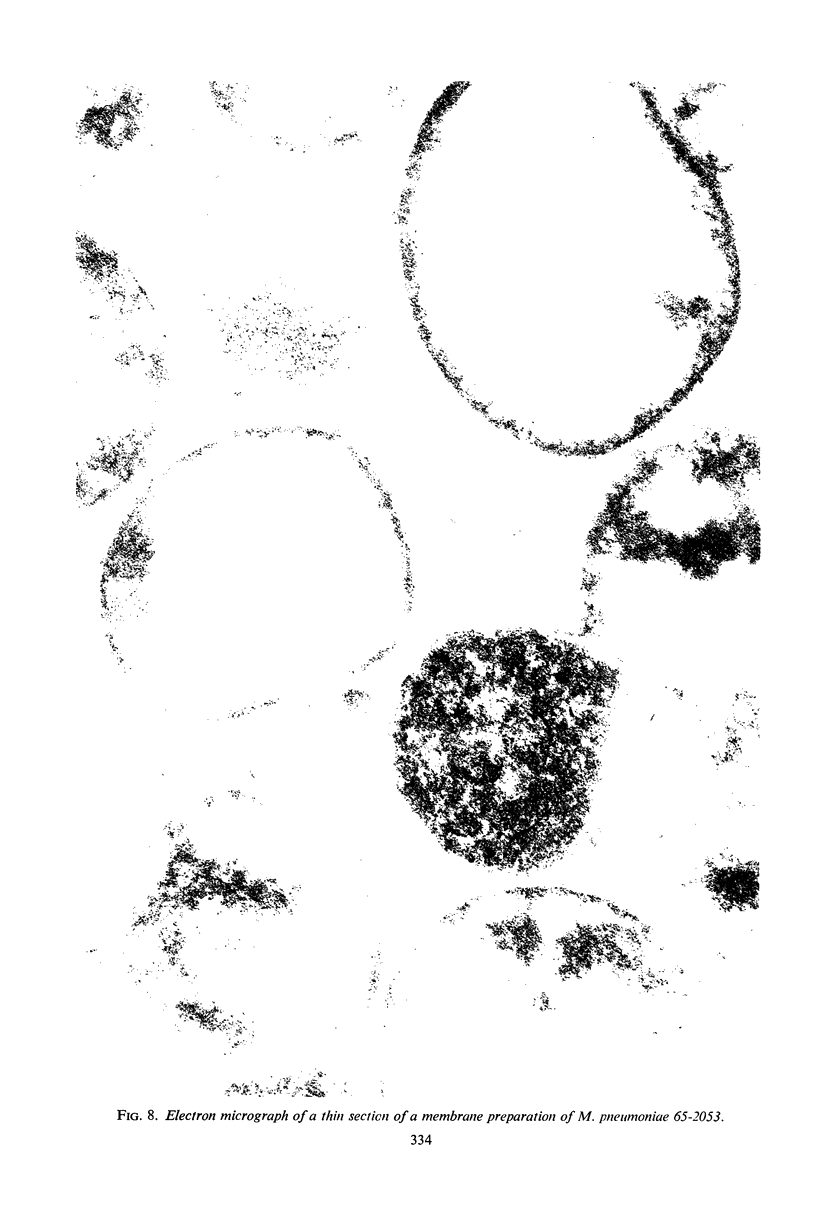


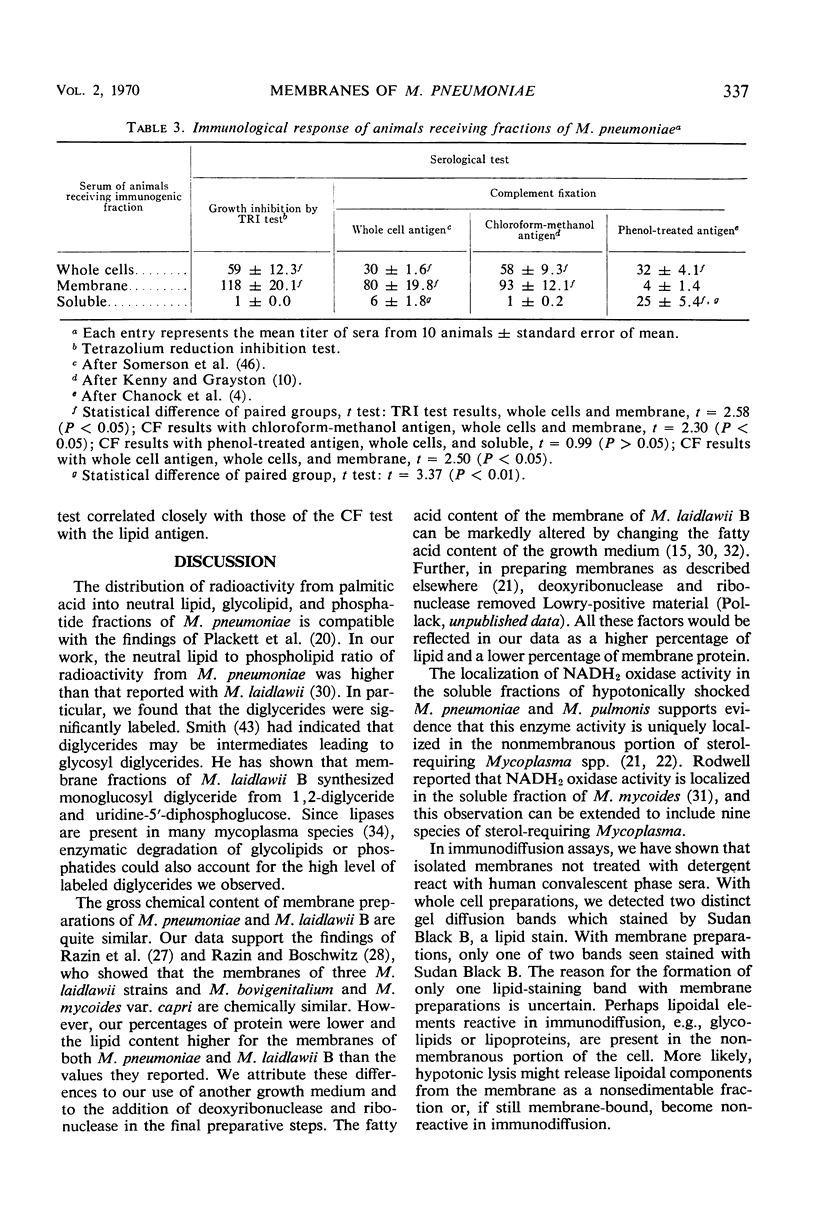


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckman B. L., Kenny G. E. Immunochemical analysis of serologically active lipids of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1171–1180. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1171-1180.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CERIOTTI G. Determination of nucleic acids in animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1955 May;214(1):59–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R. M., JAMES W. D., FOX H. H., TURNER H. C., MUFSON M. A., HAYFLICK L. Growth of Eaton PPLO in broth and preparation of complement fixing antigen. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Aug-Sep;110:884–889. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanock R. M., Fox H. H., James W. D., Gutekunst R. R., White R. J., Senterfit L. B. Epidemiology of M. pneumoniae infection in military recruits. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):484–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conant R. M., Somerson N. L., Senterfit L. B. Immunodiffusion reactions between human sera and Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Nov;129(2):401–407. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DITTMER J. C., LESTER R. L. A SIMPLE, SPECIFIC SPRAY FOR THE DETECTION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS ON THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAMS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:126–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENNY G. E., GRAYSTON J. T. EATON PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISM (MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE) COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGEN: EXTRACTION WITH ORGANIC SOLVENTS. J Immunol. 1965 Jul;95:19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner H. W. Preparative isolation of monogalactosyl and digalactosyl diglycerides by thin-layer chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jan;9(1):139–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J., AHRENS E. H., Jr The separation of complex lipide mixtures by the use of silicic acid chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1958 Aug;233(2):311–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane I., Razin S. Immunological analysis of Mycoplasma membranes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):187–194. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.187-194.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lansink A. G. Thin layer chromatography and histochemistry of Sudan black B. Histochemie. 1968;16(1):68–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00306212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemcke R. M., Marmion B. P., Plackett P. Immunochemical analysis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):691–702. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemcke R. M., Plackett P., Shaw E. J., Marmion B. P. Immunochemical analysis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. 2. Properties of chloroform-methanol extract from M. pneumoniae. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1968 Apr;46(2):123–139. doi: 10.1038/icb.1968.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANILOFF J., MOROWITZ H. J., BARRNETT R. J. STUDIES OF THE ULTRASTRUCTURE AND RIBOSOMAL ARRANGEMENTS OF THE PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISM A5969. J Cell Biol. 1965 Apr;25:139–150. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmion B. P., Plackett P., Lemcke R. M. Immunochemical analysis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. 1. Methods of extraction and reaction of fractions from M. pneumoniae and from M. mycoides with homologous antisera and with antisera against Streptococcus MG. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1967 Apr;45(2):163–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElhaney R. N., Tourtellotte M. E. Mycoplasma membrane lipids: variations in fatty acid composition. Science. 1969 Apr 25;164(3878):433–434. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3878.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLS B. W. SEPARATION OF THE LIPIDS OF PHOTOSYNTHETIC TISSUES: IMPROVEMENTS IN ANALYSIS BY THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 27;70:417–422. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90771-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plackett P., Marmion B. P., Shaw E. J., Lemcke R. M. Immunochemical analysis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. 3. Separation and chemical identification of serologically active lipids. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1969 Apr;47(2):171–195. doi: 10.1038/icb.1969.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. D., Razin S., Cleverdon R. C. Localization of Enzymes in Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1965 Sep;90(3):617–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.3.617-622.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. D., Razin S., Pollack M. E., Cleverdon R. C. Fractionation of mycoplasma cells for enzyme localization. Life Sci. 1965 May;4(9):973–977. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90200-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. D., Somerson N. L., Senterfit L. B. Effect of pH on the immunogenicity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):612–619. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.612-619.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. D., Tourtellotte M. E. Synthesis of saturated long chain fatty acids from sodium acetate-1-C14 by Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):636–641. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.636-641.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott B., Caldes G., James W. D., Chanock R. M. Phospholipid hapten of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):497–500. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Wong D., Chanock R. M., Taylor-Robinson D., Canchola J., Valdesuso J. Significance of antibody to mycoplasma as measured by metabolic-inhibition techniques. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):664–675. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27712.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S., ARGAMAN M., AVIGAN J. CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF MYCOPLASMA CELLS AND MEMBRANES. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:477–487. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENTHAL H. L., PFLUKE M. L., BUSCAGLIA S. A stable iron reagent for determination of cholesterol. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Aug;50(2):318–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTTEM S., RAZIN S. LIPASE ACTIVITY OF MYCOPLASMA. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Oct;37:123–134. doi: 10.1099/00221287-37-1-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Boschwitz C. The membrane of the Streptobacillus moniliformis L-phase. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Nov;54(1):21–32. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Cleverdon R. C. Carotenoids and cholesterol in membranes of Mycoplasma laidlawii. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Dec;41(3):409–415. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Tourtellotte M. E., McElhaney R. N., Pollack J. D. Influence of lipid components of Mycoplasma laidlawii membranes on osmotic fragility of cells. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):609–616. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.609-616.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodwall A. Fatty-acid composition of Mycoplasma lipids: biomembrane with only 1 fatty acid. Science. 1968 Jun 21;160(3834):1350–1351. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3834.1350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodwell A. W. The nutrition and metabolism of mycoplasma: Progress and problems. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):88–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senterfit L. B., Jensen K. E. Antimetabolic antibodies to Mycoplasma pneumoniae measured by tetrazolium reduction inhibition. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jul;122(3):786–790. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siakotos A. N. Analytical separation of nonlipid water soluble substances and gangliosides from other lipids by dextran gel column chromatography. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Nov;42(11):913–919. doi: 10.1007/BF02632444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Barclay M., Reichman E. S., Good J. J. Separation of acidic phospholipids by one-dimensional thin-layer chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 14;137(1):80–89. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. B., Chanock R. M., Friedewald W. T., Alford R. H. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in volunteers. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):471–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27691.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F. Biosynthesis of glucosyl diglycerides by Mycoplasma laidlawii strain B. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):480–486. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.480-486.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobeslavsky O., Prescott B., James W. D., Chanock R. M. Isolation and characterization of fractions of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. II. Antigenicity and immunogenicity. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2126–2138. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2126-2138.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobeslavský O., Prescott B., James W. D., Chanock R. M. Serological and immunogenic activities of different fractions of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):682–690. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerson N. L., James W. D., Walls B. E., Chanock R. M. Growth of Mycoplasma pneumoniae on a glass surface. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):384–389. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg P., White R. J., Fuld S. L., Gutekunst R. R., Chanock R. M., Senterfit L. B. Ecology of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in marine recruits at Parris Island, South Carolina. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Jan;89(1):62–73. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Purcell R. H., Wong D. C., Chanock R. M. A colour test for the measurement of antibody to certain mycoplasma species based upon the inhibition of acid production. J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Mar;64(1):91–104. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN HANDEL E., ZILVERSMIT D. B. Micromethod for the direct determination of serum triglycerides. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Jul;50(1):152–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VORBECK M. L., MARINETTI G. V. SEPARATION OF GLYCOSYL DIGLYCERIDES FROM PHOSPHATIDES USING SILICIC ACID COLUMN CHROMATOGRAPHY. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jan;6:3–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]