Abstract
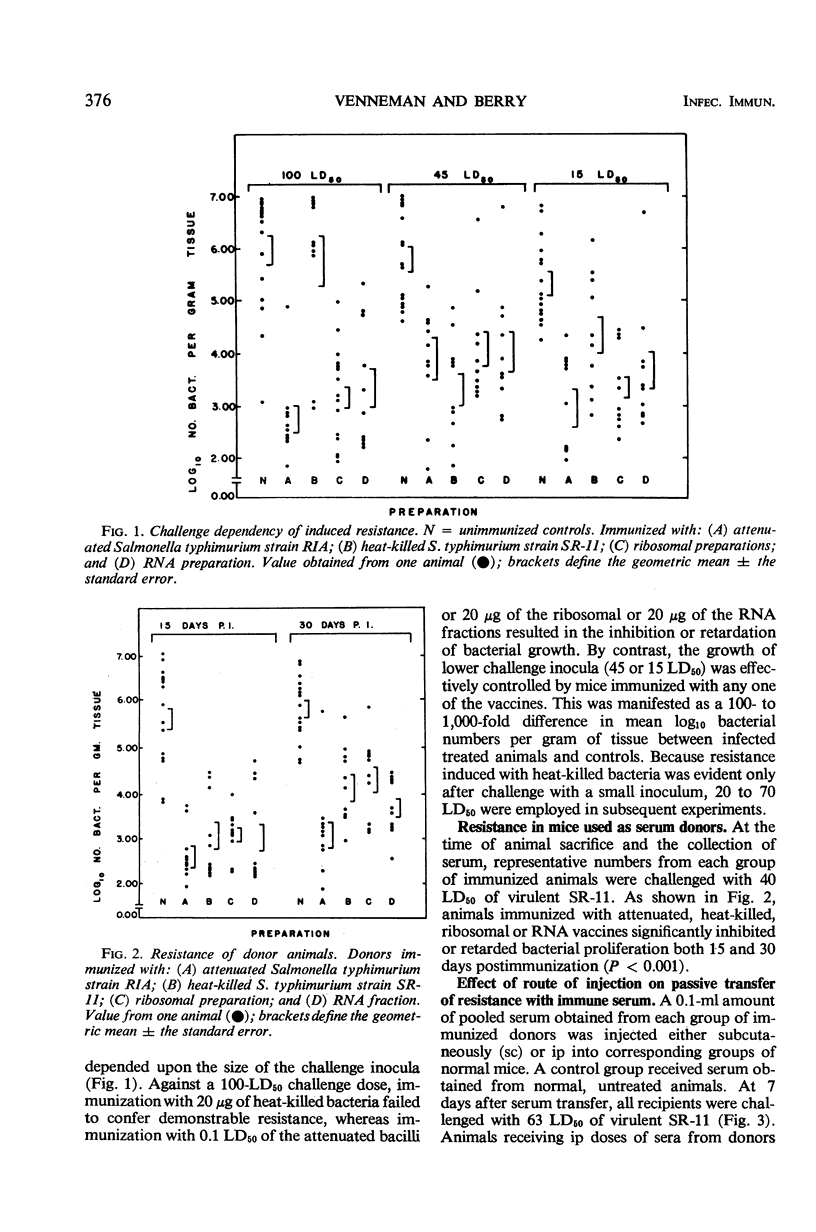
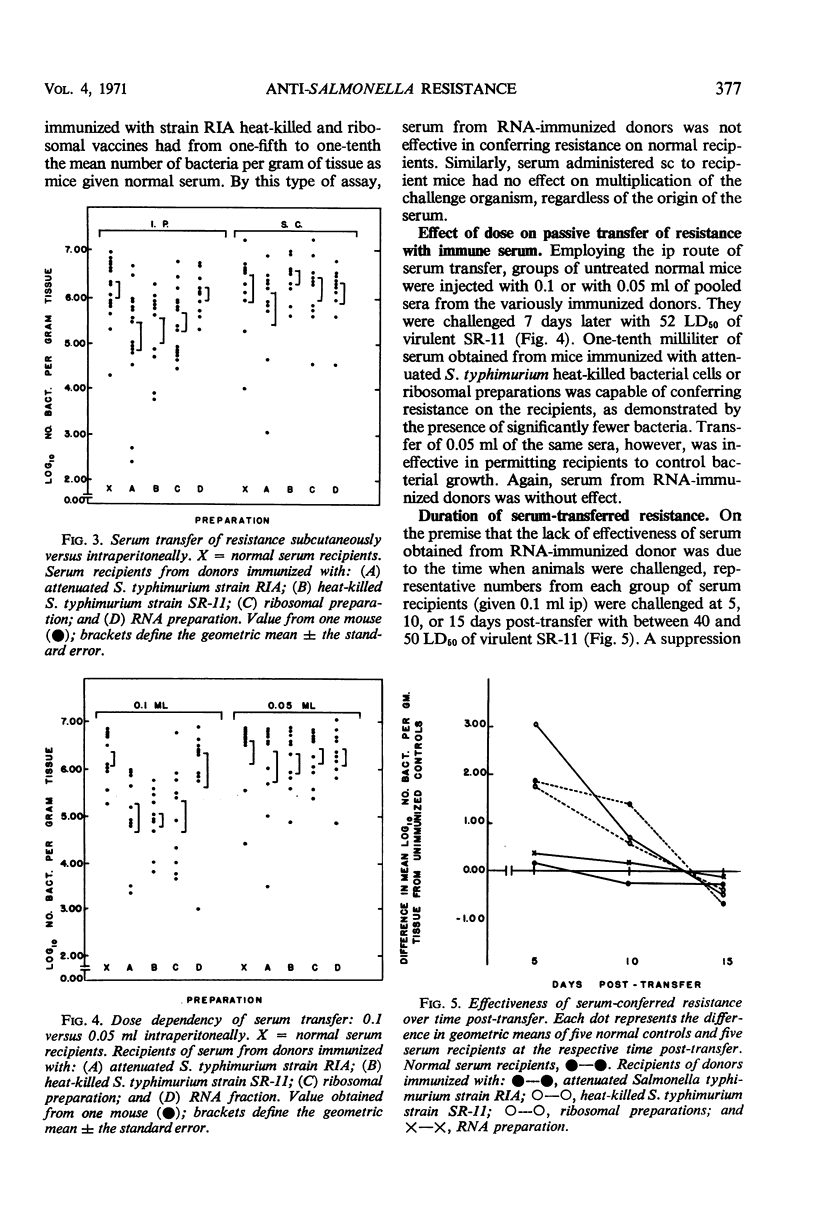
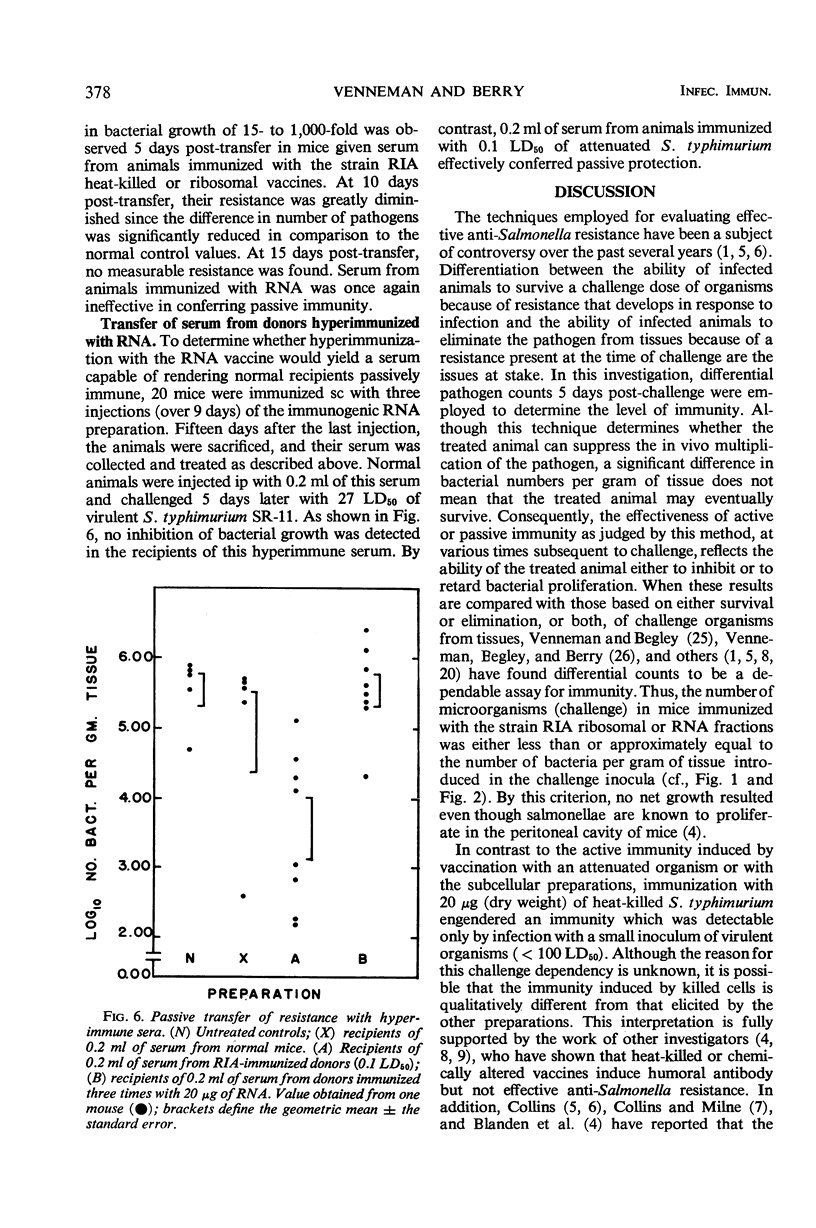
Serum obtained from animals immunized with attenuated Salmonella typhimurium strain RIA, heat-killed bacterial suspensions, or immunogenic ribosomal preparations was capable of passively conferring protection on normal recipient mice to challenge infection with virulent S. typhimurium strain SR-11. Protection was measured by the ability of a recipient animal to reduce the total number of challenge organisms significantly below that found in challenged control mice. Intraperitoneal administration of 0.1 ml of pooled sera was more effective than 0.05 ml in transferring resistance. The transfer of equivalent amounts of immune serum subcutaneously did not result in demonstrable resistance. In all cases in which serum transfer was effective, resistance was maximal at 5 days, greatly diminished by 10 days, and gone by 15 days post-transfer. Pooled serum obtained from normal donor mice or 0.2 ml of serum from mice hyperimmunized with immunogenic ribonucleic acid preparations did not possess the capacity to confer demonstrable resistance on normal recipients.
Full text
PDF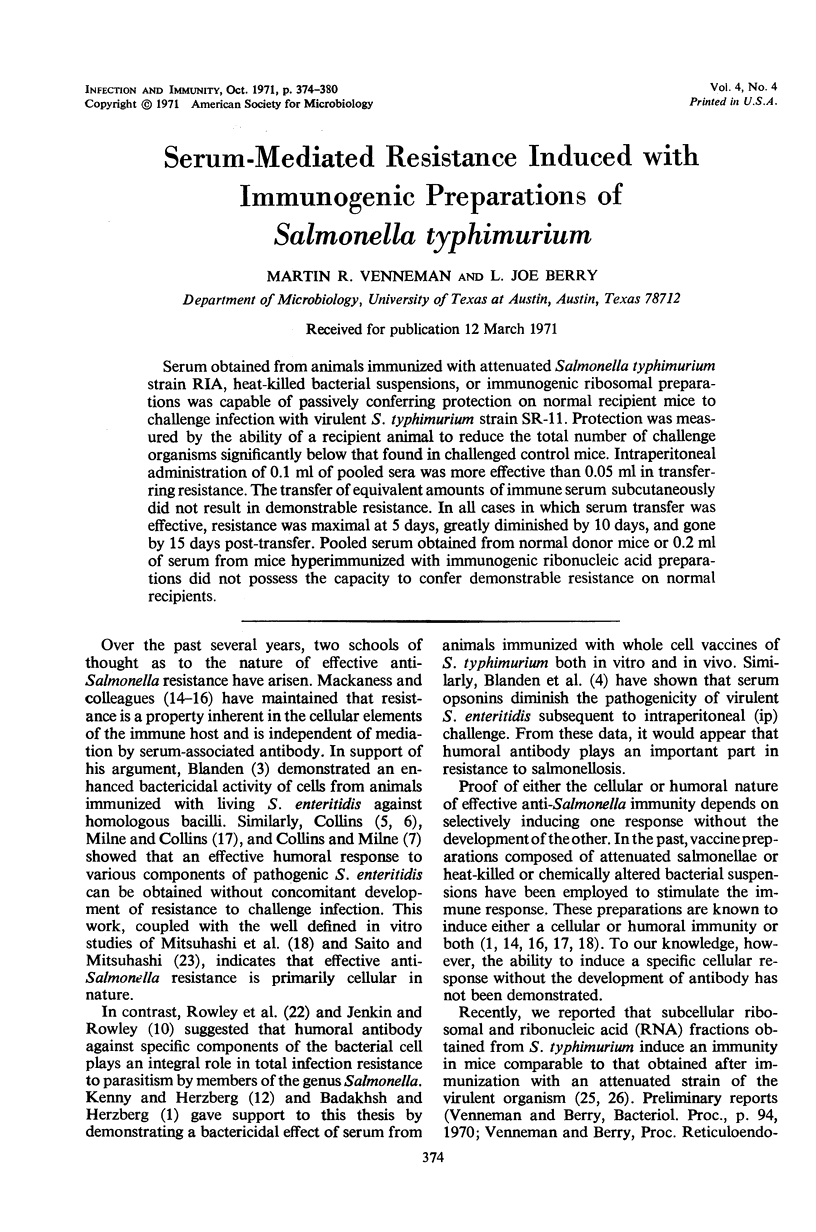



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badakhsh F. F., Herzberg M. Deoxycholate-treated, nontoxic, whole-cell vaccine protective against experimental salmonellosis of mice. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):738–744. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.738-744.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Mackaness G. B., Collins F. M. Mechanisms of acquired resistance in mouse typhoid. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):585–600. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V. Modification of macrophage function. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1968 Jun;5(3):179–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Effect of specific immune mouse serum on the growth of Salmonella enteritidis in mice preimmunized with living or ethyl alcohol-killed vaccines. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):676–683. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.676-683.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Effect of specific immune mouse serum on the growth of Salmonella enteritidis in nonvaccinated mice challenged by various routes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):667–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.667-675.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Milne M. Heat-labile antigens of Salmonella enteritidis. II. Mouse-protection studies. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):549–557. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.549-557.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDEBO L., HOLME T. PREPARATION OF BIOLOGICALLY ACTIVE FRACTIONS OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. 3. EXTRACTION OF IMMUNOGENIC COMPONENTS. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;63:228–234. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.63.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBSON D. Resistance to reinfection in experimental mouse typhoid. J Hyg (Lond) 1957 Sep;55(3):334–343. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400037244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKIN C. R., ROWLEY D. BASIS FOR IMMUNITY TO TYPHOID IN MICE AND THE QUESTION OF "CELLULAR IMMUNITY". Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Dec;27:391–404. doi: 10.1128/br.27.4.391-404.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami M., Osawa N., Mitsuhashi S. Experimental salmonellosis. VII. Comparison of the immunizing effect of live vaccine and materials extracted from Salmonella enteritidis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1585–1589. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1585-1589.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny K., Herzberg M. Antibody response and protection induced by immunization with smooth and rough strains in experimental salmonellosis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):406–417. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.406-417.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny K., Herzberg M. Early antibody response in mice to either infection or immunization with Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):773–778. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.773-778.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. THE IMMUNOLOGICAL BASIS OF ACQUIRED CELLULAR RESISTANCE. J Exp Med. 1964 Jul 1;120:105–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITSUHASHI S., SATO I., TANAKA T. Experimental salmonellosis. Intracellular growth of Salmonella enteritidis ingested in mononuclear phagocytes of mice, and cellular basis of immunity. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jun;81:863–868. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.6.863-868.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V. Cellular immunity. Prog Allergy. 1967;11:89–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V., Collins F. M. Host-parasite relations in mouse typhoid. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):573–583. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne M., Collins F. M. Heat-labile antigens of Salmonella enteritidis. I. Extraction of antigens. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):543–548. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.543-548.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Previte J. J. Immunogenicity of irradiated Salmonella typhimurium cells and endotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2165–2170. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2165-2170.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D., Auzins I., Jenkin C. R. Further studies regarding the question of cellular immunity in mouse typhoid. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1968 Aug;46(4):447–463. doi: 10.1038/icb.1968.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito K., Mitsuhashi S. Experimental Salmonellosis VI. In Vitro Transfer of Cellular Immunity of Mouse Mononuclear Phagocytes. J Bacteriol. 1965 Sep;90(3):629–634. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.3.629-634.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Berry L. J. Cell-mediated resistance induced with immunogenic preparations of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):381–387. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.381-387.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Bigley N. J., Berry L. J. Immunogenicity of Ribonucleic Acid Preparations Obtained from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):574–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.574-582.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Bigley N. J. Isolation and partial characterization of an immunogenic moiety obtained from Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):140–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.140-148.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


