Abstract
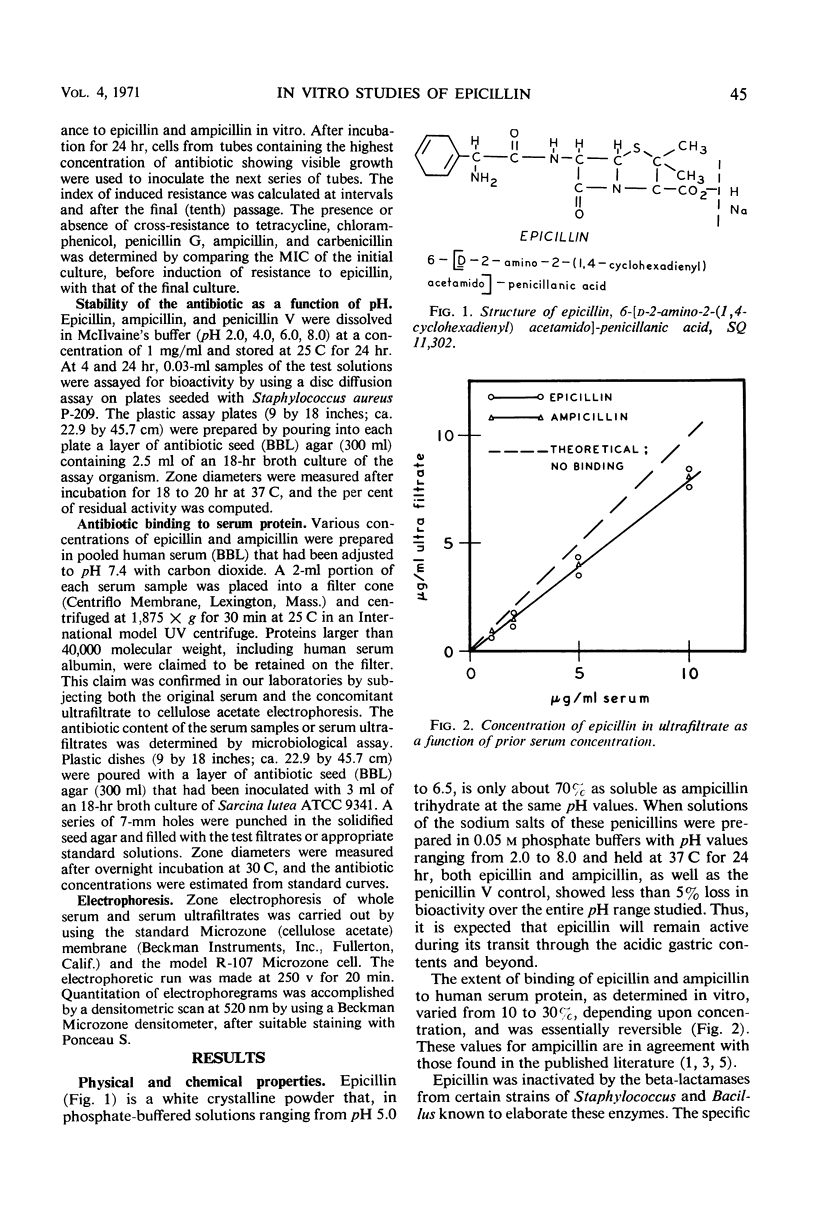
A new semisynthetic penicillin, structurally related to ampicillin, has been assigned the generic name epicillin, 6-[d-2-amino-2-(1, 4-cyclohexadienyl) acetamido]-penicillanic acid. The antimicrobial spectrum and level of activity of epicillin in vitro are similar to those of ampicillin. In studies with recent clinical isolates, these two antibiotics, when compared with carbenicillin, showed consistently higher antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Escherichia coli, and Proteus species. When tested against Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates, on the other hand, epicillin exhibited a level of intrinsic activity superior to that of ampicillin but less than that of carbenicillin. Epicillin is an amphoteric substance that is sensitive to penicillinase, is acid-stable, and is minimally, but reversibly, bound to human serum protein.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACRED P., BROWN D. M., HARDY T. L., MANSFORD K. R. A NEW APPROACH TO STUDYING THE PROTEIN-BINDING PROPERTIES OF PENICILLINS. Nature. 1963 Aug 24;199:758–759. doi: 10.1038/199758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolfini J. E., Applegate H. E., Bach G., Basch H., Bernstein J., Schwartz J., Weisenborn F. L. A new class of semisynthetic penicillins and cephalosporins derived from D-2-(1,4-cyclohexadienyl)glycine. J Med Chem. 1971 Feb;14(2):117–119. doi: 10.1021/jm00284a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M. Clinical pharmacology of the new penicillins. 1. The importance of serum protein binding in determining antimicrobial activity and concentration in serum. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1966 Mar-Apr;7(2):166–179. doi: 10.1002/cpt196672166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
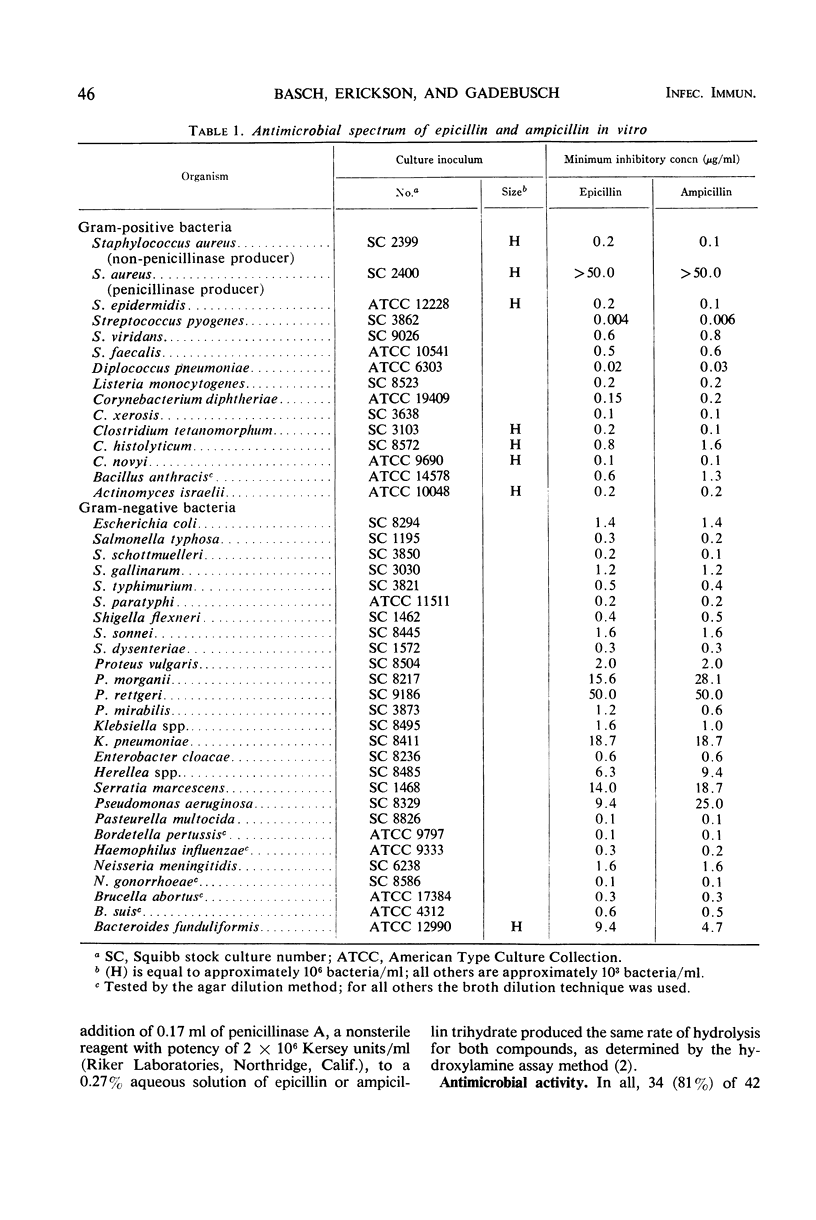
- Rolinson G. N., Sutherland R. The binding of antibiotics to serum proteins. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1965 Dec;25(3):638–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1965.tb01788.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON R. G., SCHERP H. W. The specific hapten of group C (group II alpha) meningococcus. I. Preparation and immunological behavior. J Immunol. 1958 Oct;81(4):331–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



