Abstract
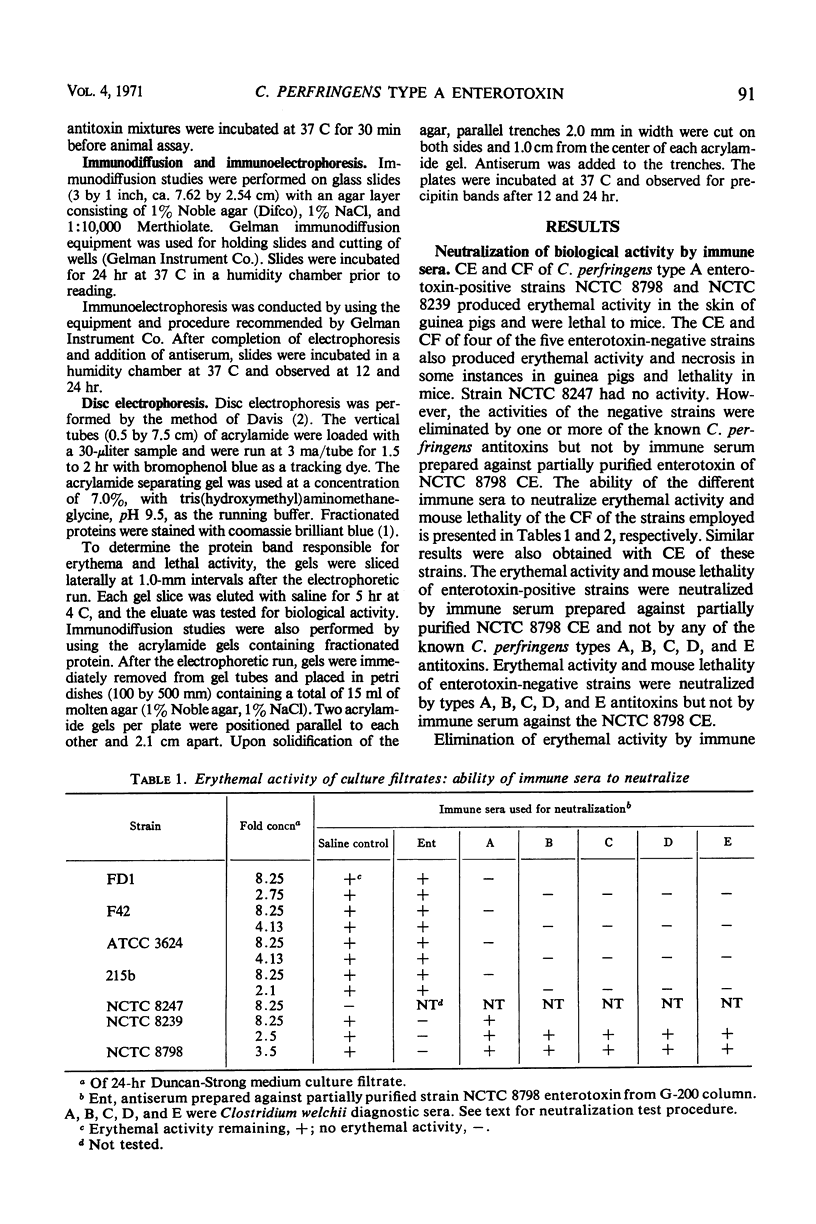
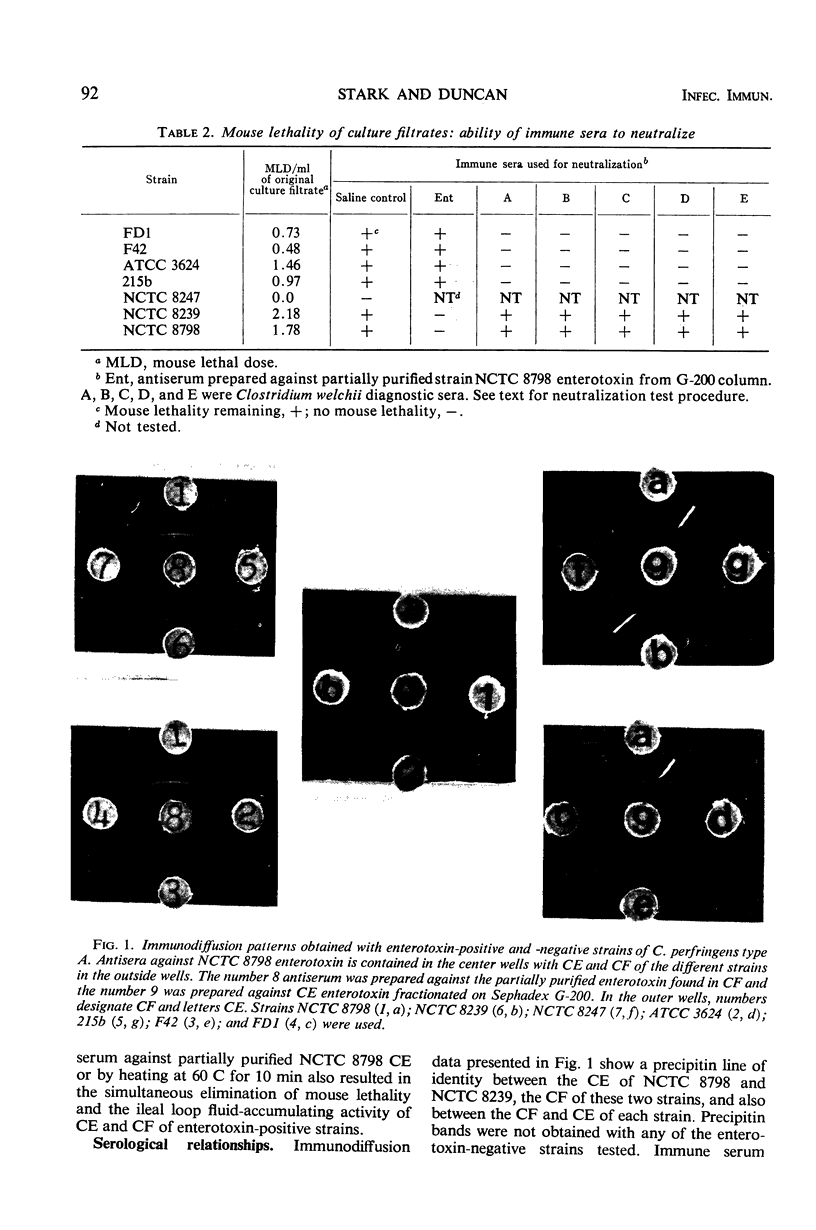
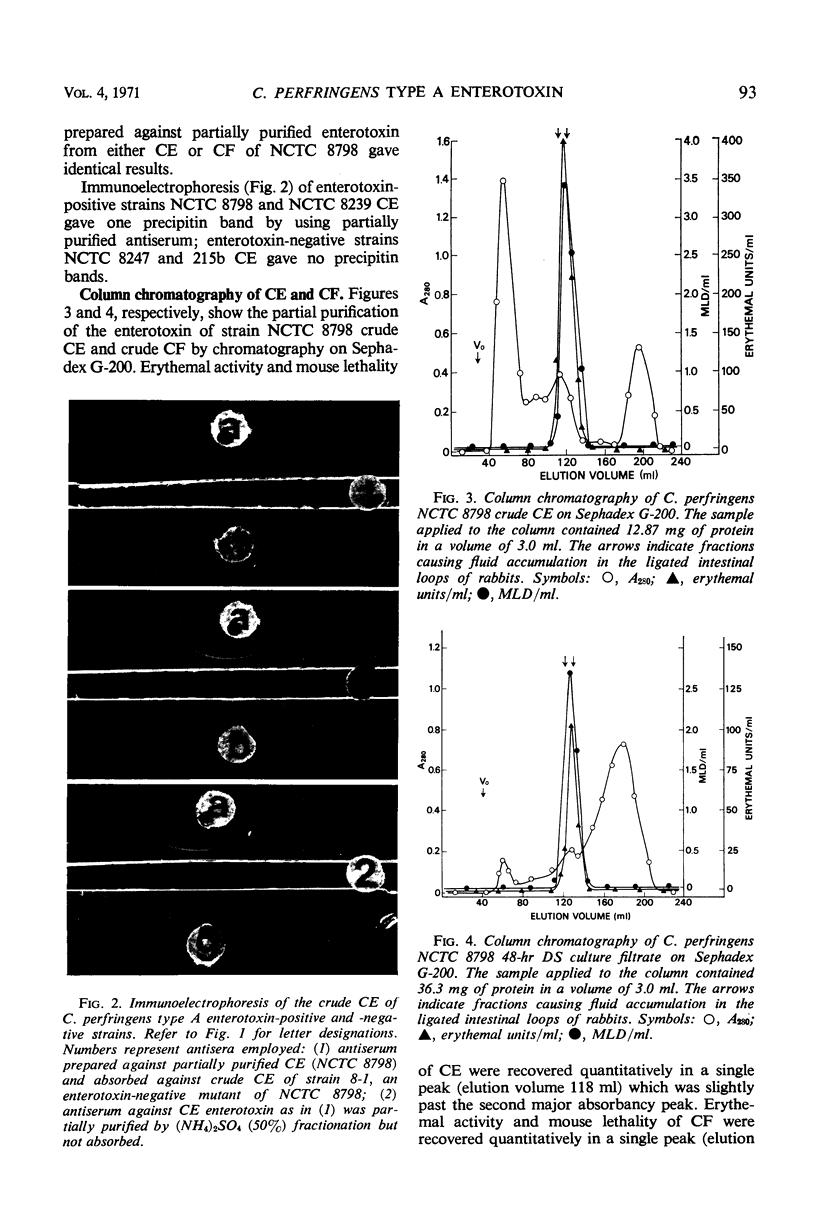
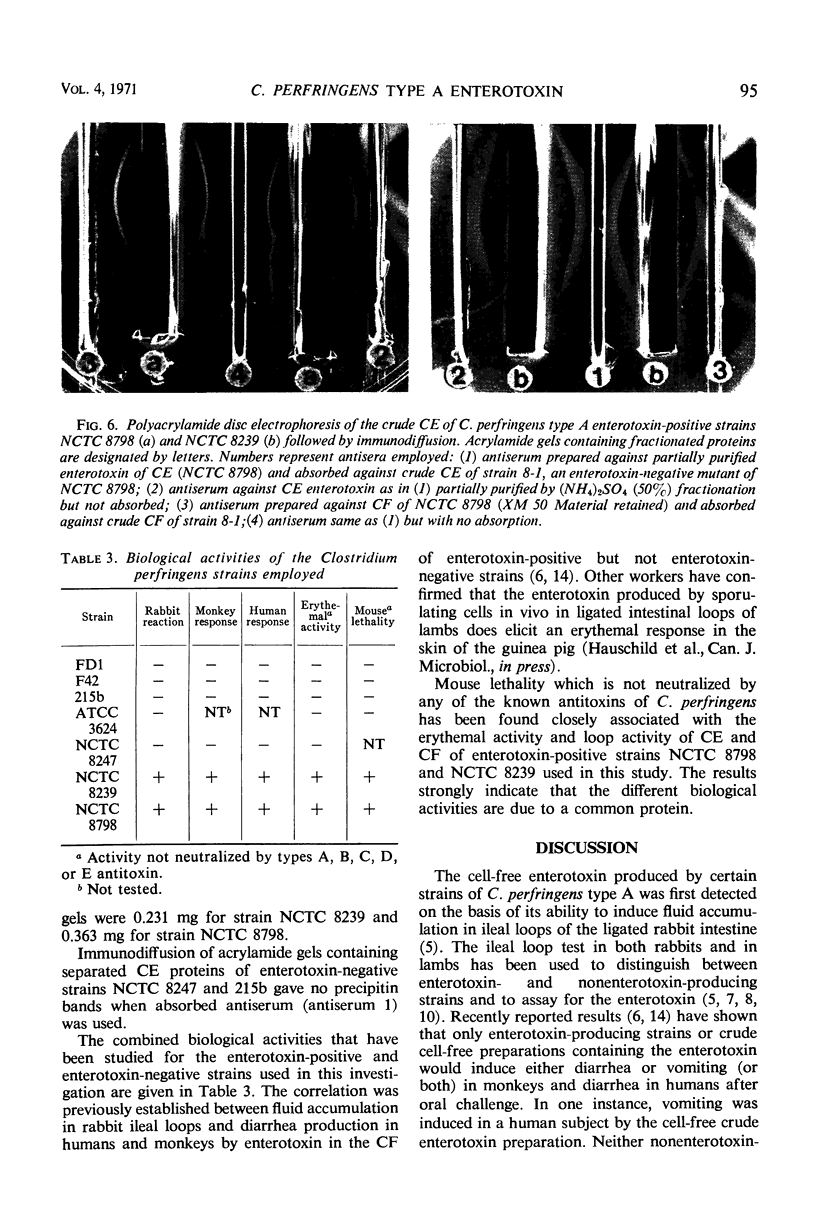
An enterotoxin with the ability to induce fluid accumulation in rabbit ileal loops, erythema in the skin of guinea pigs, and lethality in mice appears in cell extracts (CE) and culture filtrates (CF) of sporulating cells of some Clostridium perfringens type A strains. All activities in CE and CF were eluted simultaneously from a Sephadex G-200 column. Different elution patterns were obtained for these activities present in CE and CF. Rabbit immune serum against CF and the active CE fractions eliminated the three biological activities in CE and CF. These activities present in CF and CE were not eliminated by any of the known antitoxins present in diagnostic serum against C. perfringens types A, B, C, D, and E. Immunodiffusion studies with immune serum against active CE fractions and CF indicated a precipitin line of identity between CF and CE of NCTC 8798 and other enterotoxin-positive strains but not enterotoxin-negative strains. Disc electrophoresis of active G-200 fractions on 7.0% polyacrylamide gels revealed a single area containing erythemal activity and mouse lethality. Immunodiffusion with acrylamide gels, containing crude fractionated enterotoxin, and immune serum against partially purified enterotoxin revealed a single precipitin band in the same area as the biological activities. Immunoelectrophoresis of CE of enterotoxin-positive and enterotoxin-negative strains also showed one precipitin band which occurred only with enterotoxin-positive strains. These findings suggest that one component is responsible for the biological activities attributed to the enterotoxin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chrambach A., Reisfeld R. A., Wyckoff M., Zaccari J. A procedure for rapid and sensitive staining of protein fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. L., Strong D. H. Clostridium perfringens Type A Food Poisoning I. Response of the Rabbit Ileum as an Indication of Enteropathogenicity of Strains of Clostridium perfringens in Monkeys. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):167–170. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.167-170.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. L., Strong D. H. Experimental production of diarrhea in rabbits with Clostridium perfringens. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Jul;15(7):765–770. doi: 10.1139/m69-134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. L., Strong D. H. Ileal loop fluid accumulation and production of diarrhea in rabbits by cell-free products of Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):86–94. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.86-94.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. L., Strong D. H. Improved medium for sporulation of Clostridium perfringens. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Jan;16(1):82–89. doi: 10.1128/am.16.1.82-89.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. L., Sugiyama H., Strong D. H. Rabbit ileal loop response to strains of Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1560–1566. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1560-1566.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBBS B. C., SMITH M. E., OAKLEY C. L., WARRACK G. H., CRUICKSHANK J. C. Clostridium welchii food poisoning. J Hyg (Lond) 1953 Mar;51(1):75–101. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400015515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschild A. H. Erythemal activity of the cellular enteropathogenic factor of Clostridium perfringens type A. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Aug;16(8):651–654. doi: 10.1139/m70-112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschild A. H., Niilo L., Dorward W. J. Clostridium perfringens type A infection of ligated intestinal loops in lambs. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Aug;16(8):1235–1239. doi: 10.1128/am.16.8.1235-1239.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschild A. H., Niilo L., Dorward W. J. Experimental enteritis with food poisoning and classical strains of Clostridium perfringens type A in lambs. J Infect Dis. 1967 Dec;117(5):379–386. doi: 10.1093/infdis/117.5.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niilo L. Mechanism of Action of the Enteropathogenic Factor of Clostridium perfringens Type A. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):100–106. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.100-106.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






