Fig. 3.
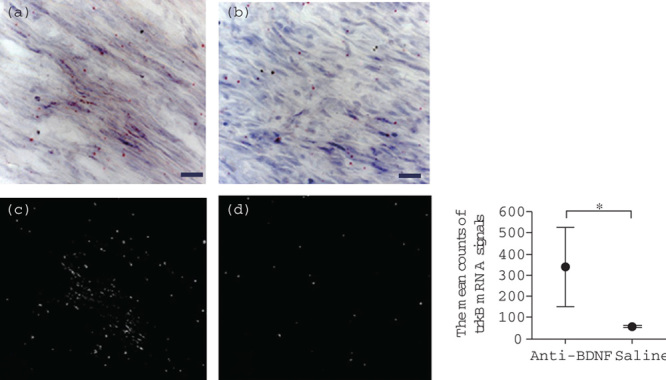
Effects of anti-BDNF administration on trkB mRNA expression in the trigeminal ganglion after IAN transection. Photographs showing the expression of trkB mRNA at postoperative week 2 in the anti-BDNF-treated (a) and saline (vehicle) control (b) groups evaluated by ISH histochemistry are shown. A few isolated signals for trkB mRNA are observed in the regenerating nerve fibers in the anti-BDNF-treated group. The red dots indicate trkB mRNA signals (scale bars=20 μm). (c and d) taken in the dark field indicate the signals of trkB mRNA in the anti-BDNF and the saline groups, respectively. Quantitative analysis obtained from the dark field images shows a comparison of the mean counts of the trkB mRNA signals between these groups (the right panel). These mean counts at the injury site in the saline (vehicle) control and the anti-BDNF-treated groups show 57.0±5.6 and 340.7±184.9, respectively. A significant difference exists between the two groups (Student’s t-test, *P<0.05). BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; IAN, inferior alveolar nerve; ISH, in-situ hybridization; trkB, tropomyosin receptor kinase B.
