Abstract
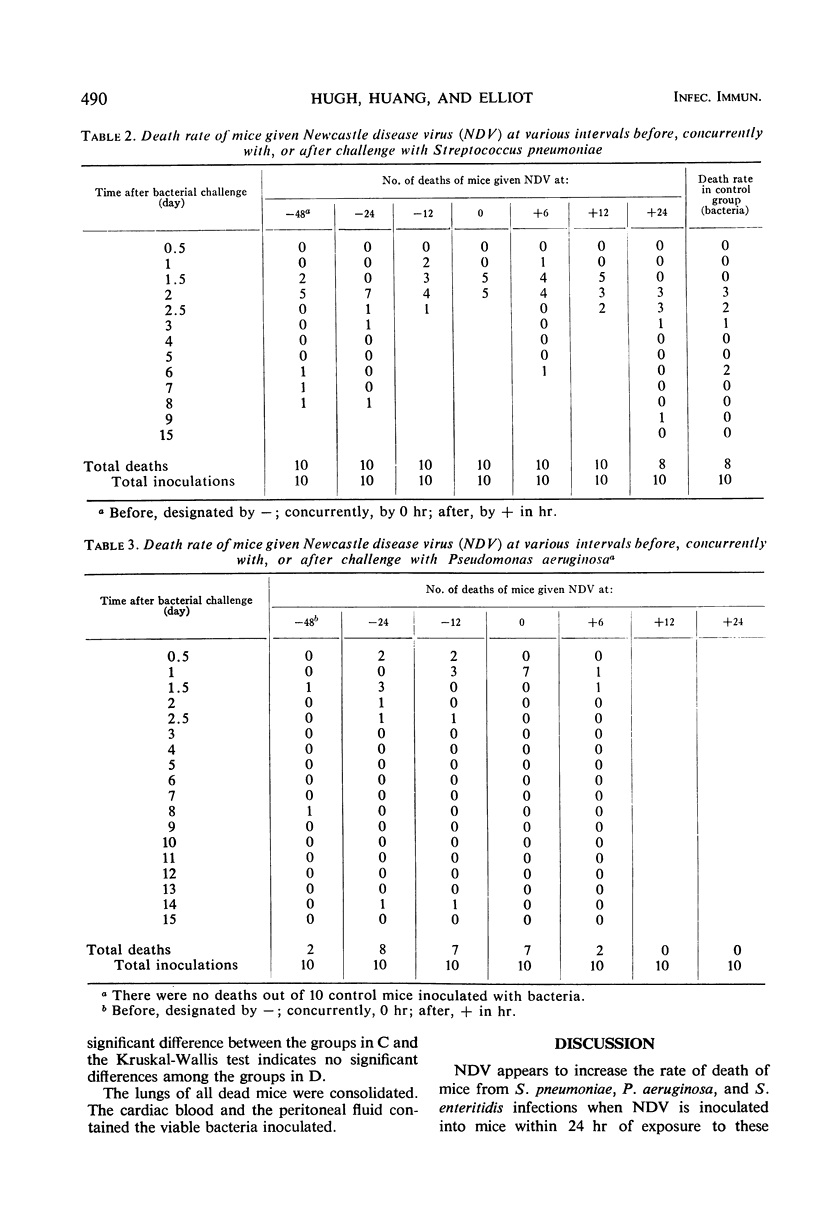
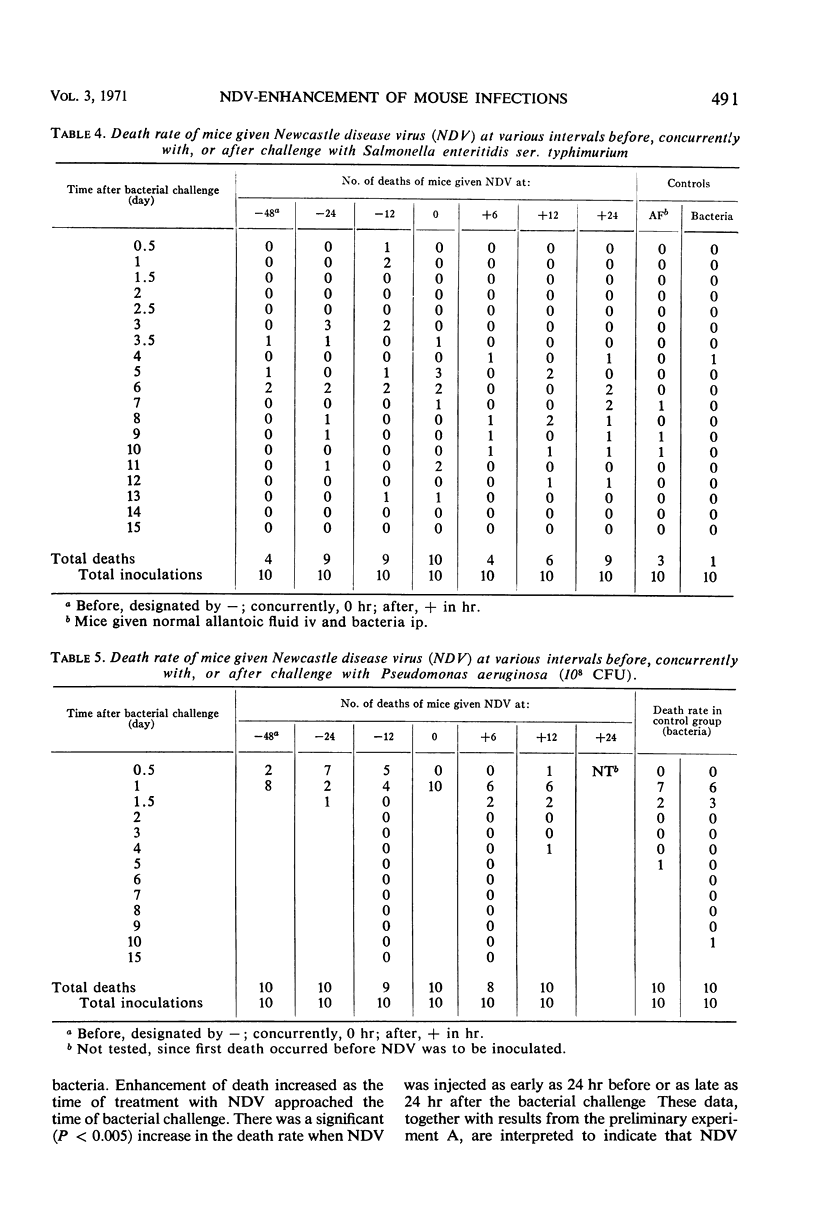
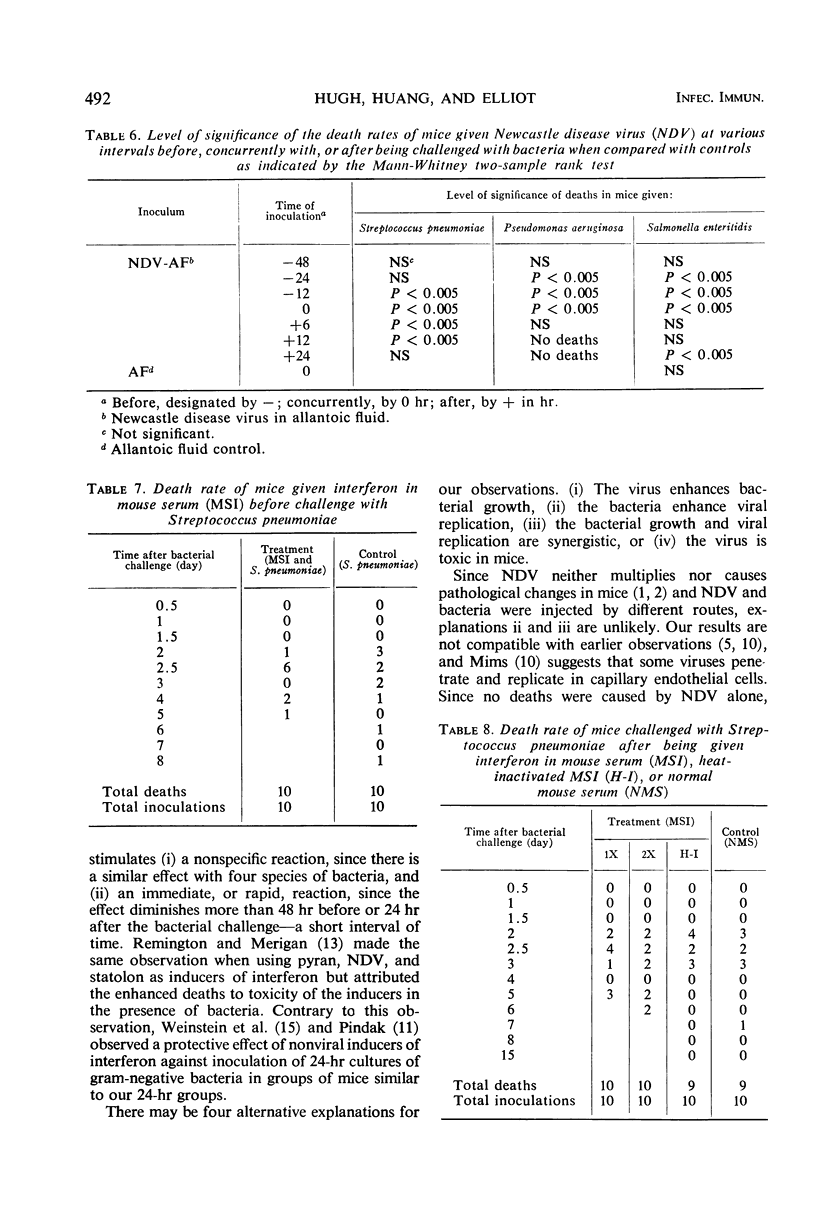
This report describes an attempt to define the factors which incite secondary bacterial pneumonias. Groups of mice were given bacteria intraperitoneally and, at various intervals, Newcastle disease virus intravenously. There was an increase in the number of deaths and in the rates of death in these groups, when compared with a control group which was given only bacteria. These results were obtained with Streptococcus pneumoniae (Diplococcus pneumoniae), Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Salmonella enteritidis ser. typhimurium. Newcastle disease virus increased the mortality rate of mice with bacterial infections when the two agents were given within 24 hr.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARON S., BUCKLER C. E. CIRCULATING INTERFERON IN MICE AFTER INTRAVENOUS INJECTION OF VIRUS. Science. 1963 Sep 13;141(3585):1061–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.141.3585.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron S., Buckler C. E., Friedman R. M., McCloskey R. V. Role of interferon during viremia. II. Protective action of circulating interferon. J Immunol. 1966 Jan;96(1):17–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron S., Buckler C. E., McCloskey R. V., Kirschstein R. L. Role of interferon during viremia. I. Production of circulating interferon. J Immunol. 1966 Jan;96(1):12–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumming J. G. The alliance between streptococci and virus infections. Med Ann Dist Columbia. 1968 Dec;37(12):644–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M., Postic B. Renal excretion of interferon. Nature. 1967 Jun 17;214(5094):1230–1231. doi: 10.1038/2141230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. Y., Gordon F. B. Production of interferon in mice: effect of altered gaseous environments. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Oct;16(10):1551–1556. doi: 10.1128/am.16.10.1551-1556.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIMS C. A. ASPECTS OF THE PATHOGENESIS OF VIRUS DISEASES. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Mar;28:30–71. doi: 10.1128/br.28.1.30-71.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pindak F. F. Resistance to bacterial infection induced by statolon and pyran. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jan;19(1):188–189. doi: 10.1128/am.19.1.188-189.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postic B., DeAngelis C., Breinig M. K., Monto H. O. Effect of temperature on the induction of interferons by endotoxin and virus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1277–1281. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1277-1281.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Merigan T. C. Resistance to virus challenge in mice infected with protozoa or bacteria. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Sep;131(4):1184–1188. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-34066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELLERS R. F., FITZPATRICK M. An assay of interferon produced in rhesus monkey and calf kidney tissue cultures using bovine enterovirus M6 as challenge. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Dec;43:674–683. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. J., Waitz J. A., Came P. E. Induction of resistance to bacterial infections of mice with poly I-poly C. Nature. 1970 Apr 11;226(5241):170–170. doi: 10.1038/226170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



