Abstract
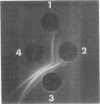
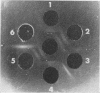
Many of the demonstrable antigens derived from mycobacteria are common to members of different species. Agglutination tests have yielded the most specific characterizations. An antigen which may be associated with the specific agglutination is soluble in phenol and can be extracted and separated from other antigens by use of this solvent. Phenol-soluble antigens have been extracted from representative cultures of Mycobacterium kansasii, M. gastri, and M. marinum. Most representatives of each of these species yielded an antigen which was characteristic of the species but was distinct from antigen derived from the other two species.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnbaum S. E., Affronti L. F. Mycobacterial polysaccharides. II. Comparison of polysaccharides from strains of four species of mycobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):58–63. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.58-63.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobby G. L., Redmond W. B., Runyon E. H., Schaefer W. B., Wayne L. G., Wichelhausen R. H. A study on pulmonary disease associated with mycobacteria other than Mycobacterium tuberculosis: identification and characterization of the mycobacteria. 18. A report of the Veterans Administration-Armed Forces Cooperative Study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 Jun;95(6):954–971. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.95.6.954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARLETT R., YOUMANS G. P. Antigenic relationships between mycobacteria as determined by agar diffusion precipitin techniques. Am Rev Tuberc. 1956 May;73(5):637–649. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1956.73.5.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer W. B. Serologic identification and classification of the atypical mycobacteria by their agglutination. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1965 Dec;92(6):85–93. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1965.92.6P2.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacquet A., Tison F., Devulder B. Les variétes scotochromogènes de Mycobacterium kansasii. Etude bactériologique et biochimique. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Apr;108(4):514–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayne L. G. Classification and identification of mycobacteria. 3. Species within group 3. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1966 Jun;93(6):919–928. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1966.93.6.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayne L. G., Doubek J. R. Diagnostic key to mycobacteria encountered in clinical laboratories. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Jun;16(6):925–931. doi: 10.1128/am.16.6.925-931.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayne L. G., Doubek J. R., Diaz G. A. Classification and indentification of mycobacteria. IV. Some important scotochromogens. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 Jul;96(1):88–95. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.96.1.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayne L. G., Gross W. M. Isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from mycobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1481–1482. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1481-1482.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayne L. G. Selection of characters for an Adansonian analysis of mycobacterial taxonomy. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1382–1391. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1382-1391.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]