Abstract
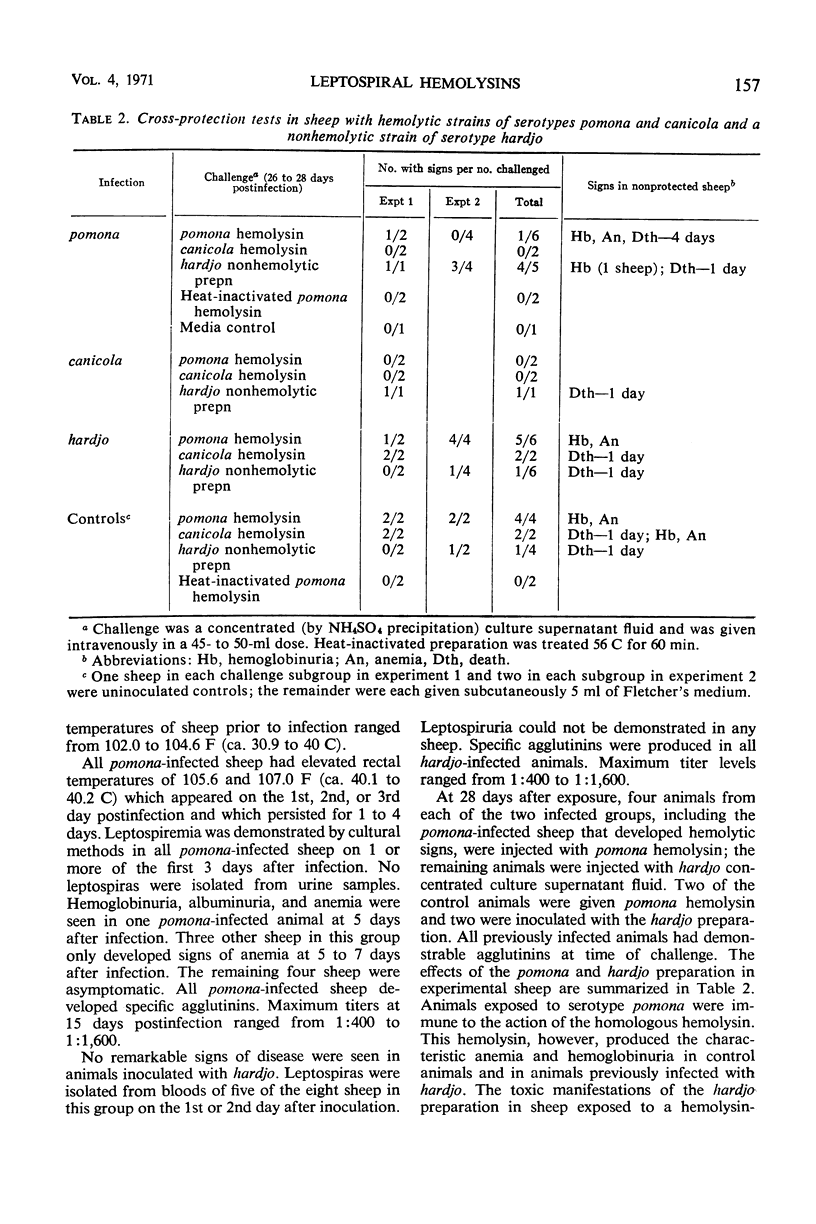
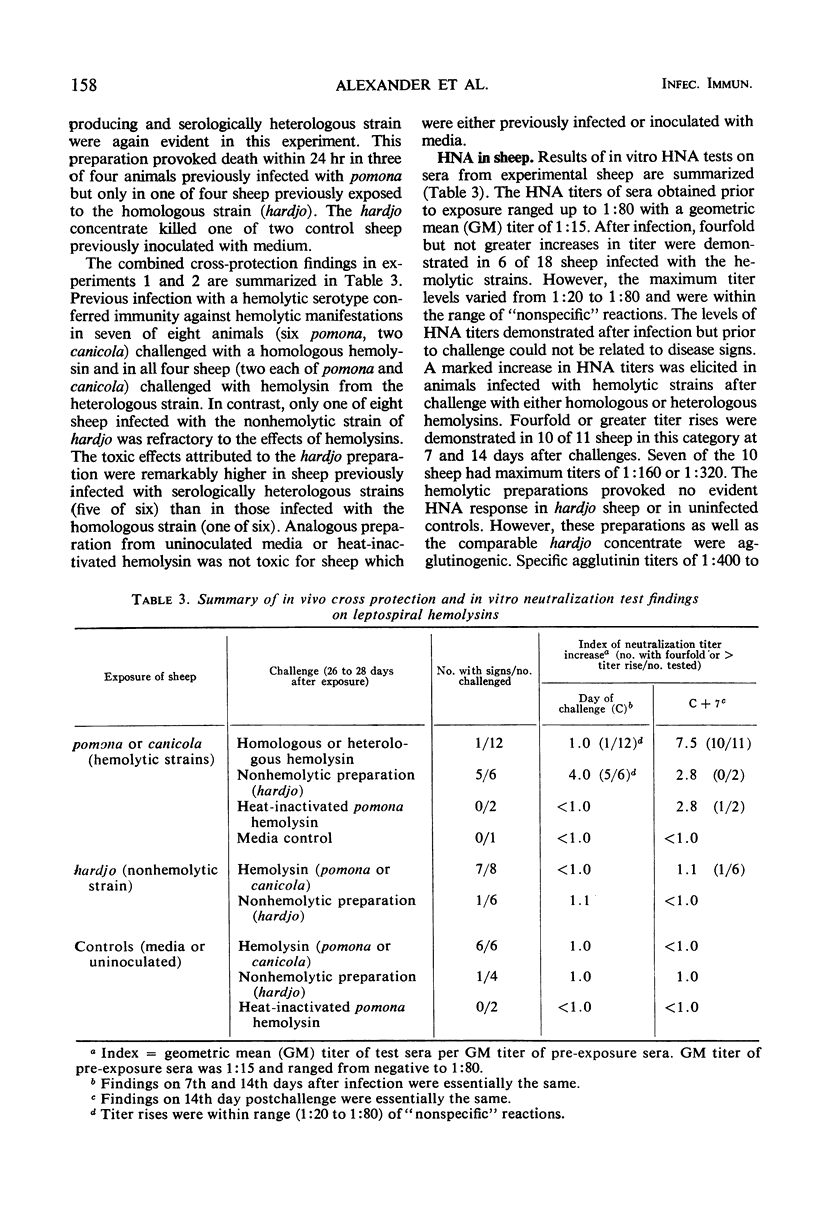
Cross-neutralization studies on leptospiral hemolysins from strains of two antigenically different serotypes, pomona and canicola, were conducted in sheep. A third strain of serotype hardjo that does not produce hemolysin and is antigenically distinct was included for control purposes. Concentrated hemolysins, prepared from supernatant fluids of canicola or pomona cultures, produced hemolytic anemia in sheep after intravenous injection. Sheep previously infected with hemolysin-producing strains were refractory to effects of homologous or heterologous hemolysins. On the other hand, infection with hardjo did not confer immunity to the action of hemolysins. Hemolysin-neutralizing antibodies were demonstrable in sheep previously infected with pomona or canicola only after challenge with homologous or heterologous hemolysins. Cross-neutralization between two hemolysins were demonstrable in vitro. Hemolysin-neutralizing antibody titers did not correlate with agglutinin titers. Concentrated supernatant fluid of the hardjo culture provoked toxic reactions predominantly in sheep previously infected with pomona or canicola. The causes of these untoward reactions were not determined.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER A. D., SMITH O. H., HIATT C. W., GLEISER C. A. Presence of hemolysin in cultures of pathogenic leptospires. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Feb;91(2):205–211. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haapala D. K., Rogul M., Evans L. B., Alexander A. D. Deoxyribonucleic acid base composition and homology studies of Leptospira. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):421–428. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.421-428.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAZAR J., CHORVATH B. [Contribution to the study of the antigen structure of the hemolysin of Leptospira]. Cesk Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 1962 Nov;11:353–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEMENES F. (CROSS-IMMUNITY STUDIES ON VIRULENT STRAINS OF LEPTOSPIRES BELONGING TO DIFFERENT SEROTYPES.) Z Immunitats Allergieforsch. 1964 Aug;127:209–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plesko I., Lataste-Dorolle C. Intertype immunity relations of Leptospira strains belonging to the "Australis" serogroup. Biologia (Bratisl) 1970;25(6):403–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH E. E., GALTON M. M. Isolation and identification of Leptospira hardjo from cattle in Louisiana. Am J Vet Res. 1960 May;21:422–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSELL C. M. A hemolysin associated with leptospirae. J Immunol. 1956 Dec;77(6):405–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH R. E., REYNOLDS I. M., SAKAI T. Experimental leptospirosis in pregnant ewes. I. Clinical, bacteriological and serological features. Cornell Vet. 1960 Jan;50:34–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



