Abstract
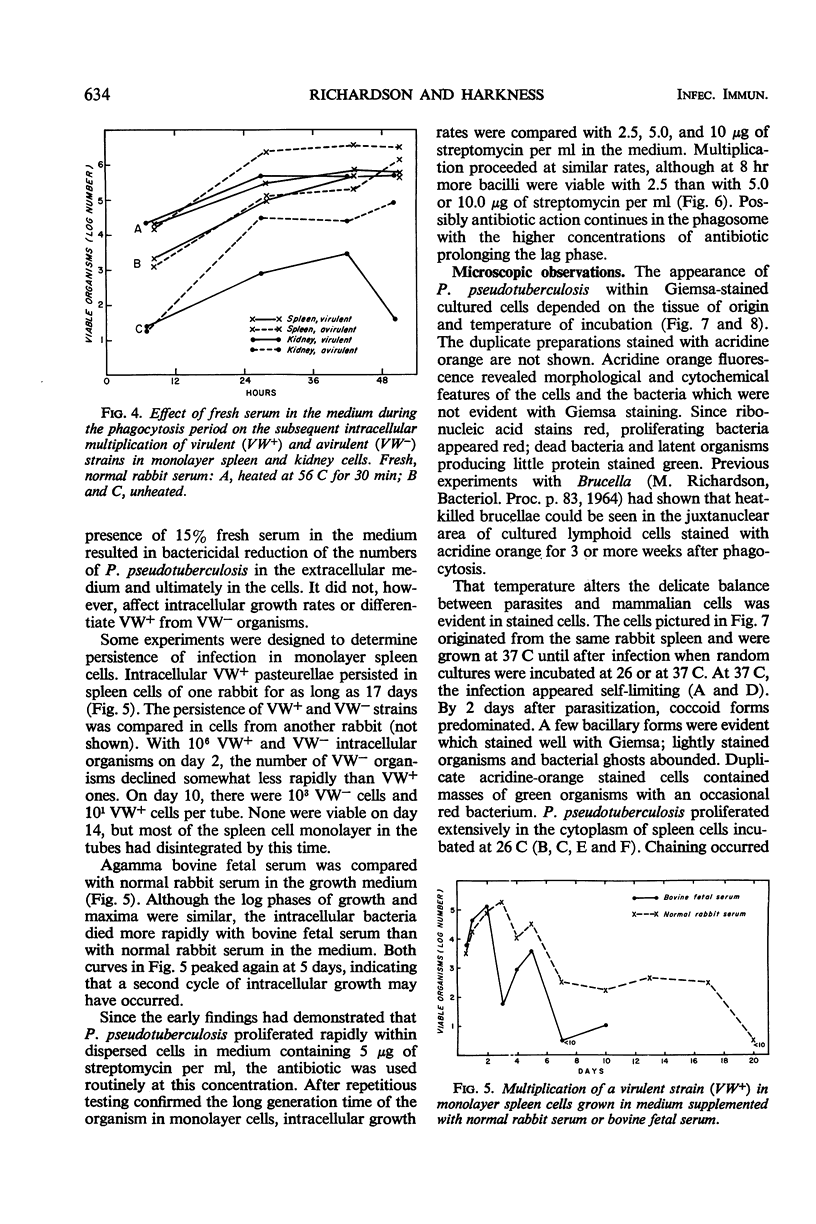
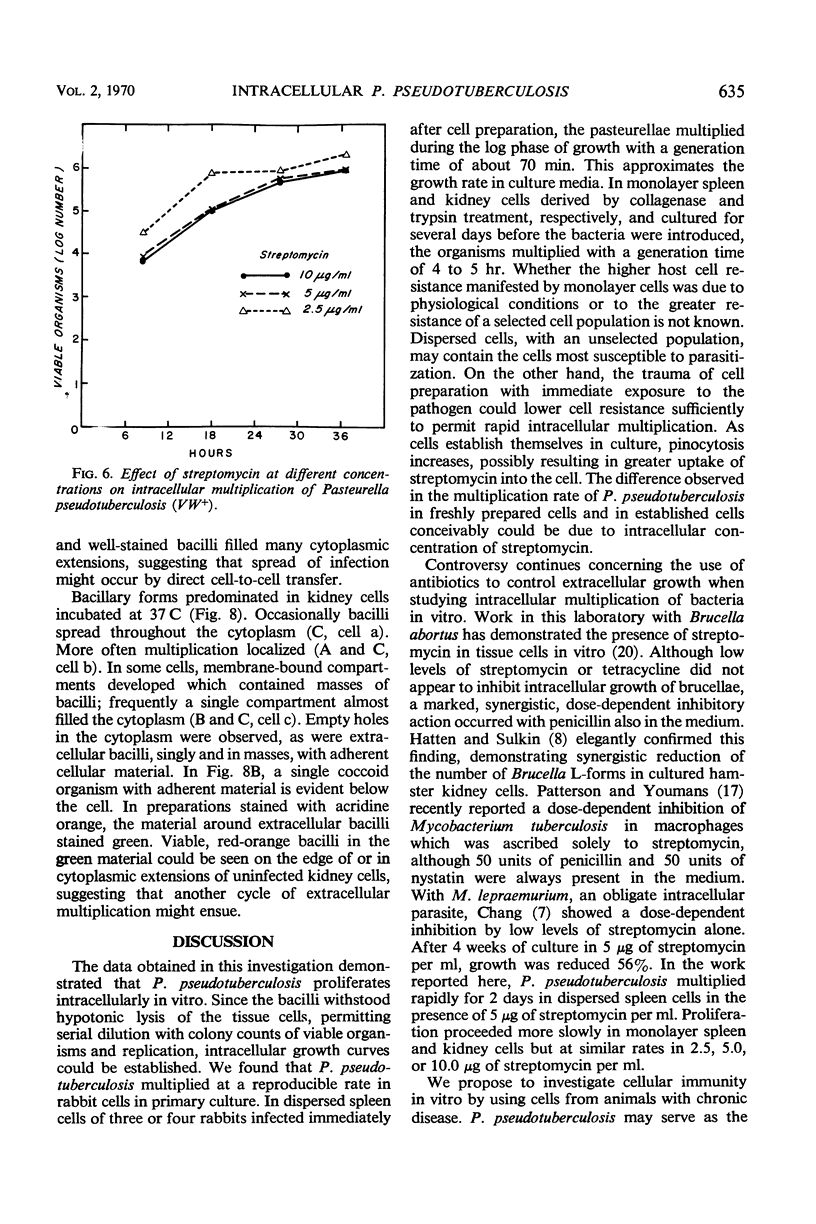
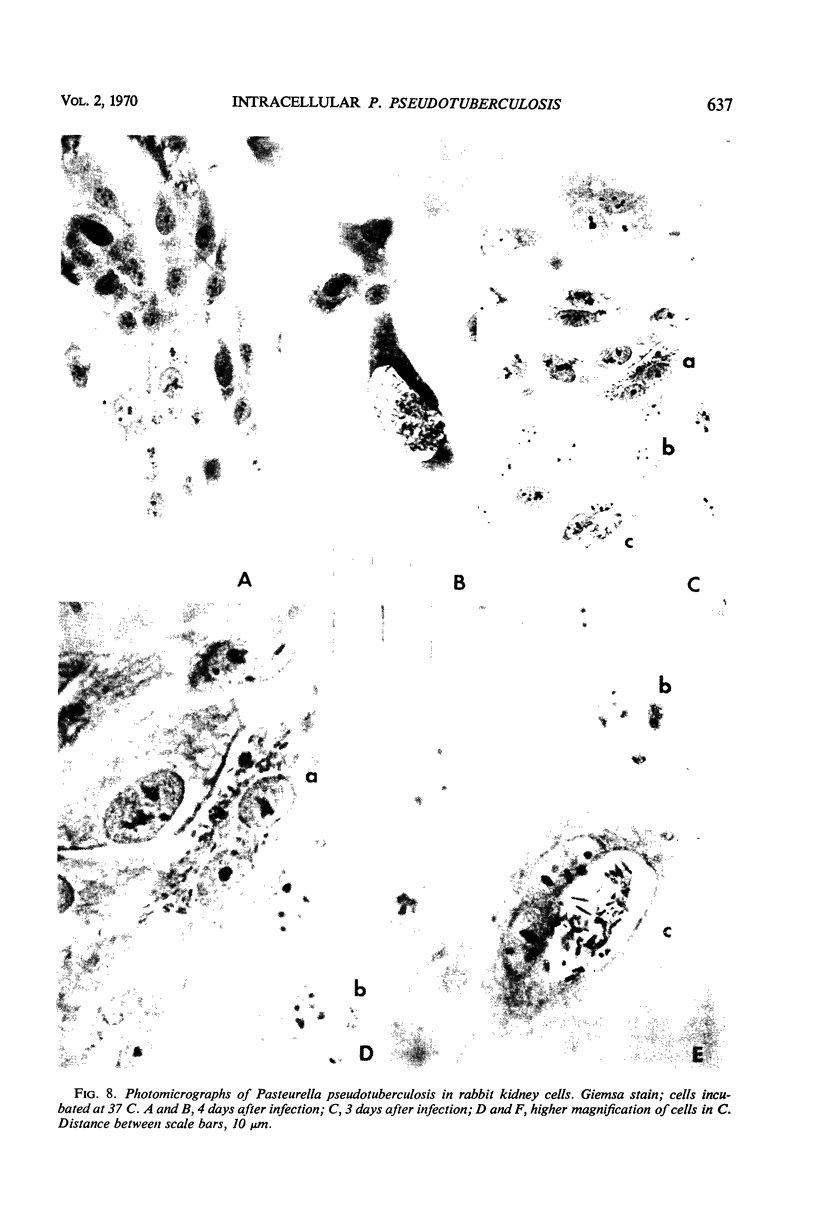
Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis multiplied within rabbit cells in primary culture. Spleen cells from rabbits were either dispersed mechanically, exposed to the organism immediately after cell preparation, and grown as a pellet or the cells were dispersed enzymatically and grown as a monolayer for 4 to 6 days before the bacteria were introduced. Intracellular multiplication proceeded at a logarithmic rate for 1 to 2 days, with a generation time of about 70 min in pelleted cells and 4 to 5 hr in monolayered cells. Under the conditions employed, the wild-type virulent strain and an avirulent mutant multiplied at similar rates. Atmosphere, constituents of the medium, and multiplicity of infection influenced intracellular proliferation. The organism also proliferated in kidney cells. Microscopic observation of stained cells indicated limited growth of the pathogen in spleen cells at 37 C. In kidney cells, the pasteurellae localized in compartments; frequently, a single compartment with masses of proliferating organisms almost filled the cytoplasm.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERTALANFFY F. D. Fluorescence microscope method for detection of pulmonary malignancies. Can Med Assoc J. 1960 Jul 30;83:211–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUBAKER R. R., SURGALLA M. J. THE EFFECT OF CA++ AND MG++ ON LYSIS, GROWTH, AND PRODUCTION OF VIRULENCE ANTIGENS BY PASTEURELLA PESTIS. J Infect Dis. 1964 Feb;114:13–25. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROWS T. W., BACON G. A. V and W antigens in strains of Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1960 Feb;41:38–44. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R., Beesley E. D., Surgalla M. J. Pasteurella pestis: Role of Pesticin I and Iron in Experimental Plague. Science. 1965 Jul 23;149(3682):422–424. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3682.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. Growth of Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis in simulated intracellular and extracellular environments. J Infect Dis. 1967 Dec;117(5):403–417. doi: 10.1093/infdis/117.5.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAUGH D. C., RANDALL R. The role of multiplication of Pasteurella pestis in mononuclear phagocytes in the pathogenesis of flea-borne plague. J Immunol. 1959 Oct;83:348–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. T. Suppressive activity of streptomycin on the growth of Mycobacterium lepraemurium in macrophage cultures. Appl Microbiol. 1969 May;17(5):750–754. doi: 10.1128/am.17.5.750-754.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., SMITH J. L. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. VI. A differential plating medium for the estimation of the mutation rate to avirulence. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:605–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.605-608.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatten B. A., Sulkin S. E. Intracellular production of Brucella L forms . II. Induction and survival of Brucella abortus L forms in tissue culture. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):14–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.14-20.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANSSEN W. A., FUKUI G. M., SURGALLA M. J. A study of the fate of Pasteurella pestis following intracardial injection into guinea pigs. J Infect Dis. 1958 Sep-Oct;103(2):183–187. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANSSEN W. A., LAWTON W. D., FUKUI G. M., SURGALLA M. J. THE PATHOGENESIS OF PLAGUE. I. A STUDY OF THE CORRELATION BETWEEN VIRULENCE AND RELATIVE PHAGOCYTOSIS RESISTANCE OF SOME STRAINS OF PASTEURELLA PESTIS. J Infect Dis. 1963 Sep-Oct;113:139–143. doi: 10.1093/infdis/113.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen W. A., Surgalla M. J. Plague bacillus: survival within host phagocytes. Science. 1969 Feb 28;163(3870):950–952. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3870.950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp W. Die Pseudotuberkulose des Menschen. Klinik, Diagnose, Therapie und Epidemiologie. Ther Umsch. 1968 Apr;25(4):195–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWTON W. D., FUKUI G. M., SURGALLA M. J. Studies on the antigens of Pasteurella pestis and Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis. J Immunol. 1960 May;84:475–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R. J., Youmans G. P. Multiplication of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Within Normal and "Immune" Mouse Macrophages Cultivated With and Without Streptomycin. Infect Immun. 1970 Jan;1(1):30–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.1.30-40.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON M., HOLT J. N. MULTIPLICATION OF BRUCELLA IN CULTURED LYMPHOID AND NONLYMPHOID CELLS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1163–1168. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1163-1168.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON M., HOLT J. N. Synergistic action of streptomycin with other antibiotics of intracellular Brucella abortus in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:638–646. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.638-646.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson M. Antibody elicited by Brucella abortus antigen in vitro: prolonged production by cell suspensions. J Immunol. 1969 Jan;102(1):77–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]