Abstract
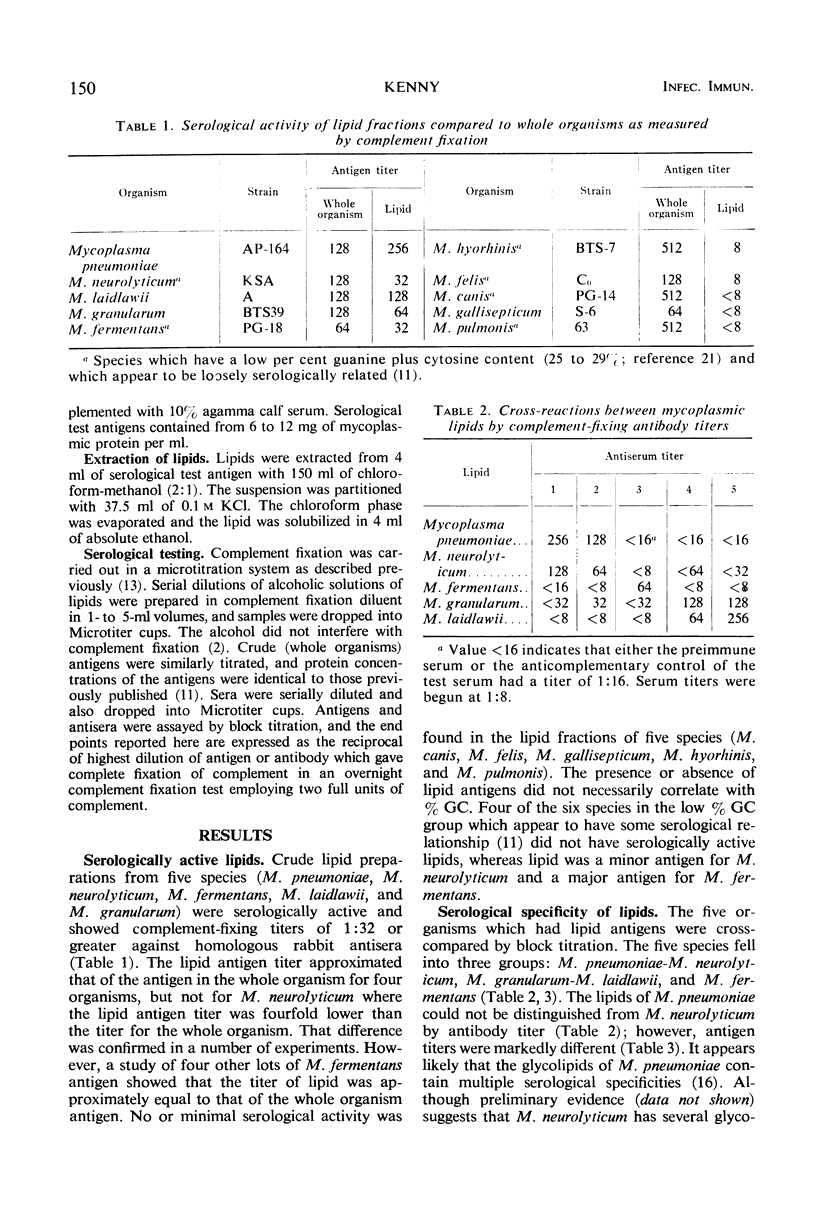
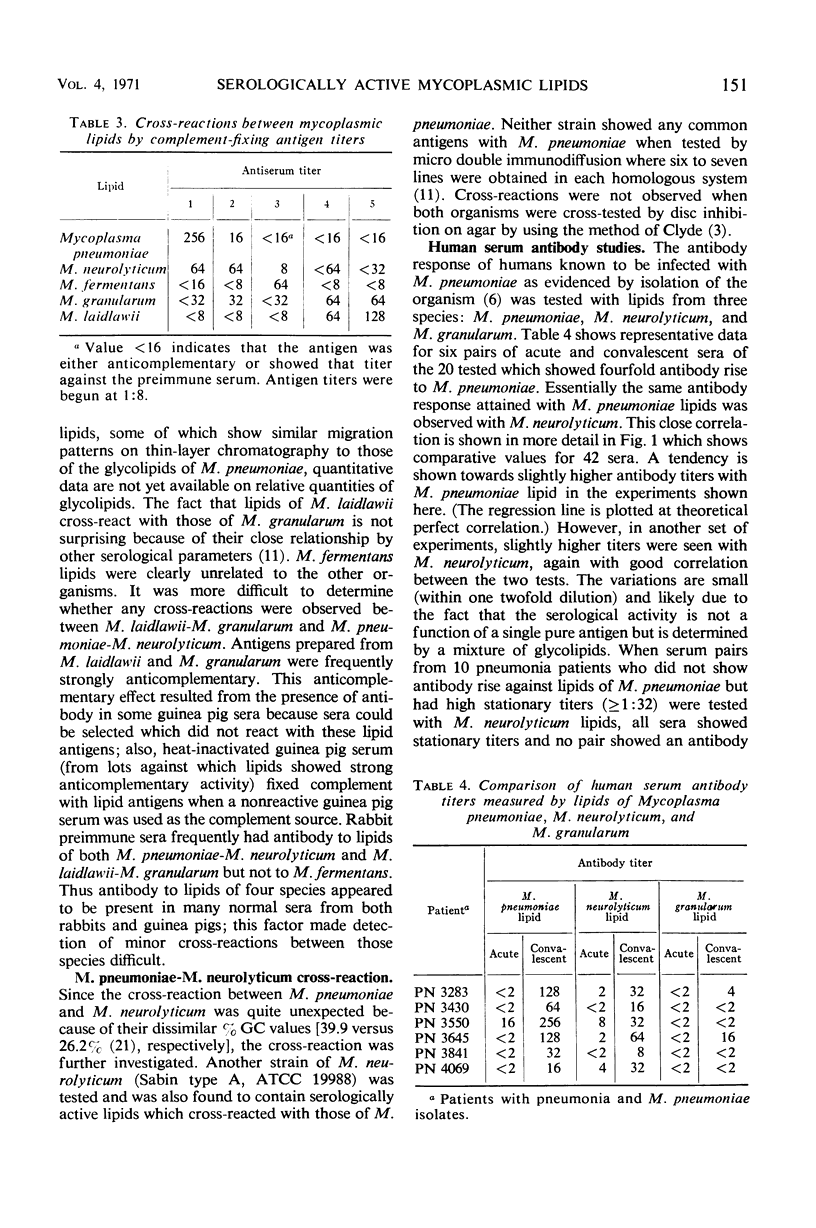
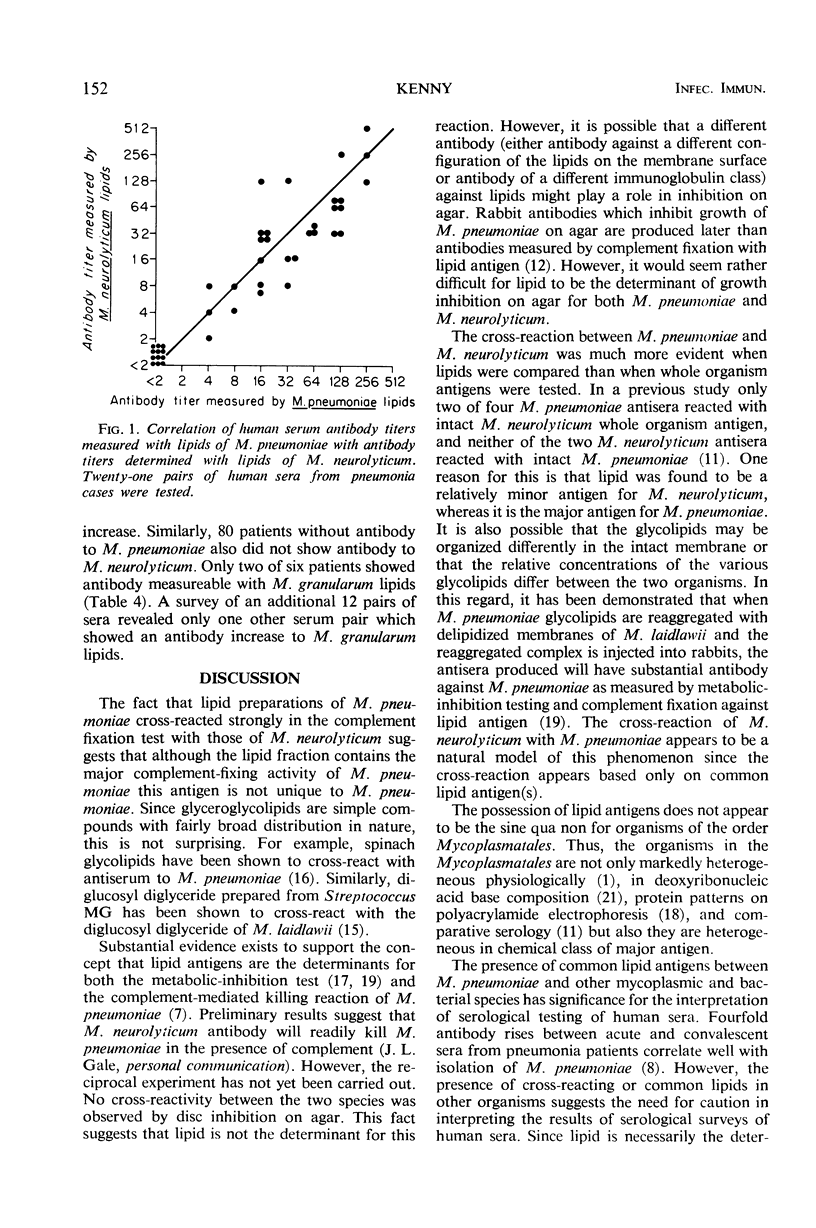
The complement-fixing activity of crude lipid extracts of 10 Mycoplasma species was compared with that of whole organism antigens employing immune rabbit serum. Five species (M. pneumoniae, M. neurolyticum, M. granularum, M. laidlawii, and M. fermentans) showed serological activity, whereas the remaining five species (M. canis, M. felis, M. gallisepticum, M. hyorhinis, and M. pulmonis) did not show significant activity in their lipid fractions. The lipid fractions of the five species which had serological activity in their lipid fractions showed three groups of serological specificity. M. pneumoniae cross-reacted with M. neurolyticum, M. granularum cross-reacted with M. laidlawii, and M. fermentans showed specific activity. Acute and convalescent sera from human pneumonia patients from whom M. pneumoniae had been isolated showed antibody increases which could be measured nearly as well by lipids of M. neurolyticum as by those of M. pneumoniae. Only a few human convalescent sera showed antibody measureable by lipids of M. granularum, M. pneumoniae did not cross-react with M. neurolyticum by other serological parameters such as growth inhibition on agar or double immunodiffusion, indicating that only the lipid antigens of these two species cross-react.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckman B. L., Kenny G. E. Immunochemical analysis of serologically active lipids of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1171–1180. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1171-1180.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYDE W. A., Jr MYCOPLASMA SPECIES IDENTIFICATION BASED UPON GROWTH INHIBITION BY SPECIFIC ANTISERA. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:958–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeb B. J., Kenny G. E. Characterizion of Mycoplasma pulmonis variants isolated from rabbits. II. Basis for differentiation of antigenic subtypes. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1425–1429. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1425-1429.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENNY G. E., GRAYSTON J. T. EATON PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISM (MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE) COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGEN: EXTRACTION WITH ORGANIC SOLVENTS. J Immunol. 1965 Jul;95:19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy H. M., Kenny G. E., McMahan R., Mansy A. M., Grayston J. T. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in an urban area. Five years of surveillance. JAMA. 1970 Nov 30;214(9):1666–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale J. L., Kenny G. E. Complement dependent killing of Mycoplasma pneumoniae by antibody: kinetics of the reaction. J Immunol. 1970 May;104(5):1175–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingdale M. R., Lemcke R. M. The antigens of Mycoplasma hominis. J Hyg (Lond) 1969 Dec;67(4):585–602. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400042042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Heat-lability and organic solvent-solubility of mycoplasma antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):676–681. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Immunogenicity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):510–515. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.510-515.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Serological comparison of ten glycolytic Mycoplasma species. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1044–1055. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1044-1055.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmion B. P., Plackett P., Lemcke R. M. Immunochemical analysis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. 1. Methods of extraction and reaction of fractions from M. pneumoniae and from M. mycoides with homologous antisera and with antisera against Streptococcus MG. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1967 Apr;45(2):163–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plackett P., Marmion B. P., Shaw E. J., Lemcke R. M. Immunochemical analysis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. 3. Separation and chemical identification of serologically active lipids. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1969 Apr;47(2):171–195. doi: 10.1038/icb.1969.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plackett P., Shaw E. J. Glucolipids from Mycoplasma laidlawii and Streptococcus MG. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):61C–62C. doi: 10.1042/bj1040061c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. D., Somerson N. L., Senterfit L. B. Isolation, Characterization, and Immunogenicity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Membranes. Infect Immun. 1970 Sep;2(3):326–339. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.3.326-339.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Mycoplasma taxonomy studiedy electrophoresis of cell proteins. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):687–694. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.687-694.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Prescott B., Chanock R. M. Immunogenicity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae glycolipids: a novel approach to the production of antisera to membrane lipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):590–597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B. THE FILTRABLE MICROORGANISMS OF THE PLEUROPNEUMONIA GROUP. Bacteriol Rev. 1941 Mar;5(1):1–67. doi: 10.1128/br.5.1.1-67.1941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. O., Wittler R. G., Burris C. Deoxyribonucleic acid base compositions of selected mycoplasmas and L-phase variants. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):341–343. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.341-343.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


