Abstract
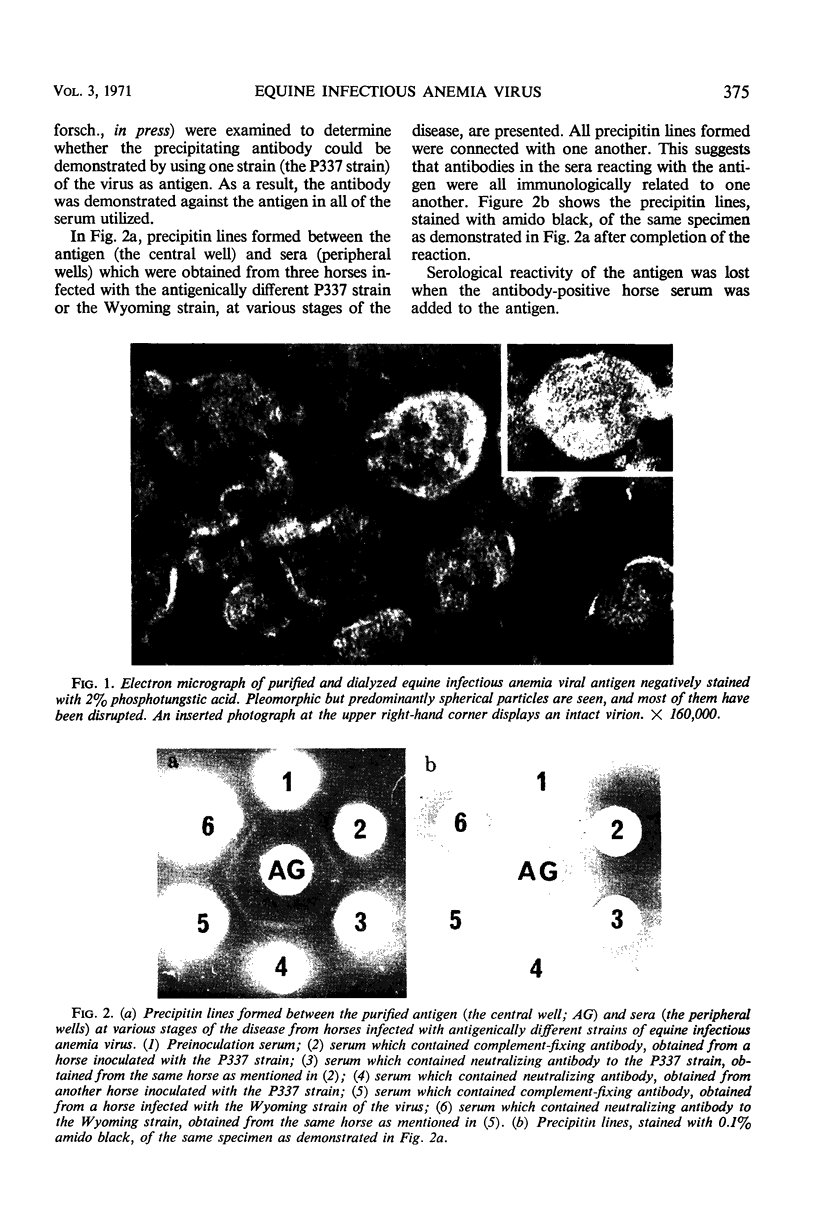
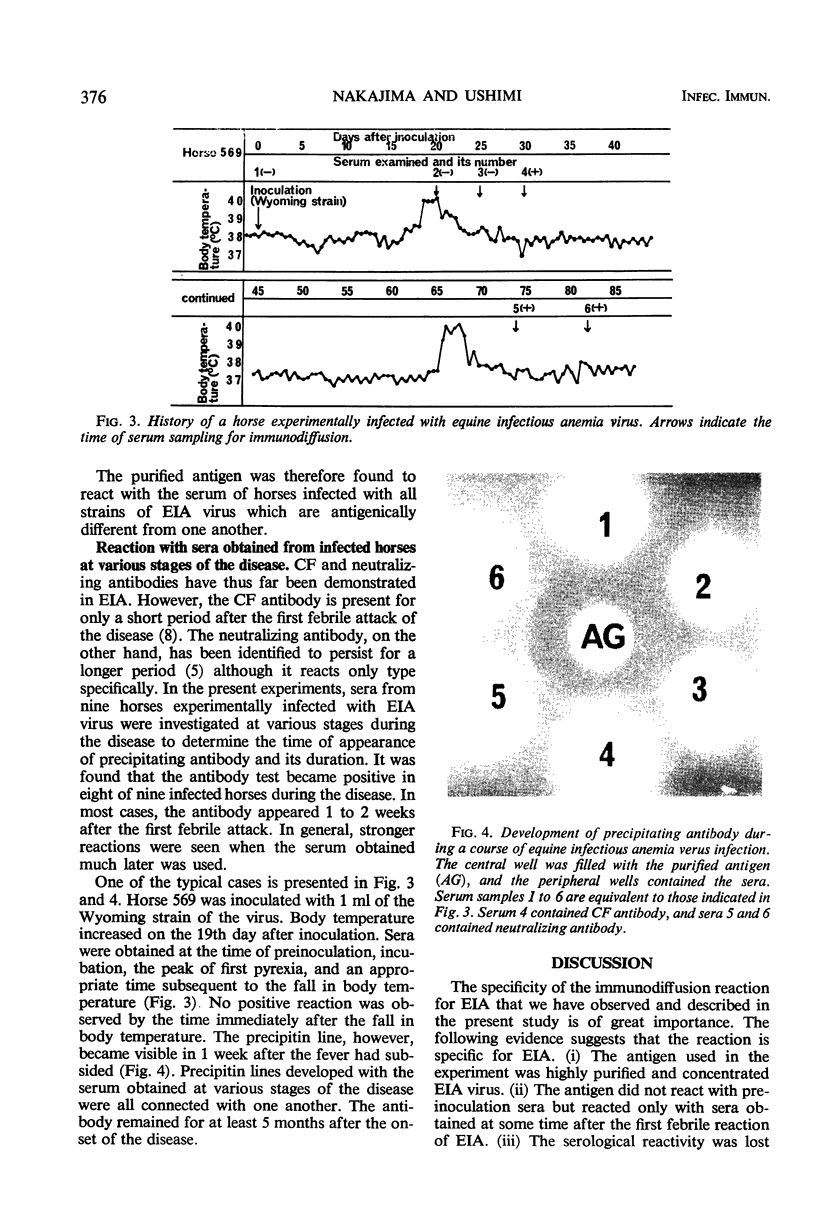
Antigenicity of purified equine infectious anemia (EIA) virus was examined by immunodiffusion against sera obtained from horses experimentally infected with EIA virus. The purified virus reacted with the infected horse serum, and virus-specific precipitating antibody was demonstrated. Furthermore, it was found that purified EIA virus reacted against the serum of horses infected with all strains of EIA virus which were antigenically different from one another. From the result, group-specific components of the virus rather than strain-specific ones were considered to be involved in the reaction. Serological reactivity was lost by adding antiserum from the infected horse to the antigen. The precipitating antibody usually appeared in the serum 1 to 2 weeks after the first febrile attack of EIA and remained for a longer period. Some characteristics of the purified antigen and specificity of the reaction for EIA are described.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coggins L., Norcross N. L. Immunodiffusion reaction in equine infectious anemia. Cornell Vet. 1970 Apr;60(2):330–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Kono Y. Propagation and titration of equine infectious anemia virus in horse leukocyte culture. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1967 Spring;7(1):8–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Kono Y. Serial passages of equine infectious anemia virus in horse leukocyte culture. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1967 Spring;7(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono Y. Characteristics of the complement-fixing antigen of equine infectious anemia virus. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1968 Fall;8(3):117–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono Y., Kobayashi K. Complement fixation test of equine infectious anemia. II. Relationship between CF antibody response and the disease. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1966 Winter;6(4):204–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono Y. Viremia and immunological responses in horses infected with equine infectious anemia virus. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1969 Spring;9(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima H., Tajima M., Tanaka S., Ushimi C. Physicochemical studies of equine infectionus anemia virus. 3. Purification and electron microscopic observation of the virus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1969;28(3):348–360. doi: 10.1007/BF01240949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima H., Tanaka S., Ushimi C. Fractionation of equine infectious anemia virus by diethylaminoethyl cellulose chromatography and sucrose density gradient centrifugation. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1968 Summer;8(2):57–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima H., Tanaka S., Ushimi C. Physicochemical studies of equine infectious anemia virus. I. Buoyant density of the virus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1969;26(4):389–394. doi: 10.1007/BF01250949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima H., Tanaka S., Ushimi C. Physicochemical studies of equine infectious anemia virus. II. Sensitivity of the virus to trypsin. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1969;26(4):395–397. doi: 10.1007/BF01250950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima H., Tanaka S., Ushimi C. Physicochemical studies of equine infectious anemia virus. IV. Determination of the nucleic acid type in the virus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;31(3):273–280. doi: 10.1007/BF01253762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima M., Nakajima H., Ito Y. Electron microscopy of equine infectious anemia virus. J Virol. 1969 Oct;4(4):521–527. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.4.521-527.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]