Abstract
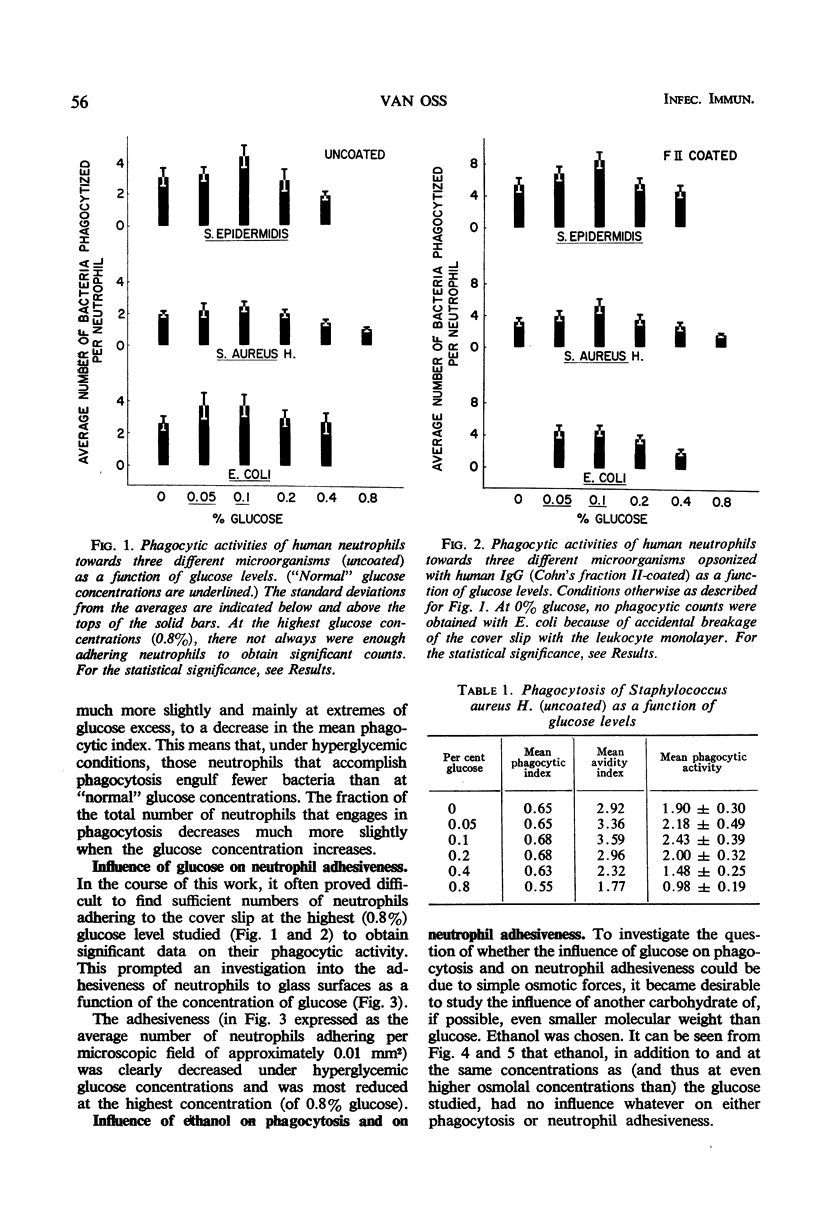
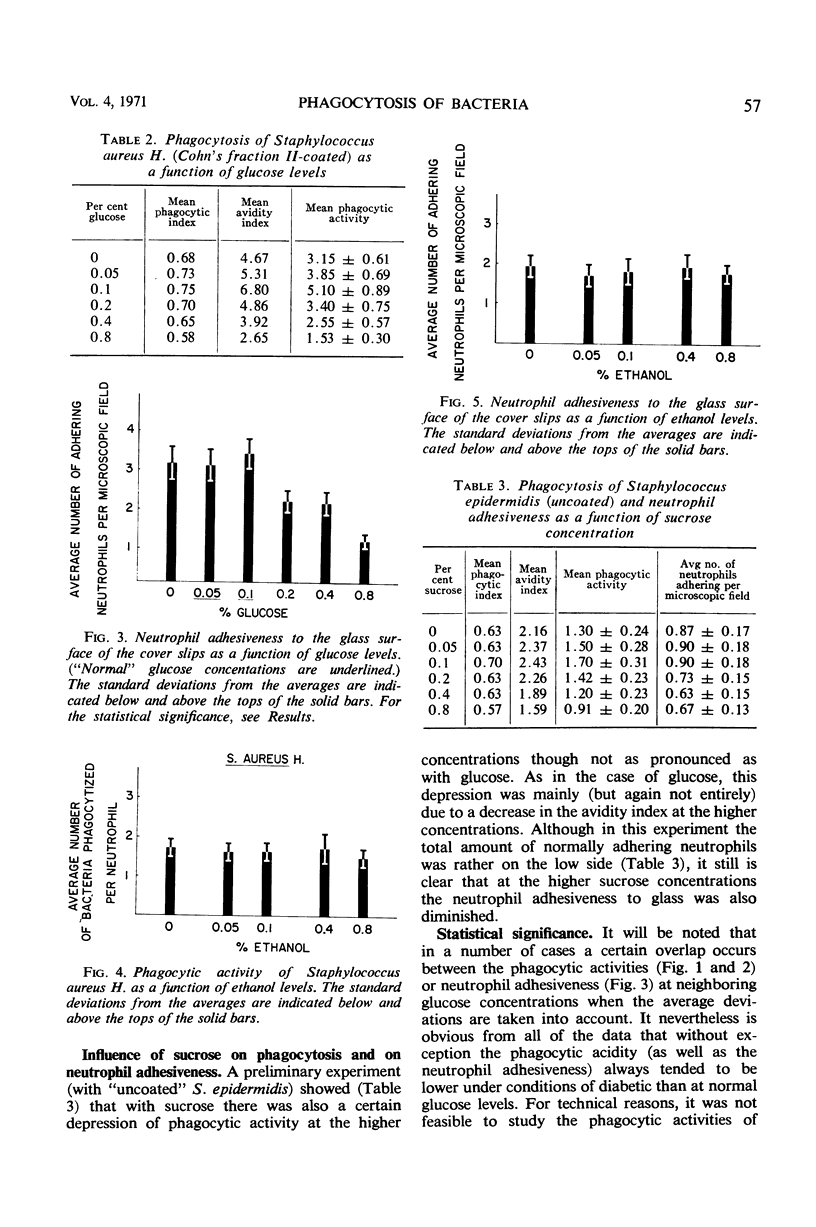
A previously developed in vitro method for studying the phagocytosis of bacteria and particles by human neutrophils was used to investigate the influence of different glucose levels on phagocytosis. It was found that high glucose levels (200, 400, and 800 mg of glucose/100 ml) significantly depressed the phagocytosis of Staphylococcus epidermidis, S. aureus, and Escherichia coli. At very low glucose levels, a somewhat decreased phagocytic activity was noted. The strongest phagocytic activity occurred at glucose concentrations of 50 and 100 mg/100 ml. A second effect noted at the higher (200, 400 and 800 mg/100 ml) glucose concentrations was a decreased adhesiveness of the neutrophils to solid surfaces. The mechanism of the decrease in phagocytosis and in neutrophil adhesiveness at higher glucose levels is unknown, but it is not linked to increased osmotic pressures due to the presence of glucose, as ethanol, at the same and even higher osmolal concentrations, had no effect on the phagocytosis. These results show that not only the phagocytic activity of those neutrophils that do adhere to a solid surface is diminished at higher glucose concentrations but also that fewer neutrophils adhere to solid surfaces at higher glucose levels. These two phenomena combined may provide at least part of the explanation for the well-known decrease in resistance to bacterial infections of diabetics.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baciu I., Derevenco V., Vitebski V., Ilea V., Grosu M. Influenţa insulinei şi a glucozei asupra funcţiei fagocitare şi mobilităii leucocitelor. Stud Cercet Endocrinol. 1967;18(2):121–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drachman R. H., Root R. K., Wood W. B., Jr Studies on the effect of experimental nonketotic diabetes mellitus on antibacterial defense. I. Demonstration of a defect in phagocytosis. J Exp Med. 1966 Aug 1;124(2):227–240. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.2.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERLINGS-PETERSEN B. T., PONDMAN K. W. Erythrophagocytosis: A study of the antigen-antibody-complement reaction. Vox Sang. 1962 Nov-Dec;7:655–674. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1962.tb04594.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JETER W. S., McKEE A. P., MASON R. J. Inhibition of immune phagocytosis of Diplococcus pneumoniae by human neutrophiles with antibody against complement. J Immunol. 1961 Apr;86:386–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita A. [Phagocytic ability of neutrophilic leukocytes and hematologic changes in normal persons on a low calorie diet]. Naika Hokan. 1968 Sep;15(9):311–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. The action of drugs on intracellular tubercle bacilli. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1952 Jul;64(3):429–446. doi: 10.1002/path.1700640302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marble A., White H. J., Fernald A. T. THE NATURE OF THE LOWERED RESISTANCE TO INFECTION IN DIABETES MELLITUS. J Clin Invest. 1938 Jul;17(4):423–430. doi: 10.1172/JCI100969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A., Baum J. Chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear leukocytes from patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1971 Mar 25;284(12):621–627. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197103252841201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsome J. Phagocytosis by human neutrophils. Nature. 1967 Jun 10;214(5093):1092–1094. doi: 10.1038/2141092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rode H. N., Gordon J. Inhibition of the mixed leukocyte culture reaction (MLC) by pre-incubation of the leukocytes with sucrose. J Immunol. 1969 Mar;102(3):786–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohmann H. Uber die Phagozytose der Leukozyten bei Diabetikern. Folia Haematol Int Mag Klin Morphol Blutforsch. 1966;85(3):267–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D., Turner K. J. Number of molecules of antibody required to promote phagocytosis of one bacterium. Nature. 1966 Apr 30;210(5035):496–498. doi: 10.1038/210496a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Oss C. J., Stinson M. W. Immunoglobulins as aspecific opsonins. I. The influence of polyclonal and monoclonal immunoglobulins on the in vitro phagocytosis of latex particles and Staphylococci by human neutrophils. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Nov;8(5):397–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



