Abstract
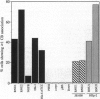
Coiled bodies (CBs) are nuclear organelles whose structures appear to be highly conserved in evolution. In rapidly cycling cells, they are typically located in the nucleoplasm but are often found in contact with the nucleolus. The CBs in human cells contain a unique protein, called p80-coilin. Studies on amphibian oocyte nuclei have revealed a protein within the "sphere" organelle that shares significant structural similarity to p80-coilin. Spheres and CBs are also highly enriched in small nuclear ribonucleoproteins and other RNA-processing components. We present evidence that, like spheres, CBs contain U7 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and associate with specific chromosomal loci. Using biotinylated 2'-O-methyl oligonucleotides complementary to the 5' end of U7 snRNA and fluorescence in situ hybridization, we show that U7 is distributed throughout the nucleoplasm, excluding nucleoli, and is concentrated in CBs. Interestingly, we found that CBs often associate with subsets of the histone, U1, and U2 snRNA gene loci in interphase HeLa-ATCC and HEp-2 monolayer cells. However, in a strain of suspension-grown HeLa cells, called HeLa-JS1000, we found a much lower rate of association between CBs and snRNA genes. Possible roles for CBs in the metabolism of these various histone and snRNAs are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albig W., Drabent B., Kunz J., Kalff-Suske M., Grzeschik K. H., Doenecke D. All known human H1 histone genes except the H1(0) gene are clustered on chromosome 6. Genomics. 1993 Jun;16(3):649–654. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein L. B., Manser T., Weiner A. M. Human U1 small nuclear RNA genes: extensive conservation of flanking sequences suggests cycles of gene amplification and transposition. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2159–2171. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein L. B., Manser T., Weiner A. M. Human U1 small nuclear RNA genes: extensive conservation of flanking sequences suggests cycles of gene amplification and transposition. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2159–2171. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasch K., Ochs R. L. Nuclear bodies (NBs): a newly "rediscovered" organelle. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Oct;202(2):211–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90068-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callan H. G., Gall J. G., Murphy C. Histone genes are located at the sphere loci of Xenopus lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1991 Dec;101(4):245–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00365156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmo-Fonseca M., Pepperkok R., Carvalho M. T., Lamond A. I. Transcription-dependent colocalization of the U1, U2, U4/U6, and U5 snRNPs in coiled bodies. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):1–14. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter K. C., Taneja K. L., Lawrence J. B. Discrete nuclear domains of poly(A) RNA and their relationship to the functional organization of the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(5):1191–1202. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.5.1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan E. K., Takano S., Andrade L. E., Hamel J. C., Matera A. G. Structure, expression and chromosomal localization of human p80-coilin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Oct 25;22(21):4462–4469. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.21.4462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart D., Romain P. L., Huebner K., Pockwinse S., Pilapil S., Cannizzaro L. A., Lian J. B., Croce C. M., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. A human histone H2B.1 variant gene, located on chromosome 1, utilizes alternative 3' end processing. J Cell Biochem. 1992 Dec;50(4):374–385. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240500406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S. Perichromatin fibrils are in situ forms of nascent transcripts. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;4(3):86–90. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Puvion E. The ultrastructural visualization of nucleolar and extranucleolar RNA synthesis and distribution. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;65:255–299. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61962-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Stephenson E. C., Erba H. P., Diaz M. O., Barsacchi-Pilone G. Histone genes are located at the sphere loci of newt lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1981;84(2):159–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00399128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Tsvetkov A., Wu Z., Murphy C. Is the sphere organelle/coiled body a universal nuclear component? Dev Genet. 1995;16(1):25–35. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020160107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. E., Böhni R., Schneiderman M. H., Ramamurthy L., Schümperli D., Marzluff W. F. Regulation of histone mRNA in the unperturbed cell cycle: evidence suggesting control at two posttranscriptional steps. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2416–2424. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-García L. F., Segura-Valdez M. L., Ochs R. L., Rothblum L. I., Hannan R., Spector D. L. Nucleologenesis: U3 snRNA-containing prenucleolar bodies move to sites of active pre-rRNA transcription after mitosis. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Sep;5(9):955–966. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.9.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Carmo-Fonseca M. Localisation of splicing snRNPs in mammalian cells. Mol Biol Rep. 1993 Aug;18(2):127–133. doi: 10.1007/BF00986767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., Tse W. T., Menninger J. C., John K. M., Harris P., Shalev O., Chilcote R. R., Marchesi S. L., Watkins P. C., Bennett V. Hereditary spherocytosis associated with deletion of human erythrocyte ankyrin gene on chromosome 8. Nature. 1990 Jun 21;345(6277):736–739. doi: 10.1038/345736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannironi C., Orr A., Hatch C., Pilch D., Ivanova V., Bonner W. The relative expression of human histone H2A genes is similar in different types of proliferating cells. DNA Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;13(2):161–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1994.13.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F. Histone 3' ends: essential and regulatory functions. Gene Expr. 1992;2(2):93–97. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matera A. G., Weiner A. M., Schmid C. W. Structure and evolution of the U2 small nuclear RNA multigene family in primates: gene amplification under natural selection? Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5876–5882. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier U. T., Blobel G. NAP57, a mammalian nucleolar protein with a putative homolog in yeast and bacteria. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(6 Pt 1):1505–1514. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.6.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavelitz T., Rusché L., Matera A. G., Scharf J. M., Weiner A. M. Concerted evolution of the tandem array encoding primate U2 snRNA occurs in situ, without changing the cytological context of the RNU2 locus. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 3;14(1):169–177. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb06987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L. Macromolecular domains within the cell nucleus. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:265–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuma R. S., Stolk J. A., Roth M. B. Identification and characterization of a sphere organelle protein. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):767–773. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. H., Gall J. G. U7 small nuclear RNA in C snurposomes of the Xenopus germinal vesicle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6257–6259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]