Abstract
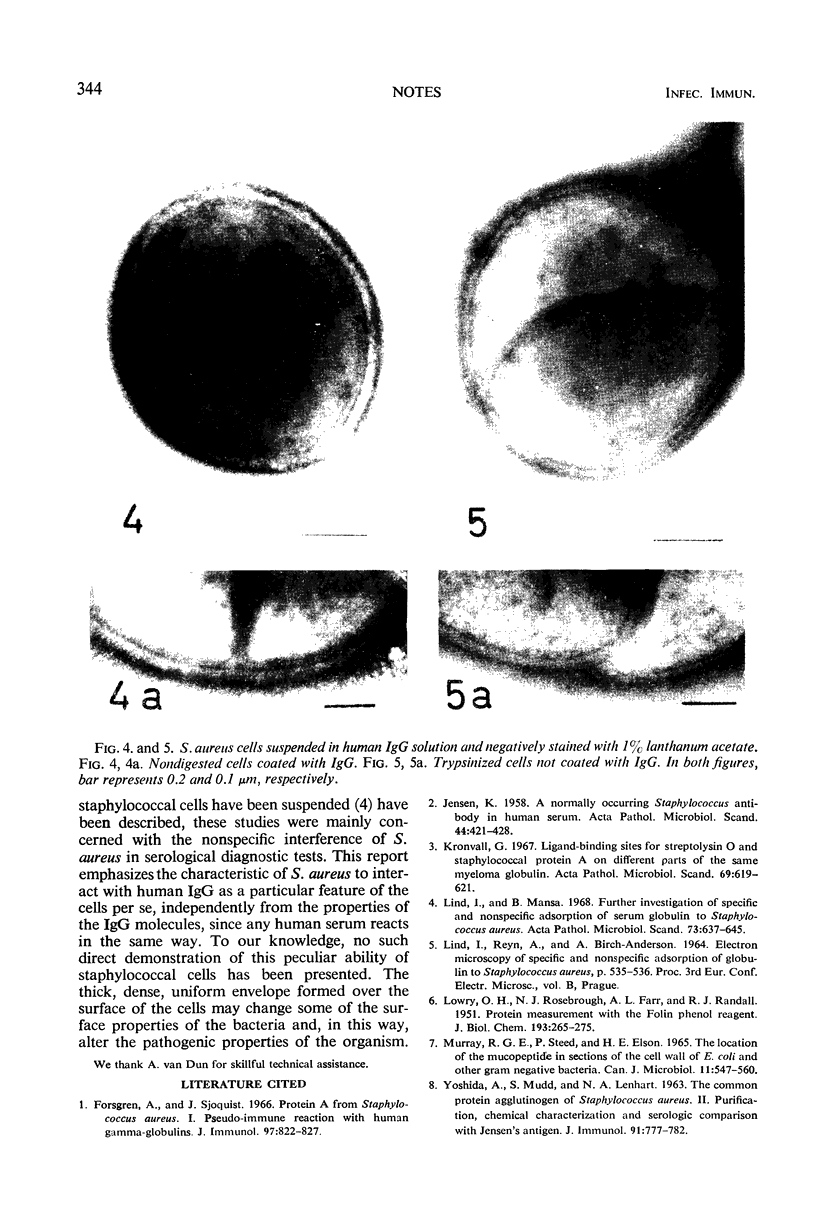
Staphylococcus aureus cells suspended in a human immunoglobulin G (IgG) solution adsorbed nearly 90% of the IgG; electron micrographs showed the cells enclosed in a thick, dense envelope of IgG.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. Ligand-binding sites for streptolysin O and staphylococcal protein A on different parts of the same myeloma globulin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1967;69(4):619–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1967.tb03776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind I., Mansa B. Further investigation of specific and non-specific adsorption of serum globulins to Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;73(4):637–645. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1968.tb03221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. G., STEED P., ELSON H. E. THE LOCATION OF THE MUCOPEPTIDE IN SECTIONS OF THE CELL WALL OF ESCHERICHIA COLI AND OTHER GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Jun;11:547–560. doi: 10.1139/m65-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIDA A., MUDD S., LENHART N. A. THE COMMON PROTEIN AGGLUTINOGEN OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. II. PURIFICATION, CHEMICAL CHARACTERIZATION, AND SEROLOGIC COMPARISON WITH JENSEN'S ANTIGEN. J Immunol. 1963 Dec;91:777–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







