Abstract
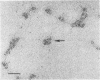
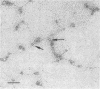
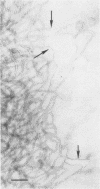
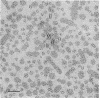
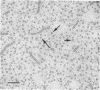
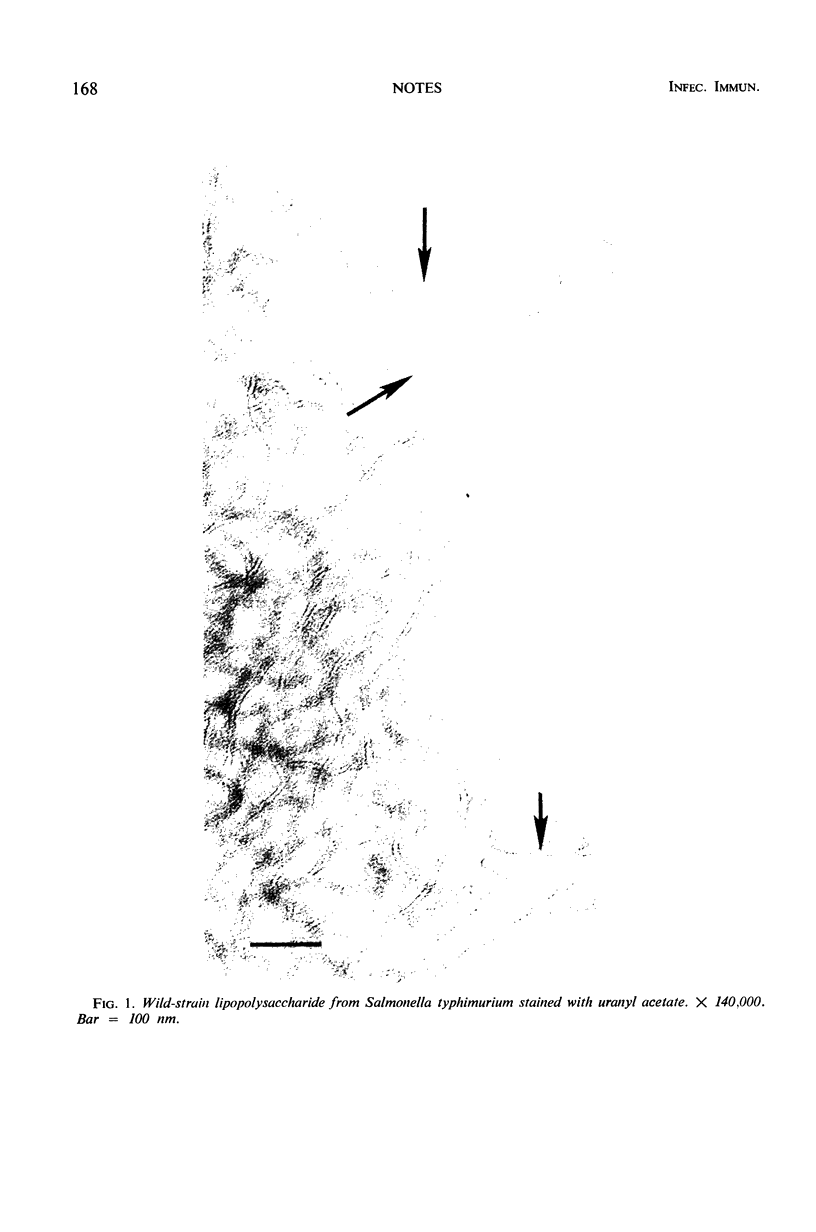
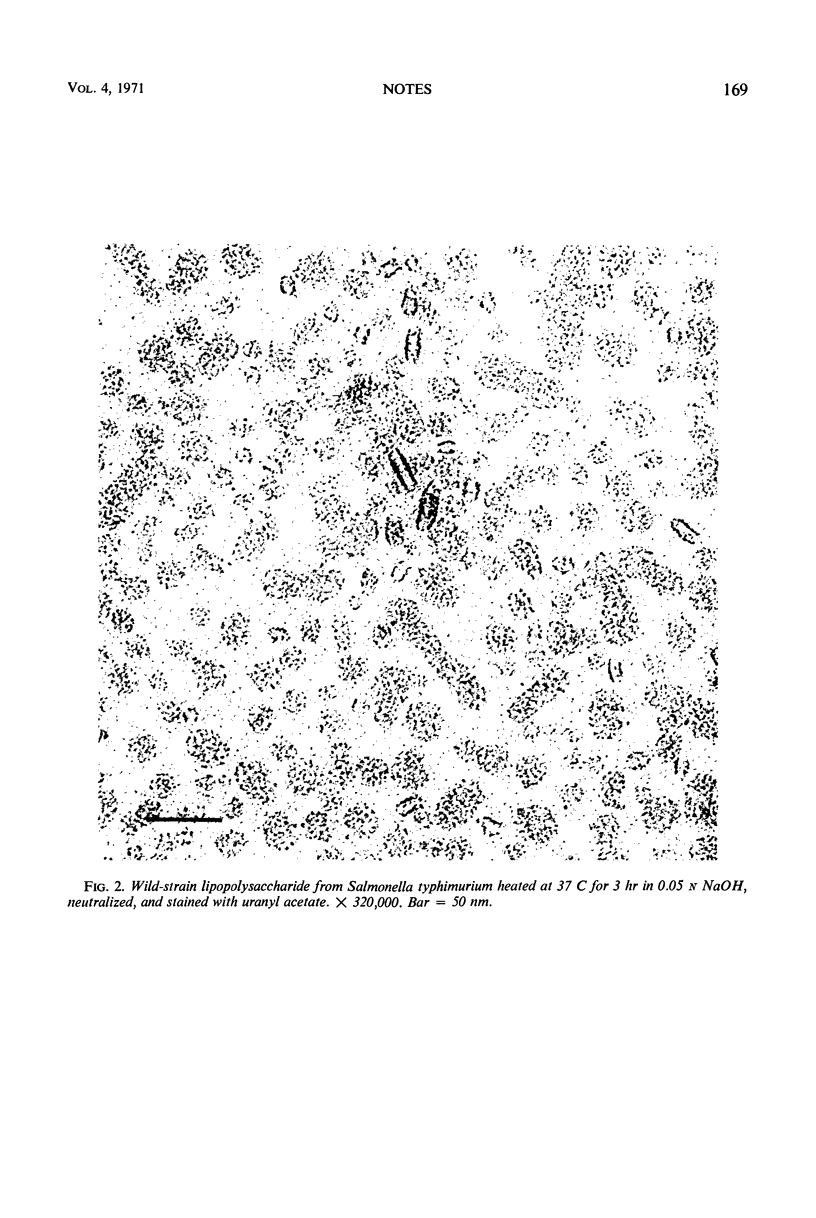
Additional evidence for a bilayer structure in isolated gram-negative lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is demonstrated. Both heating in an electron beam and cleavage of ester-bound fatty acids by alkali were found to split the bilayer structure of LPS into apparent monolayers. The altered structure of LPS resulting from alkaline hydrolysis may explain some of the altered biological activities possessed by the hydrolyzed product.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gimber P. E., Rafter G. W. The interaction of Escherichia coli endotoxin with leukocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Dec;135(1):14–20. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90510-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. A., Harris D. L., Green D. E. Effect of Bordetella endotoxin upon mitochondrial respiration and energized processes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Oct;128(1):219–230. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämmerling U., Westphal O. Synthesis and use of O-stearoyl polysaccharides in passive hemagglutination and hemolysis. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):46–50. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E., WESTPHAL O., LUDERITZ O. Effects of lecithin, cholesterol, and serum on erythrocyte modification and antibody neutralization by enterobacterial lipopolysaccharides. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Mar;88(3):339–341. doi: 10.3181/00379727-88-21582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E., WESTPHAL O., LUDERITZ O., GORZYNSKI E. A., EICHENBERGER E. Studies of enterobacterial lipopolysaccharides; effects of heat and chemicals on erythrocyte-modifying, antigenic, toxic and pyrogenic properties. J Immunol. 1956 May;76(5):377–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwa M., Milner K. C., Ribi E., Rudbach J. A. Alteration of physical, chemical, and biological properties of endotoxin by treatment with mild alkali. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1069–1077. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1069-1077.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble R. E., Koch-Weser D. In vitro inhibition of leukocyte uptake of radioactive endotoxin by components of normal serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Feb;121(2):541–545. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W., Jr, Graham J. A., Nath K. The morphologic structure of isolated bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarnes R. C. Host defense against bacterial endotoxemia: mechanism in normal animals. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):300–316. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarnes R. C. The inactivation of endotoxin after interaction with certain proteins of normal serum. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):644–662. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenney S. R., Rafter G. W. Leukocyte adenosine triphosphatases and the effect of endotoxin on their activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90558-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripodi D., Nowotny A. Relation of structure to function in bacterial O-antigens. V. Nature of active sites in endotoxic lipopolysaccharides of Serratia marcescens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):604–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]