Abstract
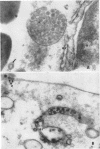
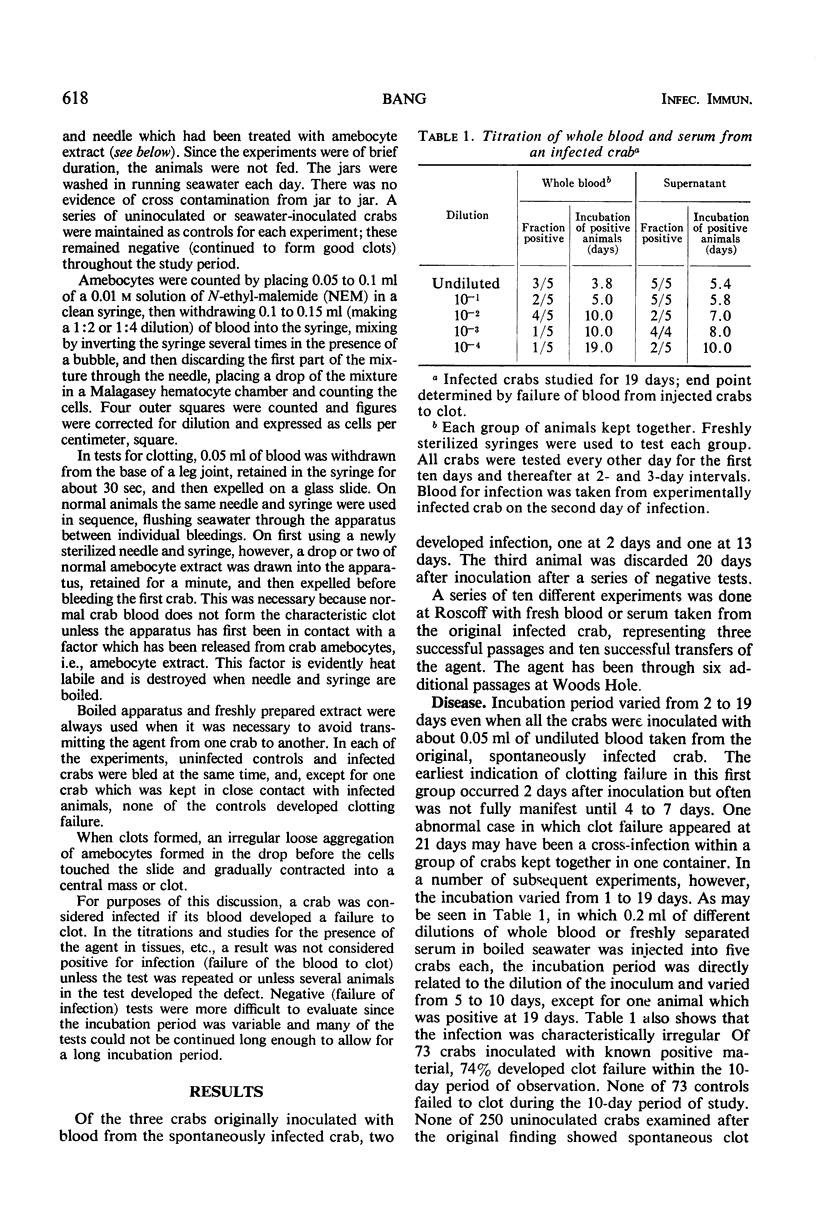
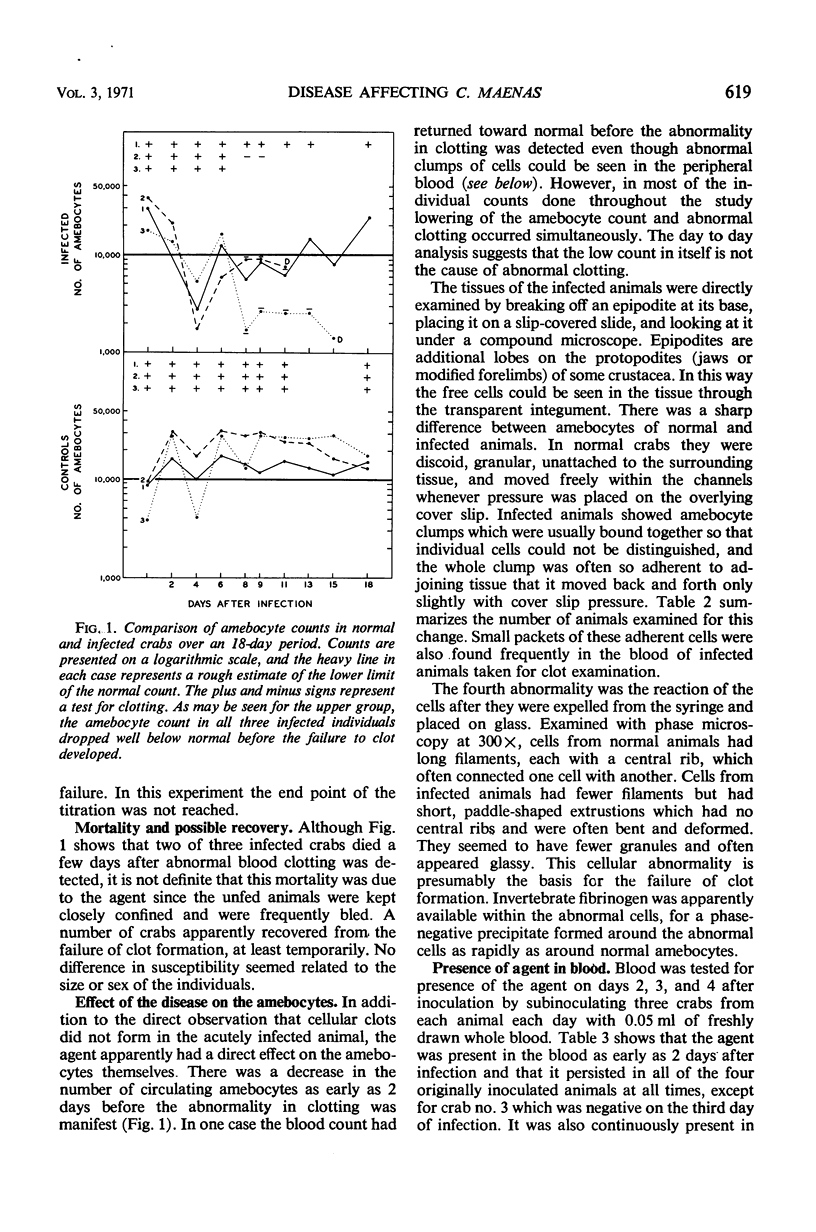
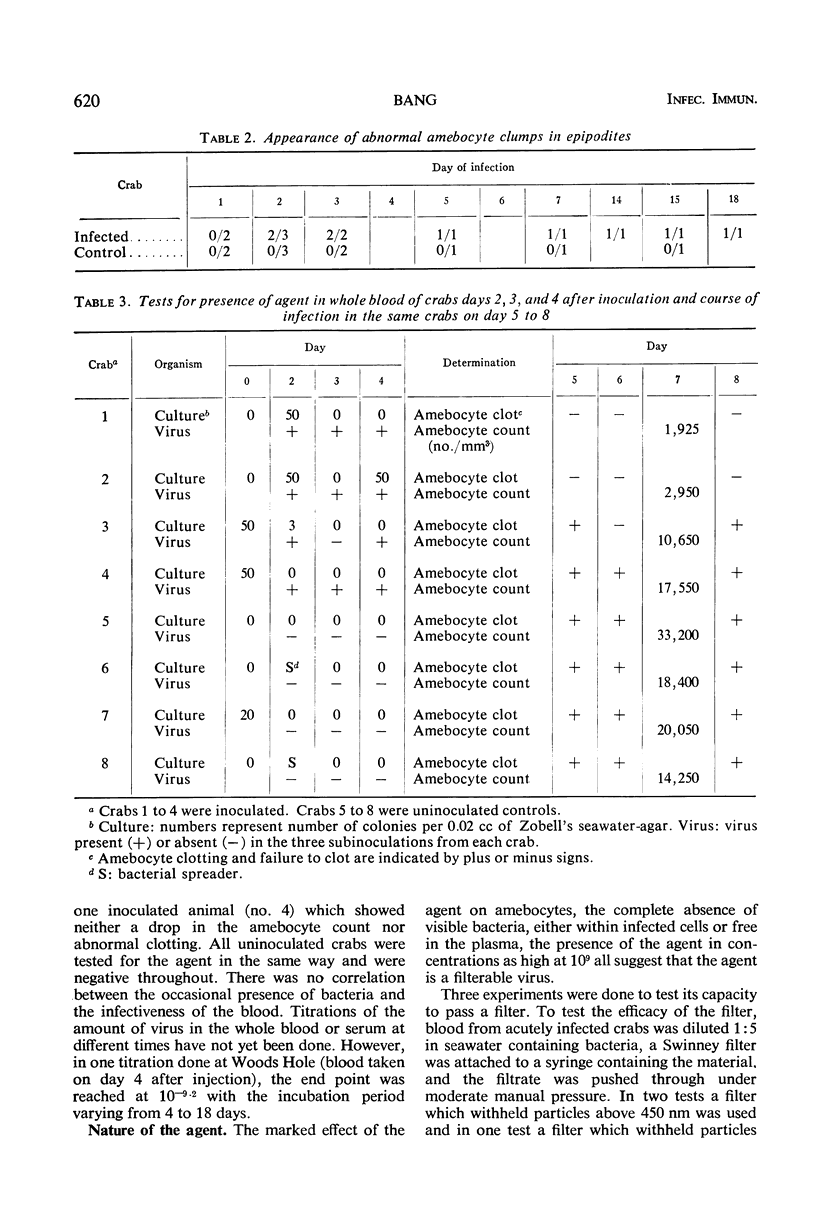
A transmissible infection of the shore crab (“crabe enragée”), Carcinus maenas, was discovered in one of about 700 of this species collected by the Station Biologique, Roscoff, France. The infection has been transferred by subinoculation through four serial passages in crabs collected at Roscoff and through six more passages in C. maenas collected at Woods Hole, Mass. The agent causes abnormal cellular clotting, a drop in the peripheral amebocyte count, clumping of amebocytes in the peripheral tissue and blood, and abnormal behavior of the amebocytes of the infected animal on glass. Mortality over a period of some weeks is negligible. Electron microscopy shows characteristic virus particles, about 55 to 125 nm in size, in the infected amebocytes. The agent is present in large amounts in the whole blood and serum, is filterable, heat labile, and has been preserved in the frozen state. Final identification will depend upon purification, growth in tissue culture, and further electron microscopy.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bang F. B. Cellular aspects of blood clotting in the seastar and the hermit crab. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Feb;7(2):161–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanley C. A. Probable neoplastic disease of the hematopoietic system in oysters, Crassostrea virginica and Crassostrea gigas. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1969 Jul;31:541–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francki R. I., Grivell C. J. An electron microscope study of the distribution of tomato spotted wilt virus in systemically infected Datura stramonium leaves. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):969–978. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90345-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN J., BANG F. B. THE ROLE OF ENDOTOXIN IN THE EXTRACELLULAR COAGULATION OF LIMULUS BLOOD. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1964 Sep;115:265–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]