Abstract
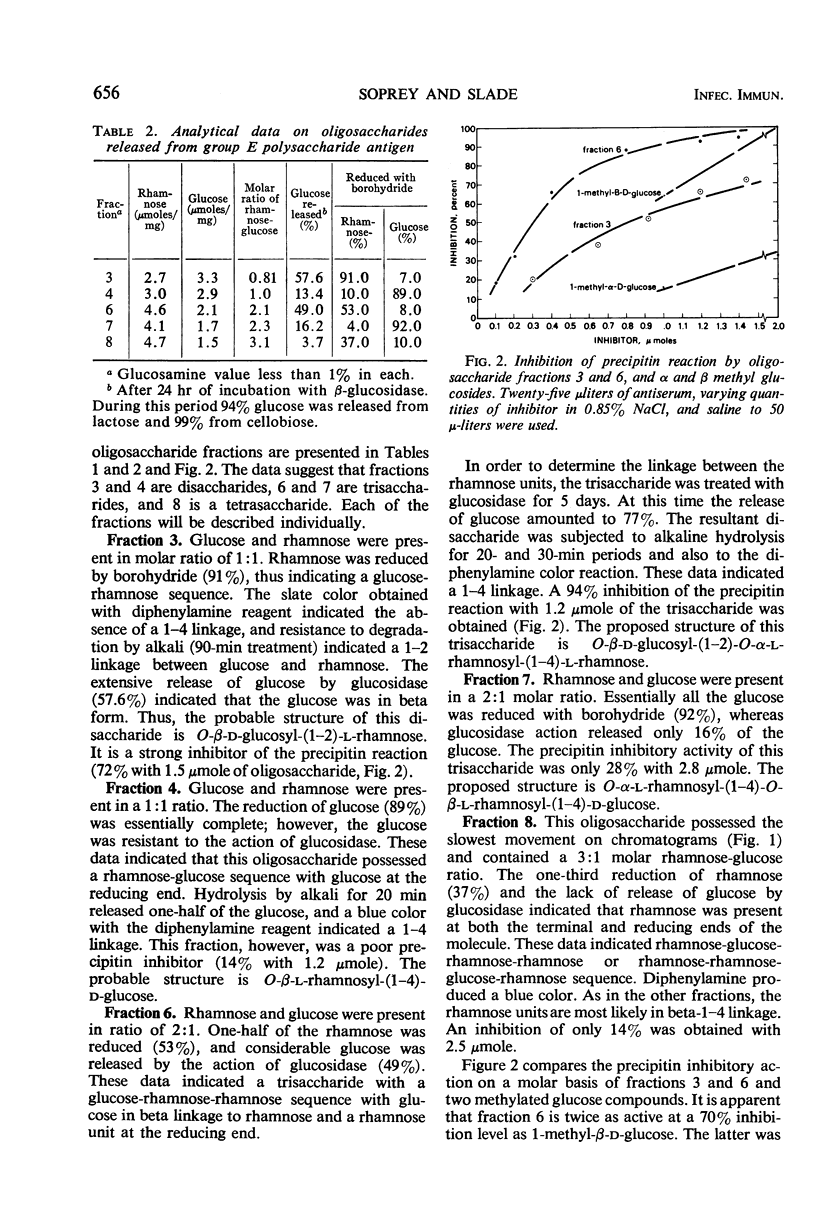
The streptococcal group E cell wall polysaccharide antigen was extracted from strain K129 cells with hot trichloroacetic acid and purified. It contained rhamnose and glucose in a 2:1 molar ratio, 2% protein, 1% phosphorus, and was free of muramic acid and glycerol. No type polysaccharide antigen was present. The reaction of specific group E rabbit antiserum with the polysaccharide was effectively inhibited by d-glucose and β-glucosides such as 1-methyl-β-d-glucose, cellobiose, and gentiobiose. The 1-methyl-α-d-glucose was one-half as effective as the beta isomer. l-Rhamnose and N-acetyl-d-glucosamine were ineffective. Partial acid hydrolysis of the antigen followed by chromatographic separation of the oligosaccharides resulted in the isolation and analysis of five fractions. These fractions were di-, tri-, and tetrasaccharides. A study of these fractions by chemical analysis, reduction with borohydride, inhibition of the antigen-antibody reaction, release of glucose by β-glucosidase, and other evidence indicate that β-d-glucose is the immunodominant sugar in the antigen. A glucose-rhamnose trisaccharide (1:2 molar ratio) was the most effective inhibitor of the precipitin reaction; the glucose was readily released by β-glucosidase, and one-half of the rhamnose was reduced with borohydride. This trisaccharide is considered to be a repeating unit in the native polysaccharide and probably has the following structure: O-β-d-glucosyl-(1-2)-O-α-l-rhamnosyl- (1-4)-l-rhamnose. A glucose-rhamnose disaccharide in which the hexose and pentose are linked as in the trisaccharide was an effective inhibitor of the precipitin reaction. Strain K129 cells do not appear to contain a type polysaccharide antigen.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. H., Payne J. B. Bacteria recovered from swine affected with cervical lymphadenitis (jowl abscess). Am J Vet Res. 1969 Sep;30(9):1607–1612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLEIWEIS A. S., KRAUSE R. M. THE CELL WALLS OF GROUP D STREPTOCOCCI. I. THE IMMUNOCHEMISTRY OF THE TYPE 1 CARBOHYDRATE. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:237–249. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLIER J. R. Streptococcic lymphadenitis of the pharyngeal region of swine. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1956 Dec 15;129(12):543–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chionglo D. T., Hayashi J. A. Structural basis of group G streptococcal antigenicity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman G., Williams R. E. The cell walls of streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Dec;41(3):375–387. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-3-375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHEL M. F., WILLERS J. M. IMMUNOCHEMISTRY OF GROUP F STREPTOCOCCI; ISOLATION OF GROUP SPECIFIC OLIGOSACCHARIDES. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Dec;37:381–389. doi: 10.1099/00221287-37-3-381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOREIRA-JACOB M. The streptococci of Lancefield's group E; biochemical and serological identification of the haemolytic strains. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Apr;14(2):268–280. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-2-268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno T., Slade H. D. Composition and properties of a group A streptococcal teichoic acid. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):747–752. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.747-752.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J. B., Armstrong C. H. Somatic antigens of Streptococcus group E. II. Separation and a partial physicochemical characterization. Appl Microbiol. 1970 May;19(5):823–829. doi: 10.1128/am.19.5.823-829.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLADE H. D., SLAMP W. C. Cell-wall composition and the grouping antigens of Streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1962 Aug;84:345–351. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.2.345-351.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slade H. D. Extraction of Cell-Wall Polysaccharide Antigen from Streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1965 Sep;90(3):667–672. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.3.667-672.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLERS J. M., MICHEL M. F., SYSMA M. J., WINKLER K. C. CHEMICAL ANALYSIS AND INHIBITION REACTIONS OF THE GROUP AND TYPE ANTIGENS OF GROUP F STREPTOCOCCI. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Jul;36:95–105. doi: 10.1099/00221287-36-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willers J. M., Deddish P. A., Slade H. D. Transformation of type polysaccharide antigen synthesis and hemolysin synthesis in streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1225–1230. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1225-1230.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAO J., JACOBS N. J., DEIBEL R. H., NIVEN C. F., Jr GROUP E STREPTOCOCCI. II. SEROLOGICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF STRAINS FROM SWINE CERVICAL ABSCESSES. J Infect Dis. 1964 Oct;114:333–340. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.4.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Moor C. E., Thal E. Beta haemolytic streptococci of the Lancefield groups E, P and U: streptococcus infrequens. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1968;34(4):377–387. doi: 10.1007/BF02046460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]