Background: RORγt is the master transcription factor in Th17 cells.
Results: USP17 stabilizes RORγt via deubiquitination, and USP17 levels are up-regulated in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Conclusion: USP17 is a positive regulator of RORγt.
Significance: USP17 could be a potential drug target to modulate RORγt-mediated autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus.
Keywords: Autoimmune Disease, Deubiquitination, T Cell Biology, Transcription Factor, Ubiquitin-dependent Protease, RORγt, Th17 Cells, USP17, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
Stable retinoic acid-related orphan nuclear receptor γt (RORγt) expression is pivotal for the development and function of Th17 cells. Here we demonstrate that expression of the transcription factor RORγt can be regulated through deubiquitination, which prevents proteasome-mediated degradation. We establish that USP17 stabilizes RORγt protein expression by reducing RORγt polyubiquitination at its Lys-360 residue. In contrast, knockdown of endogenous USP17 in Th17 cells resulted in decreased RORγt protein levels and down-regulation of Th17-related genes. Furthermore, USP17 expression was up-regulated in CD4+ T cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Our data reveal a molecular mechanism in which RORγt expression in Th17 cells can be positively regulated by USP17, thereby modulating Th17 cell functions.
Introduction
Th17 cells are characterized as a distinct subset of CD4+ T cells that play an important role in the immune responses against fungi and bacteria (1, 2). Th17 cells mediate proinflammatory functions through the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines, including IL-17A (IL-17), IL-17F, and IL-22 (2). Moreover, the involvement of Th17 cells has been implicated in the development of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and systemic lupus erythematosus (3).
It has been widely recognized that differentiation of the Th17 lineage requires TGF-β and IL-6 following T cell antigen stimulation (2). In addition, IL-1β and IL-23 are essential components of human Th17 differentiation and the expression of Th17-related genes (4, 5). However, not all Th17 cells are pathogenic. In vivo studies by Lee et al. (6) demonstrated that acquisition of the full pathogenic phenotype in Th17 cells is attributed to IL-6 and TGF-β3 and that the production of TGF-β is IL-23-dependent.
Retinoic acid-related orphan nuclear receptor γt (RORγt) has been identified as the master transcription factor required for the differentiation, maintenance, and proinflammatory functions of Th17 cells (7, 8). RORγt, which is induced by TGF-β and IL-6, directs the transcription of the related cytokines IL-17 and IL-17F in primary CD4+ T helper cells. Mice with a T cell-associated RORγt genetic deficiency exhibit decreased levels of Th17 cytokines and attenuated disease manifestations in an experimental model of autoimmune encephalomyelitis (7). So far, several factors have been identified that regulate the expression and activation of RORγt. Upstream stimulatory factor 1 (USF1) and USF2 are necessary for RORγt transcription in differentiating Th17 cells (9). Leptin promotes Th17 responses by inducing RORγt transcription both in vitro and in vivo (10), and AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 5a (ARID5A) interacts with RORγt and suppresses its activity, therefore inhibiting RORγt-induced Th17 cell differentiation (11). Despite its importance in Th17 function and differentiation, relatively little is known about the enzymes that directly regulate RORγt posttranslational modification and protein stability.
Protein ubiquitination is process that attaches ubiquitin to lysine residues on target proteins and is mediated reciprocally by both E3 ubiquitin ligases and deubiquitinating enzymes. This modification regulates a host of intracellular processes, including proteasome proteolysis, protein trafficking, and functional modulation (12, 13).
So far, many groups have confirmed that the ubiquitination system plays an important role in the differentiation and function of Th17 cells and the IL-17 signaling pathway. PDZ-LIM domain protein (PDLIM2), a nuclear ubiquitin E3 ligase, inhibits TH17 cell-mediated inflammatory responses by suppressing STAT3 signaling (14). The ubiquitin-specific protease USP25 has been identified as a negative regulator of IL-17-mediated signaling and inflammation through the removal of ubiquitination on TRAF5 and TRAF6 (15), and USP18 has been found to regulate T cell activation and Th17 cell differentiation by deubiquitinating the TAK1-TAB1 complex (16). However, the underlying mechanisms that directly regulate the ubiquitination or deubiquitination of RORγt remain unclear.
The human genome encodes almost 100 deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs)4 for ubiquitination, and these are divided into five families: the ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolases, ubiquitin-specific protease (USP), ovarian tumor, Josephin domain, and JAB1/MPN/Mov34 metalloenzyme domain zinc-dependent metalloprotease families (17). USP17, also called DUB-3, has been identified as a deubiquitinating enzyme that belongs to a subfamily of cytokine-inducible DUBs. USP17 is induced in response to IL-4 and IL-6 and is ubiquitously expressed in various tissues and cells (18). USP17 can regulate virus-induced type I IFN signaling through the deubiquitination of RIG-I and melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 (MDA5) (19). USP17 modulates the translocation and activation of the GTPase Ras by negatively regulating Ras-converting enzyme 1(RCE1) (20). Furthermore, USP17 is also indispensable for cell cycle progression and cell migration (21).
Here we identified USP17 as a deubiquitinase for RORγt that promotes Th17 cell functions. We further demonstrated that USP17 decreased the polyubiquitination and inhibited the proteasome-dependent degradation of RORγt at its Lys-360 residue, thereby promoting RORγt signaling. Consistently, a deficiency in USP17 resulted in decreased RORγt protein levels and RORγt-mediated activation of genes such as IL-17 and IL-17F. Furthermore, we also demonstrated that USP17 transcriptional levels were up-regulated in systemic lupus erythematosus compared with healthy controls. Therefore, our work identifies a novel positive regulator of RORγt that is crucial for Th17 cell functions.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Plasmids and Antibodies
RORγt, USP17, and their corresponding truncations were amplified by PCR with human cDNA from HEK293T cells. These fragments were then cloned into pIPHA-tagged, pIPMyc-tagged, or pIPFLAG-tagged vectors. The USP17C89S mutant was constructed with the QuikChange II site-directed mutagenesis kit (Stratagene). The antibodies used in this study were anti-FLAG (catalog no. M2, Sigma), anti-Myc (catalog no. 9E10, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), anti-GAPDH (catalog no. 1C4, Sungene Biotech), anti-β-actin (catalog no. C1213, Sungene Biotech), anti-RORγt (catalog no. sc-28559X, Santa Cruz Biotechnology; catalog no. 14-6988, eBioscience), anti-USP17 (catalog no. sc-103318, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), PerCP/Cy5.5 anti-human CD45RA antibody (catalog no. 304121, Biolegend), FITC anti-human CD4 antibody (catalog no. 300506, Biolegend), and phycoerythrin (PE) anti-human CD25 antibody (catalog no. 302606, Biolegend).
Cell Culture and Transfection
293T cells were cultured in DMEM (Hyclone) supplemented with 10% FBS (catalog no. 131212, ExCell Biology). Jurkat cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium (Hyclone) containing 10% FBS (catalog no. GXM0109, Hyclone), 1% sodium pyruvate, 1% non-essential amino acids. Naïve CD4+ T cells and Th17 cells were cultured in X-VIVO 15 medium (catalog no. 04-418Q, Lonza) supplemented with 10% human AB serum (Invitrogen), 1% sodium pyruvate, 1% GlutaMax, 1% non-essential amino acids, and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. Jurkat cells were activated by treatment with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (50 ng/ml) plus ionomycin (1 μm). 293T cells were transfected with the appropriate plasmids using PEI reagent (catalog no. 23966, Polysciences), and Jurkat cells were transfected by electroporation (NEPA21) according to the instructions of the manufacturer.
Th17 Induction and Expansion
Naive CD4+CD45RA+CD25− T cells were purified by FACS. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated by Ficoll (Life) density gradient centrifugation, and FACS sorting was performed to isolate the lineage: naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4-FITC, CD25-PE, and CD45RA-APC). These cells were stimulated with CD3/CD28 beads (catalog no. 11132D, Invitrogen) in the medium described above. Th17 cells were polarized in the presence of 2.5 ng/ml rhTGF-β1 (catalog no. 240-B-002, R&D Systems), 50 ng/ml rhIL-6 (catalog no. 206-IL-010, R&D Systems), 10 ng/ml rhIL-1β (catalog no. 201-LB-005, R&D Systems), and 100 ng/ml rhIL-23 (catalog no. 1290-IL-010, R&D Systems) for 7 days. Th17 cells were then harvested for a future assay.
Luciferase Reporter Assay
Human genomic DNA was used as a template to produce 0.6-kb fragments of the Il17a promoter according to Ref. 22. The product was cloned into the pGL4 basic luciferase vector. To analyze the effects of USPs on RORγt in terms of Il17a promoter activity, the Il17a luciferase reporter plasmid was cotransfected with a β-gal or Renilla luciferase reporters into 293T or Jurkat T cells. After 48 h, the cells were lysed, and luciferase assays were performed using the Dual-Luciferase reporter kit (Promega).
Immunoblotting and Coimmunoprecipitation
Cells were lysed in radioimmune precipitation assay buffer consisting of 20 nm Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 150 mm NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 1% Nonidet P-40, 10% glycerol, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 1 mm PMSF, 1 mm NaF, 1 mm Na3VO4 and 1% protease inhibitor mixture (catalog no. P8340, Sigma). Cell lysates were incubated with appropriate antibodies for 1 h at 4 °C and then with protein A/G Plus-agarose for another 1 h at 4 °C. Then beads were washed with radioimmune precipitation assay four times and detected by immunoblotting. Protein A/G Plus-agarose (catalog no. sc-2003) was purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology.
Ubiquitin Pulldown Assay
293T cells transfected with FLAG-tagged RORγt, Myc-USP17, and His-tagged ubiquitin were treated with 20 nm MG132 for 3 h before harvesting. Cells were washed with ice-cold 1× PBS and lysed in urea buffer (10 mm Tris (pH 8.0), 8 m urea, 100 mm Na2HPO4, 0.2% Triton-100, 1 mm N-ethylmaleimide, and 10 mm imidazole) at pH 8.0 for 30 min. The lysates were incubated with Ni-NTA acid beads (catalog no. 30210, Qiagen) for 3 h at room temperature. The beads were washed three times in urea buffer (pH 8.0) before incubation. After 3 h of incubation, the beads were washed twice in urea buffer (pH 8.0), twice in urea buffer (10 mm Tris (pH 6.3), 8 m urea, 100 mm Na2HPO4, 0.2% Triton X-100, and 10 mm imidazole) (pH 6.0), and once in a wash buffer (20 mm Tris at pH 8.0, 100 mm NaCl, 20% glycerol, 1 mm dithiothreitol, and 10 mm imidazole). Beads were boiled in 30 μl of 2× loading buffer for 5–10 min and separated on an SDS-PAGE gel, and then ubiquitination levels were evaluated by Western blotting with specific antibodies as indicated.
RNA Isolation and RT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted from whole cells as well as CD4+ T cells from systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients and healthy controls (RNeasy micro kit, Qiagen) following the instructions of the manufacturer. RNA concentrations were quantified with a Nanodrop ND-1000 spectrophotometer, and then RNA was reverse-transcribed into complementary DNA (PrimeScript RT reagent kit, TaKaRa). Real-time PCR was performed with SYBR Green mix (SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM, TaKaRa) using the ABI Prism 7500 sequence detection system (Applied Biosystems).
The primers used were as follows: IL-17A, 5′-ACCAATCCCAAAAGGTCCTC-3′ (forward) and 5′-GGGGACAGAGTTCATGTGGT-3′ (reverse); IL-17F, 5′-CCTCCCCCTGGAATTACACT-3′ (forward) and 5′-ACCAGCACCTTCTCCAACTG-3′ (reverse); RORγt, 5′-CTGCTGAGAAGGACAGGGAG-3′ (forward) and 5′-AGTTCTGCTGACGGGTGC-3′ (reverse); USP17, 5′-GAGCACTTGGTGGAAAGAGC-3′ (forward) and 5′-TGATGGTTCTTCATCCCACA-3′ (reverse); and GAPDH, 5′-GAGTCAACGGATTTGGTCGT-3′ (forward) and 5′-GCCATGGGTGGAATCATATTGG-3′ (reverse).
Lentiviral Constructs and Transduction
shRNA sequences were synthesized by Shanghai Sunny Biotechnology Co. Ltd., and the oligos were cloned into the shRNA lentiviral vector PLKO.1. 293T cells were cotransfected with shUSP17, del8.9, and vesicular stomatitis virus G (VSV-G) for lentivirus transduction. Forty-eight hours later, the supernatants containing virus were harvested for future knockdown assays. Th17 cells or Jurkat cells were incubated with viral supernatants containing 8 μg/ml of Polybrene overnight. The viral supernatants were replaced with fresh medium on day 2. G418 or puromycin was added to screen the cells 2 days post-transduction for stable cell lines.
The shRNA sequences were as follows: CAACAAGATGAAGAGCACCAA (shCK), AAGCAGGAAGATGCCCATGAA (shUSP17-1), AAGTCACCACTCTCATGTGAG (shUSP17-3), and GACACAGACAGGCGAGCAACG (shUSP17-3).
CD4+ T Cell Isolation
Human peripheral blood was collected from SLE patients who fulfilled the American College of Rheumatology criteria for the diagnosis of SLE as well as from healthy donors. The patients were between 23 and 56 years old and were recruited from the Rheumatology Department of Huashan Hospital (Shanghai, China). The SLE patients were divided into two groups according to the disease activity index (SLEDAI): an inactive group (SLEDAI <10) and an active group (SLEDAI >10). CD4+ T cells were isolated from whole blood using a human CD4+ T cell enrichment mixture (StemCell Technologies). Total RNA was extracted following the same method as that used for RNA isolation.
RESULTS
USP17 Up-regulates the Activation of RORγt-dependent Il17a Promoter Transcriptional Activity
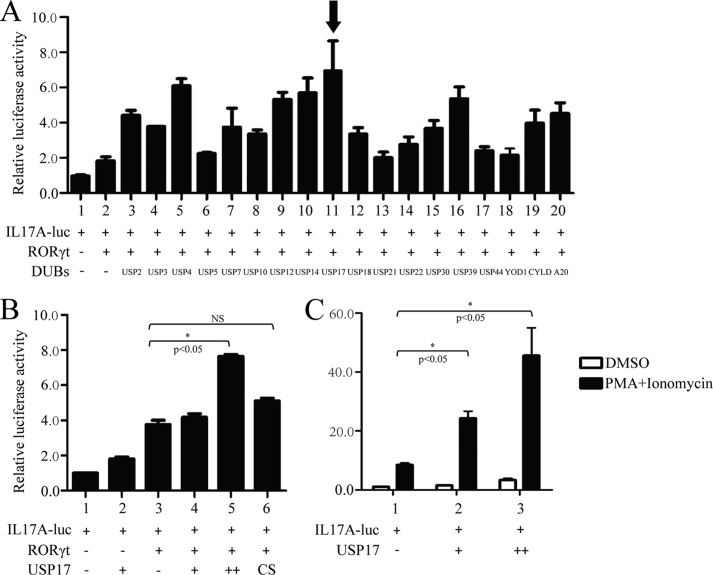
To investigate whether certain ubiquitinases can regulate RORγt-mediated transcriptional activity, we constructed 0.6-kb Il17a promoter reporter plasmids to which RORγt could bind directly (22). Subsequently, we screened the effects of DUBs on RORγt-mediated transcriptional activities via the cotransfection of 18 DUBs with RORγt and luciferase constructs derived from the Il17a promoter into 293T cells. USP17 significantly up-regulated RORγt-mediated luciferase activity among the 18 DUBs (Fig. 1A). Moreover, USP17 increased RORγt-mediated Il17a promoter activity, whereas the enzyme-inactive mutant USP17C89S could not (Fig. 1B). Simultaneously, we constructed stable Jurkat cell lines that expressed RORγt (supplemental Fig. S1). Similar luciferase experiments were performed in FLAG-RORγt-Jurkat cells. A significant dose-dependent effect of USP17 was observed after T cell activation (Fig. 1C). These results suggest that USP17 operates directly on RORγt to enhance RORγt-mediated Il17a promoter activation and that the enzymatic activity of USP17 is essential for positive regulation.
FIGURE 1.
USP17 up-regulates RORγt-mediated Il17a promoter transcriptional activity. A, the effects of DUB family members with RORγt on Il17a promoter activity. The Il17a luciferase reporter and a control β-gal luciferase reporter were cotransfected into 293T cells with the indicated 18 plasmids. Forty-eight hours later, cells were harvested, and luciferase activity was detected. B, FLAG-tagged RORγt and increasing amounts of USP17 (1 and 2 μg) or its mutant, USP17C89S, were cotransfected into 293T cells with the Il17a luciferase reporter. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were lysed, and luciferase activity was measured. NS, not significant. C, Myc-USP17 (3 and 6 μg) and the Il17a luciferase reporter were transfected into FLAG-RORγt-Jurkat cells by electroporation. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were stimulated by 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and ionomycin for 12 h and then lysed for the luciferase assay. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide. Data are representative of more than three independent experiments, and error bars show mean ± S.D.
USP17 Interacts with RORγt
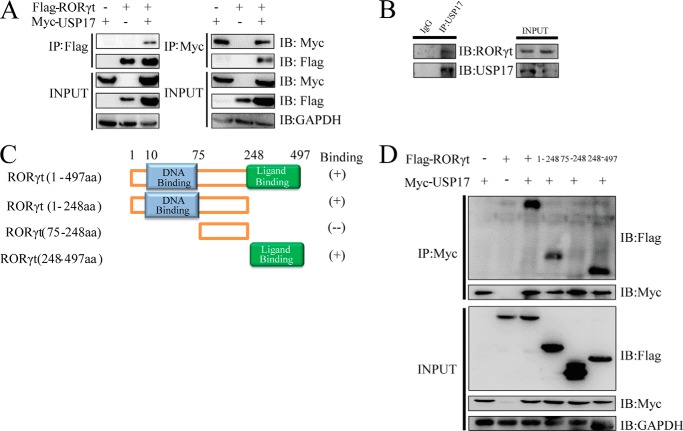
We hypothesized that USP17 may associate with RORγt, which contributes to the increased activation of Il17a promoter activity. To validate our hypothesis, Myc-tagged USP17 and FLAG-tagged RORγt were cotransfected into 293T cells for a coimmunoprecipitation assay. The results revealed that USP17 could interact with RORγt in a reciprocal fashion (Fig. 2A). Moreover, we confirmed the endogenous protein interaction between USP17 and RORγt in human primary Th17 cells (Fig. 2B).
FIGURE 2.
USP17 interacts with RORγt. A, reciprocal immunoprecipitation (IP) of FLAG-tagged RORγt and Myc-tagged USP17. A plasmid encoding FLAG-tagged RORγt was cotransfected into 293T cells together with Myc-tagged USP17. Immunoprecipitation was performed with anti-FLAG or anti-Myc antibodies plus protein A/G beads. IB, immunoblot. B, naïve CD4+ T cells were polarized toward the Th17 phenotype. After 7 days, induced Th17 cells were harvested in vitro and immunoprecipitated with anti-USP17 antibody as described. C, schematic of the FLAG-tagged RORγt constructs used for detection of USP17- RORγt association. aa, amino acids. D, USP17 associates with both the N terminus and the C terminus of RORγt. The truncation mutants RORγt (amino acids 1–248), RORγt (amino acids 75–248), and RORγt (amino acids 248–497) as well as wild-type RORγt were cotransfected into 293T cells for coimmunoprecipitation. Data are representative of more than three independent experiments.
RORγt comprises an N-terminal DNA-binding domain, a hinge region, and a C-terminal ligand-binding domain (Fig. 2B). To identify the binding domains utilized by RORγt and USP17, we cotransfected Myc-tagged USP17 and FLAG-tagged, full-length RORγt or a series of truncation mutants (1–248, 75–248, and 248–497), followed by a coimmunoprecipitation assay. The results indicated that both the N-terminal DNA-binding and C-terminal ligand-binding domains of RORγt could interact with USP17 (Fig. 2C). These data suggest that the DNA-binding and ligand-binding domains of RORγt are required for its interaction with USP17.
USP17 Stabilizes and Deubiquitinates RORγt
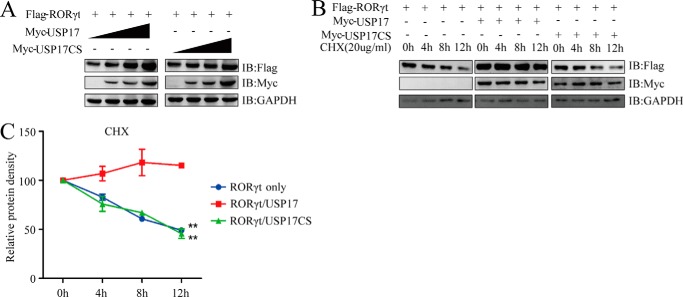
Because USP17 interacts with RORγt, and because the enzymatic activity of USP17 is essential for promoting RORγt-mediated activation of the Il17a gene promoter, we speculated that USP17 might affect RORγt stability. 293T cells were introduced with FLAG-tagged RORγt, Myc-tagged USP17, or a controlled FLAG vector, and the protein levels were determined by Western blotting. We found that USP17 stabilized RORγt in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 3A). To further validate this conclusion, we detected ectopically expressed RORγt protein levels with or without USP17 or USP17C89S in the presence of the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide at the indicated time points by Western blotting. Consistently, the overexpression of USP17, but not its enzyme-inactive mutant, had prominent effects on the stability of the RORγt protein (Fig. 3, B and C).
FIGURE 3.
USP17 stabilizes RORγt. A, FLAG-tagged RORγt (1 μg) was cotransfected with the pIPMyc empty vector or increasing doses (0.5, 1, and 1.5 μg) of Myc-tagged USP17 or its mutant, C89S, into 293T cells. After 48 h, cell lysates were collected and immunoblotted (IB) with the indicated antibodies. B, FLAG-tagged RORγt was cotransfected into 293T cells with the pIPMyc empty vector or Myc-tagged USP17. The transfected cells were treated with cycloheximide (CHX) 0, 4, 8, or 12 h before harvesting. C, quantification of RORγt protein levels by protein density (normalized to 0 h protein density). Data are representative of more than three independent experiments. Error bars show mean ± S.D. **, p < 0.01.
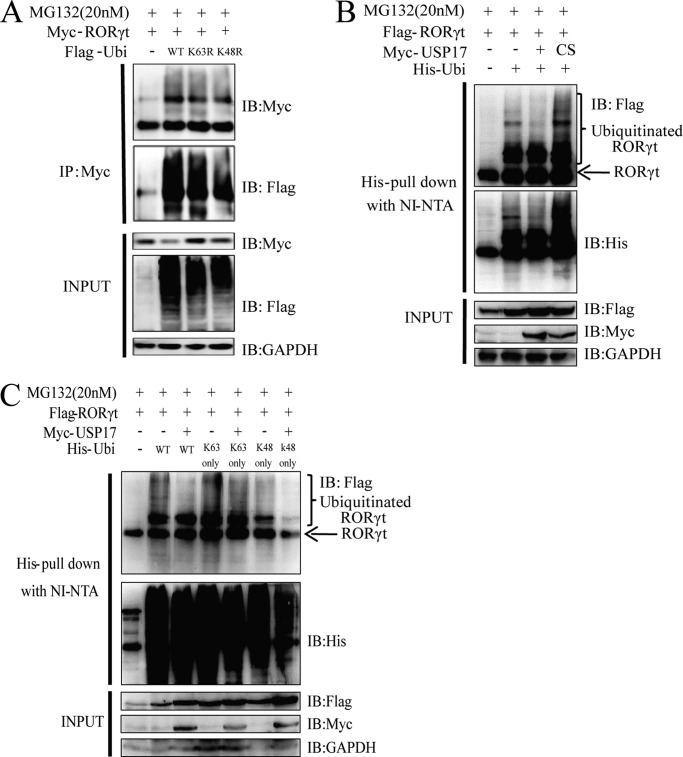
We then sought to identify whether USP17 activity depends on its deubiquitinating enzymatic activity. We first confirmed that RORγt could be ubiquitinated in 293T cells, which were cotransfected with Myc-RORγt and FLAG-ubiquitin, followed by coimmunoprecipitation with an anti-Myc antibody (Fig. 4A). To verify our hypothesis, we cotransfected FLAG-tagged RORγt with His-ubiquitin and USP17 or USP17C89S into 293T cells, and His-tagged proteins were then recovered on Ni-NTA beads under denaturing conditions. As expected, wild-type USP17, but not the USP17CS mutant, reduced the polyubiquitination of RORγt (Fig. 4B).
FIGURE 4.
USP17 deubiquitinates Lys-48-linked RORγt. A, 293T cells were transfected with Myc-tagged USP17 and FLAG-tagged ubiquitin (Ubi). Forty-eight hours later, the cell lysates were harvested, and immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed with anti-Myc antibodies plus protein A/G beads. IB, immunoblot. B, 293T cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged RORγt, Myc-tagged USP17, Myc-tagged USP17C89S (CS), and His-tagged ubiquitin. The ubiquitin pulldown assay for FLAG-tagged RORγt was performed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” C, the His-tagged ubiquitin mutants Lys-48only (K48only) and Lys-63only (K63only) were cotransfected with FLAG-tagged RORγt and Myc-tagged USP17 to detect the deubiquitination site for USP17 against RORγt. The ubiquitin pulldown assay was performed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Data are representative of more than three independent experiments.
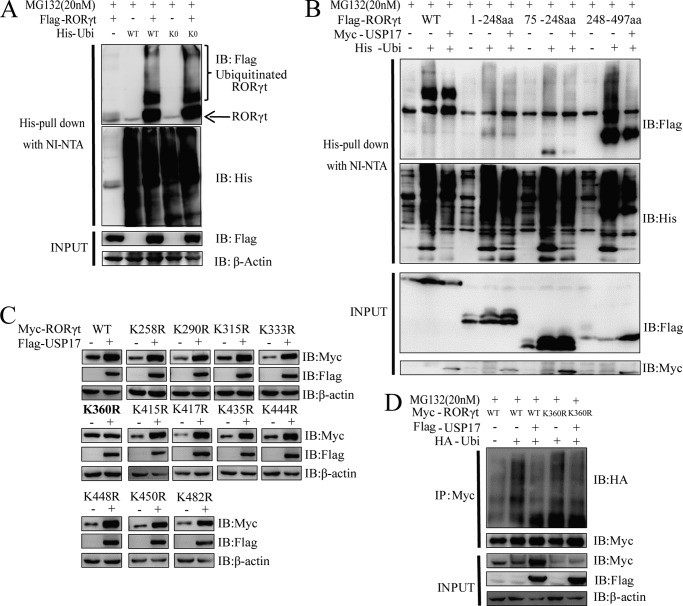
Because of the presence of seven lysine residues (Lys-6, Lys-11, Lys-27, Lys-29, Lys-33, Lys-48, and Lys-63) in ubiquitin, ubiquitin molecules can form different types of polyubiquitin chains with distinct functions. Ubiquitination via Lys-48 linkage or Lys-63 linkage is currently best characterized. Lys-48-linked polyubiquitin chains have been shown to result in the proteasomal degradation of modified proteins, whereas Lys-63-linked chains represented several non-proteolytic signals in several intracellular pathways (13). To identify which lysine residue was required for RORγt deubiquitination by USP17, we performed denaturing Ni-NTA purification by coexpressing RORγt with ubiquitin mutants (Lys-48only and Lys-63only). RORγt was more heavily deubiquitinated in the presence of USP17 with the Lys-48only mutant (Fig. 4C). Taken together, these results establish the mechanism by which USP17 promotes increased RORγt protein levels, which is that USP17 stabilizes RORγt through Lys-48-linked deubiquitination, which prevents RORγt degradation.
USP17 Deubiquitinates RORγt Mainly at Lysine 360 of RORγt
To examine the specific site of deubiquitination of RORγt by USP17, we first confirmed that RORγt had multiubiquitinating sites by cotransfection with FLAG-RORγt and the ubiquitin mutant Lys-0 (all lysine residues were mutated to arginine) into 293T cells (Fig. 5A). We performed further experiments to show that USP17 could significantly deubiquitinate the ligand-binding domain (amino acids 248–497) of RORγt with multi-, poly-, and/or monoubiquitinating sites (Fig. 5B). Then we screened the lysine mutants of the ligand-binding domain and identified lysine 360 as a potential deubiquitinating site by USP17 (Fig. 5, C and D). A point mutation of RORγt at lysine 360 into arginine (K360R mutant) could abolish USP17-mediated stabilization and accumulation of RORγt, whereas the other simultaneous mutations within this ligand-binding domain could not (Fig. 5C). Furthermore, the RORγt-K360R mutant partly abrogated the deubiquitination effect of USP17 on ubiquitinated RORγt (Fig. 5D). Taken together, these results suggest that lysine 360 is one of the major sites for RORγt stabilization, which could be deubiquitinated by USP17.
FIGURE 5.
USP17 deubiquitinates RORγt mainly at lysine 360 of RORγt. A, His-tagged wild-type ubiquitin (Ubi) and its mutant, Lys-0 (K0), were cotransfected with FLAG-tagged RORγt to detect the ubiquitination of RORγt. The ubiquitin pulldown assay was performed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” IB, immunoblot. B, FLAG-tagged wild-type RORγt, its truncation mutants, Myc-tagged USP17, and His-tagged ubiquitin. The ubiquitin pulldown assay for FLAG-tagged RORγt was performed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” aa, amino acids. C, all point mutants of RORγt were cotransfected with FLAG-tagged USP17 into 293T cells. After 48 h, cells were lysed and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. D, 293T cells were transfected with Myc-tagged wild-type RORγt, the K360R mutant, FLAG-tagged USP17, and HA-tagged ubiquitin. 48 h later, cell lysates were harvested, and immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed with anti-Myc antibodies. Data are representative of more than three independent experiments.
Knockdown of USP17 Decreases RORγt Protein Levels and the Expression of Th17-related Genes in Th17 Cells
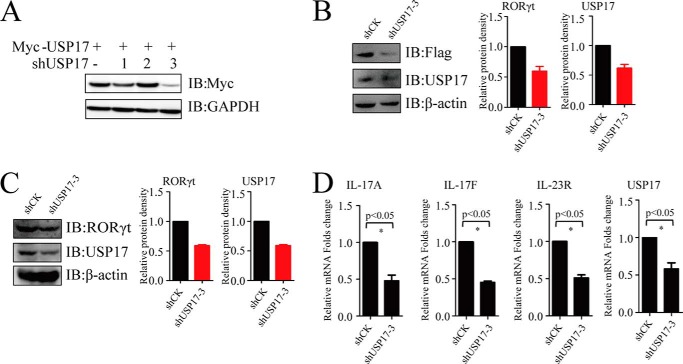
To further investigate the mechanism of USP17 by which USP17 regulates Th17 cells, we constructed three specific shRNAs against USP17 to reduce the endogenous expression of USP17 in Th17 cells. Although all three shRNAs targeted USP17, shUSP17-3 had the best knockdown efficacy (Fig. 6A). We found that the silencing of USP17 in FLAG-RORγt-Jurkat cells resulted in a decrease in RORγt protein stability (Fig. 6B). We detected the down-regulation of both endogenous RORγt and USP17 at the protein level by immunoblotting in shUSP17 knockdown human primary Th17 cells and assessed relative protein levels by quantification (Fig. 6C). Furthermore, we observed the reduction in the expression of Th17-related genes such as IL-17A, IL-17F and IL-23R, which are pivotal for Th17 cell function (Fig. 6D). These findings support the notion that USP17 is essential for the stabilization of RORγt to promote the function of primary Th17 cells.
FIGURE 6.
Knockdown of USP17 decreases RORγt protein and Th17-related gene expression in Th17 cells. A, Myc-tagged USP17 and shUSP17-1, ShUSP17-2, and ShUSP17-3 were cotransfected into 293T cells. Protein levels were detected by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-Myc antibodies. B and C, naïve CD4+T cells were polarized under Th17 conditions. After polarization, Th17 cells and FLAG-RORγt-Jurkat cells were transduced with a lentivirus containing shCK (control) or shUSP17-3. Western blotting was performed after screening for the cells with G418 or puromycin. Quantification of RORγt or USP17 protein levels was done with ImageJ software (normalized to GAPDH intensity). D, RT-PCR was performed after selecting for screening for the cells with G418 or puromycin. Data are representative of more than three independent experiments. Error bars show mean ± S.D.
The USP17 Transcription Level Is Increased Significantly in CD4+T Cells of Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
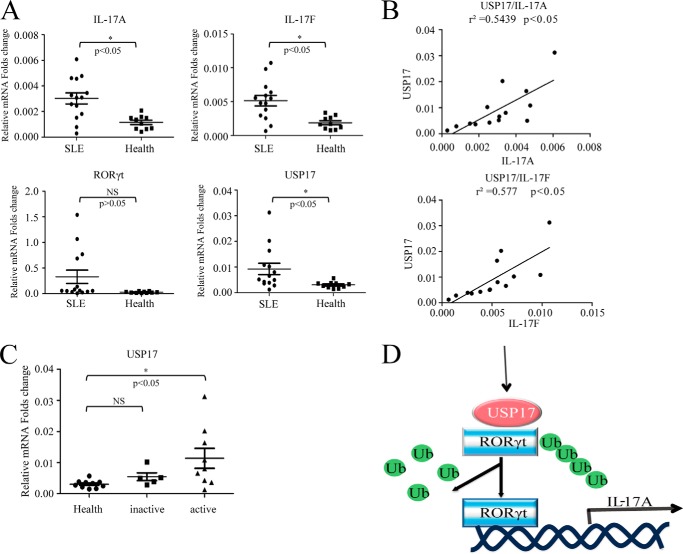
It has been well established that Th17 may have an essential role in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis (23–25). To test the relevance of USP17 and Th17 cells in SLE, we checked the expression of USP17, RORγt, and Th17-type cytokines in CD4+ T cells isolated from the peripheral blood of SLE patients. Healthy donor CD4+ T cells were used as a control. Notably, the up-regulation of USP17, IL-17A, and IL-17F mRNA levels was observed in SLE patients compared with healthy controls (Fig. 7A). Moreover, significant positive correlations between USP17 and IL-17A (r2 = 0.5439, p < 0.05) or IL-17F (r2 = 0.577, p < 0.05) were observed in these SLE patients (Fig. 7B). Additionally, USP17 was increased significantly in active SLE patients (Fig. 7C). Collectively, these data suggest that USP17 may be involved in the pathogenesis of Th17 cells in SLE patients.
FIGURE 7.
USP17 is increased significantly in CD4+ T cells of active systemic lupus erythematosus. A, CD4+ T cells were isolated from the peripheral blood of SLE patients and healthy controls. IL-17A, IL-17F, RORγt, and USP17 mRNA levels were detected via quantitative PCR analysis. B, correlation between USP17 and IL-17A or IL-17F. C, comparison of USP17 between the inactive SLE group, the active SLE group, and healthy donors. NS, not significant. D, proposed working model in which USP17 stabilizes RORγt by deubiquitination. Ub, ubiquitin. Data are representative of more than three independent experiments. Error bars show mean ± S.D.
DISCUSSION
Since the discovery of Th17 cells, numerous transcription factors that are involved in the generation of Th17 cells have been described. Among these transcription factors, RORγt plays a central role by interacting with other factors to orchestrate the functions and development of Th17 cells.
In parallel with the specific role of RORγt in Th17 cells, T-bet, GATA3, and FOXP3 also specify Th1, Th2, and regulatory T cell fates, respectively (26). Several groups have suggested the important role of ubiquitination in the function of CD4+ T cell subsets. The ubiquitin ligase Stub1, for example, negatively modulates regulatory T cell suppressive activity by promoting the degradation of Foxp3 (27), whereas the stabilization of Foxp3 by the deubiquitinase USP7 increases the suppressive capacity of regulatory T cells (28). The E3 ligase Mdm2 (29) and the deubiquitinase USP21 (30) have also been identified as regulators that mediate Th2 cell functions by regulating the stability of GATA3. However, little is known about the regulation of Th17 cells via ubiquitin-mediated modifications of RORγt, such as E3 ligases or deubiquitinases.
In this work, we reveal a novel link between the deubiquitinase USP17 and RORγt that promotes the functions of Th17 cells. We found that USP17 can interact with RORγt to promote its stability at Lys-360 via Lys-48-linked deubiquitination. In addition, USP17 increases RORγt-dependent Il17a promoter transcriptional activity. In the absence of USP17 in Th17 cells and FLAG-RORγt-Jurkat cells, endogenous RORγt protein levels are reduced markedly, along with the down-regulation of Th17-related genes. More recently, RORγt has also been identified as a key transcription factor for a subset of innate lymphoid cell differentiation (31). It remains to be determined whether USP17 also plays a role in innate lymphoid cell differentiation and function. On the other hand, substrates may have multiple DUBs for ubiquitination modification. For instance, it has been reported that more than one DUB could stabilize and deubiquitinate tumor suppressor p53, including USP7 (32) and USP10 (33). It should be interesting to further investigate the other potential DUBs and their roles in stabilizing RORγt in future studies.
In addition, we also observed increased USP17 levels in patients with active SLE, suggesting the potential role of USP17 in the pathogenesis of SLE. SLE is a chronic autoimmune disease with no currently known cure. Its pathogenic mechanism remains unclear and it has complex clinical symptoms. Our findings may provide a new direction for the pathogenesis of SLE.
Therefore, we propose the following working model for USP17 and RORγt: USP17 is induced under certain inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6 (18), leading to the stable expression of RORγt. Stable expression of RORγt then promotes the function of Th17 cells by increasing RORγt-dependent transcriptional activities (Fig. 7D). The signaling pathway for the induction of USP17 and RORγt needs to be investigated further in vivo. According to our data from SLE patient CD4+ T cells, the presence of USP17 may be used as a biomarker for SLE to assess patient disease activity. Moreover, our data suggest that the enzymatic activity of USP17 could be an attractive drug target for developing future therapeutic intervention strategies.
Supplementary Material
This work was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) Grants 2014CB541803, 2014CB541903, NSFC 81330072, 31370863, 31170825, 31200646, 31200647, 81271835, 81302532, 81270714, 31300711, and 31350110505 and by National Science and Technology Major Project Grants 2012ZX10002007-003, 2013ZX10003009–002, SMCST 11ZR1404900, and 14JC1406100. This work was also supported by the Knowledge Innovation Program of the Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, by Chinese Academy of Sciences Grant 2012KIP204, and by Chinese Academy of Sciences Fellowship for Young International Scientists 2013Y1SB0005.

This article contains supplemental Fig. S1.
- DUB
- deubiquitinating enzyme
- USP
- ubiquitin-specific protease
- SLE
- systemic lupus erythematosus
- SLEDAI
- systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index
- Ni-NTA
- nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid
- luc
- luciferase.
REFERENCES
- 1. Park H., Li Z., Yang X. O., Chang S. H., Nurieva R., Wang Y. H., Wang Y., Hood L., Zhu Z., Tian Q., Dong C. (2005) A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat. Immunol. 6, 1133–1141 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Bettelli E., Oukka M., Kuchroo V. K. (2007) T(H)-17 cells in the circle of immunity and autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 8, 345–350 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Bettelli E., Korn T., Oukka M., Kuchroo V. K. (2008) Induction and effector functions of T(H)17 cells. Nature 453, 1051–1057 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Zhou L., Ivanov I. I., Spolski R., Min R., Shenderov K., Egawa T., Levy D. E., Leonard W. J., Littman D. R. (2007) IL-6 programs T(H)-17 cell differentiation by promoting sequential engagement of the IL-21 and IL-23 pathways. Nat. Immunol. 8, 967–974 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Volpe E., Servant N., Zollinger R., Bogiatzi S. I., Hupé P., Barillot E., Soumelis V. (2008) A critical function for transforming growth factor-β, interleukin 23 and proinflammatory cytokines in driving and modulating human T(H)-17 responses. Nat. Immunol. 9, 650–657 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Lee Y., Awasthi A., Yosef N., Quintana F. J., Xiao S., Peters A., Wu C., Kleinewietfeld M., Kunder S., Hafler D. A., Sobel R. A., Regev A., Kuchroo V. K. (2012) Induction and molecular signature of pathogenic TH17 cells. Nat. Immunol. 13, 991–999 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Ivanov I. I., McKenzie B. S., Zhou L., Tadokoro C. E., Lepelley A., Lafaille J. J., Cua D. J., Littman D. R. (2006) The orphan nuclear receptor RORγt directs the differentiation program of proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell 126, 1121–1133 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Manel N., Unutmaz D., Littman D. R. (2008) The differentiation of human T(H)-17 cells requires transforming growth factor-β and induction of the nuclear receptor RORγt. Nat. Immunol. 9, 641–649 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Ratajewski M., Walczak-Drzewiecka A., Salkowska A., Dastych J. (2012) Upstream stimulating factors regulate the expression of RORγT in human lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 189, 3034–3042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Yu Y., Liu Y., Shi F. D., Zou H., Matarese G., La Cava A. (2013) Cutting edge: Leptin-induced RORγt expression in CD4+ T cells promotes Th17 responses in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 190, 3054–3058 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Saito Y., Kagami S. I., Sanayama Y., Ikeda K., Suto A., Kashiwakuma D., Furuta S., Iwamoto I., Nonaka K., Ohara O., Nakajima H. (2014) AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 5a functions as a negative regulator of RORγt-induced Th17 cell differentiation. Arthritis Rheum. 66, 1185–1194 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Haglund K., Dikic I. (2005) Ubiquitylation and cell signaling. EMBO J. 24, 3353–3359 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Pickart C. M., Fushman D. (2004) Polyubiquitin chains: polymeric protein signals. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 8, 610–616 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Tanaka T., Yamamoto Y., Muromoto R., Ikeda O., Sekine Y., Grusby M. J., Kaisho T., Matsuda T. (2011) PDLIM2 inhibits T helper 17 cell development and granulomatous inflammation through degradation of STAT3. Sci. Signal. 4, ra85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Zhong B., Liu X., Wang X., Chang S. H., Liu X., Wang A., Reynolds J. M., Dong C. (2012) Negative regulation of IL-17-mediated signaling and inflammation by the ubiquitin-specific protease USP25. Nat. Immunol. 13, 1110–1117 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Liu X., Li H., Zhong B., Blonska M., Gorjestani S., Yan M., Tian Q., Zhang D. E., Lin X., Dong C. (2013) USP18 inhibits NF-κB and NFAT activation during Th17 differentiation by deubiquitinating the TAK1-TAB1 complex. J. Exp. Med. 210, 1575–1590 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Reyes-Turcu F. E., Ventii K. H., Wilkinson K. D. (2009) Regulation and cellular roles of ubiquitin-specific deubiquitinating enzymes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 78, 363–397 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Burrows J. F., McGrattan M. J., Rascle A., Humbert M., Baek K. H., Johnston J. A. (2004) DUB-3, a cytokine-inducible deubiquitinating enzyme that blocks proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 13993–14000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Chen R., Zhang L., Zhong B., Tan B., Liu Y., Shu H. B. (2010) The ubiquitin-specific protease 17 is involved in virus-triggered type I IFN signaling. Cell Res. 20, 802–811 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Burrows J. F., Kelvin A. A., McFarlane C., Burden R. E., McGrattan M. J., De la Vega M., Govender U., Quinn D. J., Dib K., Gadina M., Scott C. J., Johnston J. A. (2009) USP17 regulates Ras activation and cell proliferation by blocking RCE1 activity. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 9587–9595 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. de la Vega M., Kelvin A. A., Dunican D. J., McFarlane C., Burrows J. F., Jaworski J., Stevenson N. J., Dib K., Rappoport J. Z., Scott C. J., Long A., Johnston J. A. (2011) The deubiquitinating enzyme USP17 is essential for GTPase subcellular localization and cell motility. Nat. Commun. 2, 259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Ichiyama K., Yoshida H., Wakabayashi Y., Chinen T., Saeki K., Nakaya M., Takaesu G., Hori S., Yoshimura A., Kobayashi T. (2008) Foxp3 inhibits RORγt-mediated IL-17A mRNA transcription through direct interaction with RORγt. J. Biol.Chem. 283, 17003–17008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Pernis A. B. (2009) Th17 cells in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Intern. Med. 265, 644–652 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Shin M. S., Lee N., Kang I. (2011) Effector T-cell subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus: update focusing on Th17 cells. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 23, 444–448 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Chen D. Y., Chen Y. M., Wen M. C., Hsieh T. Y., Hung W. T., Lan J. L. (2012) The potential role of Th17 cells and Th17-related cytokines in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis. Lupus 21, 1385–1396 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Zhou L., Chong M. M., Littman D. R. (2009) Plasticity of CD4+ T cell lineage differentiation. Immunity 30, 646–655 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Chen Z., Barbi J., Bu S., Yang H. Y., Li Z., Gao Y., Jinasena D., Fu J., Lin F., Chen C., Zhang J., Yu N., Li X., Shan Z., Nie J., Gao Z., Tian H., Li Y., Yao Z., Zheng Y., Park B. V., Pan Z., Zhang J., Dang E., Li Z., Wang H., Luo W., Li L., Semenza G. L., Zheng S. G., Loser K., Tsun A., Greene M. I., Pardoll D. M., Pan F., Li B. (2013) The ubiquitin ligase Stub1 negatively modulates regulatory T cell suppressive activity by promoting degradation of the transcription factor Foxp3. Immunity 39, 272–285 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. van Loosdregt J., Fleskens V., Fu J., Brenkman A. B., Bekker C. P., Pals C. E., Meerding J., Berkers C. R., Barbi J., Gröne A., Sijts A. J., Maurice M. M., Kalkhoven E., Prakken B. J., Ovaa H., Pan F., Zaiss D. M., Coffer P. J. (2013) Stabilization of the transcription factor Foxp3 by the deubiquitinase USP7 increases Treg-cell-suppressive capacity. Immunity 39, 259–271 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Yamashita M., Shinnakasu R., Asou H., Kimura M., Hasegawa A., Hashimoto K., Hatano N., Ogata M., Nakayama T. (2005) Ras-ERK MAPK cascade regulates GATA3 stability and Th2 differentiation through ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 29409–29419 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Zhang J., Chen C., Hou X., Gao Y., Lin F., Yang J., Gao Z., Pan L., Tao L., Wen C., Yao Z., Tsun A., Shi G., Li B. (2013) Identification of the E3 deubiquitinase ubiquitin-specific peptidase 21 (USP21) as a positive regulator of the transcription factor GATA3. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 9373–9382 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Spits H., Cupedo T. (2012) Innate lymphoid cells: emerging insights in development, lineage relationships, and function. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 30, 647–675 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Li M., Chen D., Shiloh A., Luo J., Nikolaev A. Y., Qin J., Gu W. (2002) Deubiquitination of p53 by HAUSP is an important pathway for p53 stabilization. Nature 416, 648–653 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Yuan J., Luo K., Zhang L., Cheville J. C., Lou Z. (2010) USP10 regulates p53 localization and stability by deubiquitinating p53. Cell 140, 384–396 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.