Abstract
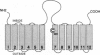
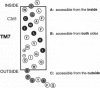
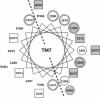
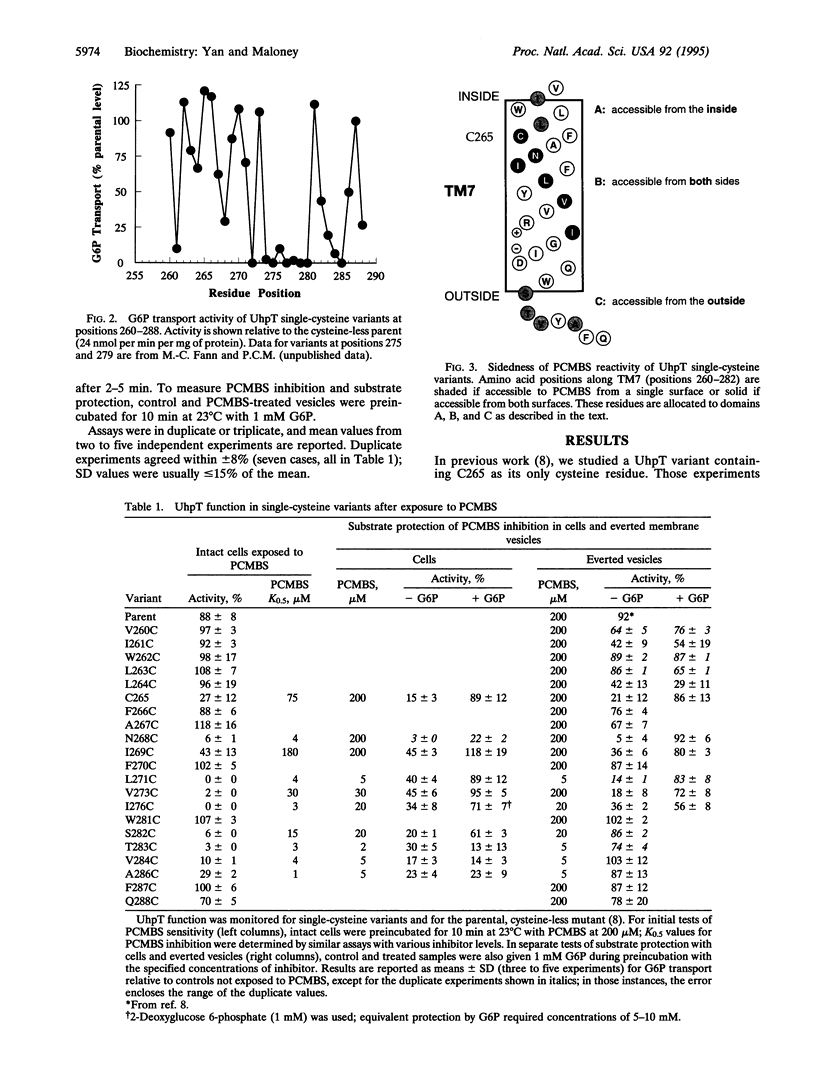
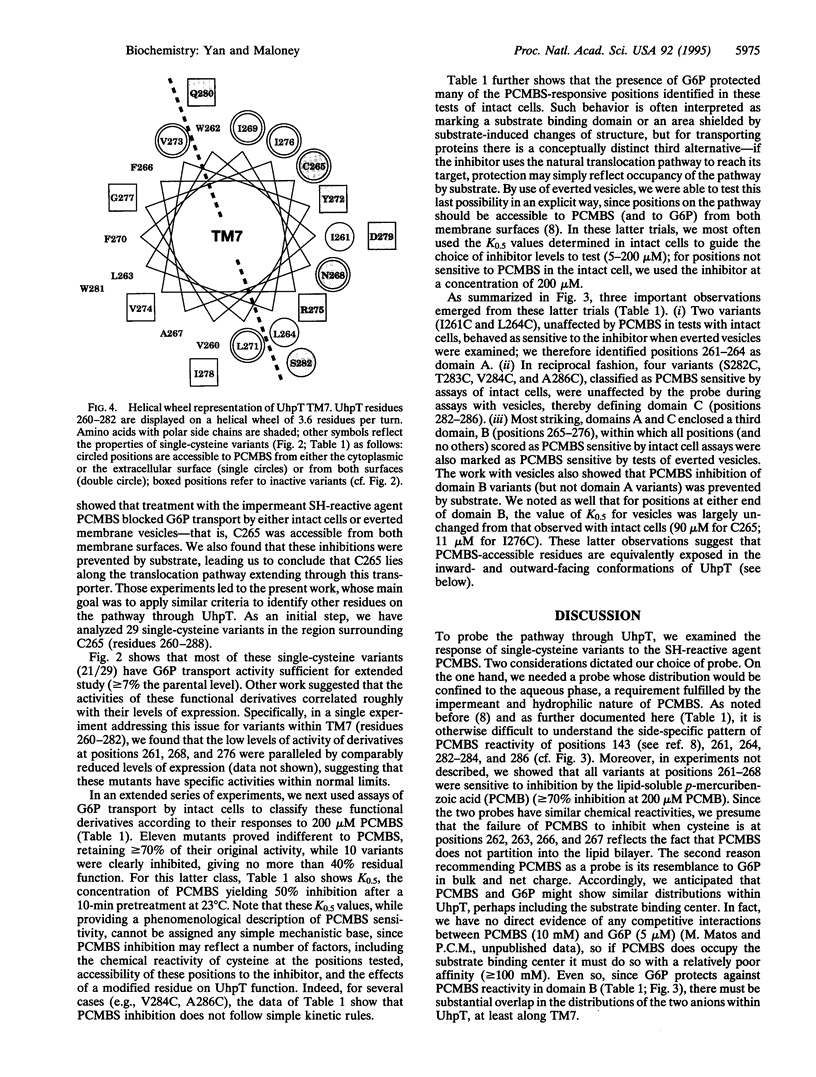
The structure of solute transporters is understood largely from analysis of their amino acid sequences, and more direct information is greatly needed. Here we report work that applies cysteine scanning mutagenesis to describe structure-function relations in UhpT, a bacterial membrane transporter. By using an impermeant SH-reactive agent to probe single-cysteine variants, we show that UhpT transmembrane segment 7 spans the membrane as an alpha-helix and that the central portion of this helix is exposed to both membrane surfaces, forming part of the translocation pathway through this transporter.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akabas M. H., Kaufmann C., Cook T. A., Archdeacon P. Amino acid residues lining the chloride channel of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 27;269(21):14865–14868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akabas M. H., Stauffer D. A., Xu M., Karlin A. Acetylcholine receptor channel structure probed in cysteine-substitution mutants. Science. 1992 Oct 9;258(5080):307–310. doi: 10.1126/science.1384130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altenbach C., Marti T., Khorana H. G., Hubbell W. L. Transmembrane protein structure: spin labeling of bacteriorhodopsin mutants. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1088–1092. doi: 10.1126/science.2160734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. J., Jung E. K., Jung C. Y. Structural basis of human erythrocyte glucose transporter function in reconstituted vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7101–7104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. L., Boublik M., Kaback H. R. Structure of the lac carrier protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):31–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich M. J., Kadner R. J. Nucleotide sequence of the uhp region of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3556–3563. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3556-3563.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson P. J. The 12-transmembrane helix transporters. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;5(4):708–721. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90144-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Island M. D., Wei B. Y., Kadner R. J. Structure and function of the uhp genes for the sugar phosphate transport system in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):2754–2762. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.2754-2762.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R., Jung K., Jung H., Wu J., Privé G. G., Zen K. What's new with lactose permease. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1993 Dec;25(6):627–636. doi: 10.1007/BF00770250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch B. A., Koshland D. E., Jr Disulfide cross-linking studies of the transmembrane regions of the aspartate sensory receptor of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10402–10406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C. A consensus structure for membrane transport. Res Microbiol. 1990 Mar-Apr;141(3):374–383. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90015-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C. Bacterial transporters. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;6(4):571–582. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marger M. D., Saier M. H., Jr A major superfamily of transmembrane facilitators that catalyse uniport, symport and antiport. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jan;18(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90081-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Osmochemistry of solute translocation. Res Microbiol. 1990 Mar-Apr;141(3):286–289. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Caruso C., Baldwin S. A., Panico M., Blench I., Morris H. R., Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E., Lodish H. F. Sequence and structure of a human glucose transporter. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):941–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3839598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Konings W. N. Secondary solute transport in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Nov 2;1183(1):5–39. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(93)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P. Ion extrusion systems in Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1986;125:328–336. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(86)25028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonna L. A., Ambudkar S. V., Maloney P. C. The mechanism of glucose 6-phosphate transport by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6625–6630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D. N., Sarabia V. E., Reithmeier R. A., Kühlbrandt W. Three-dimensional map of the dimeric membrane domain of the human erythrocyte anion exchanger, Band 3. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 15;13(14):3230–3235. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06624.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu M., Akabas M. H. Amino acids lining the channel of the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor identified by cysteine substitution. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21505–21508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan R. T., Maloney P. C. Identification of a residue in the translocation pathway of a membrane carrier. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):37–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]