Abstract
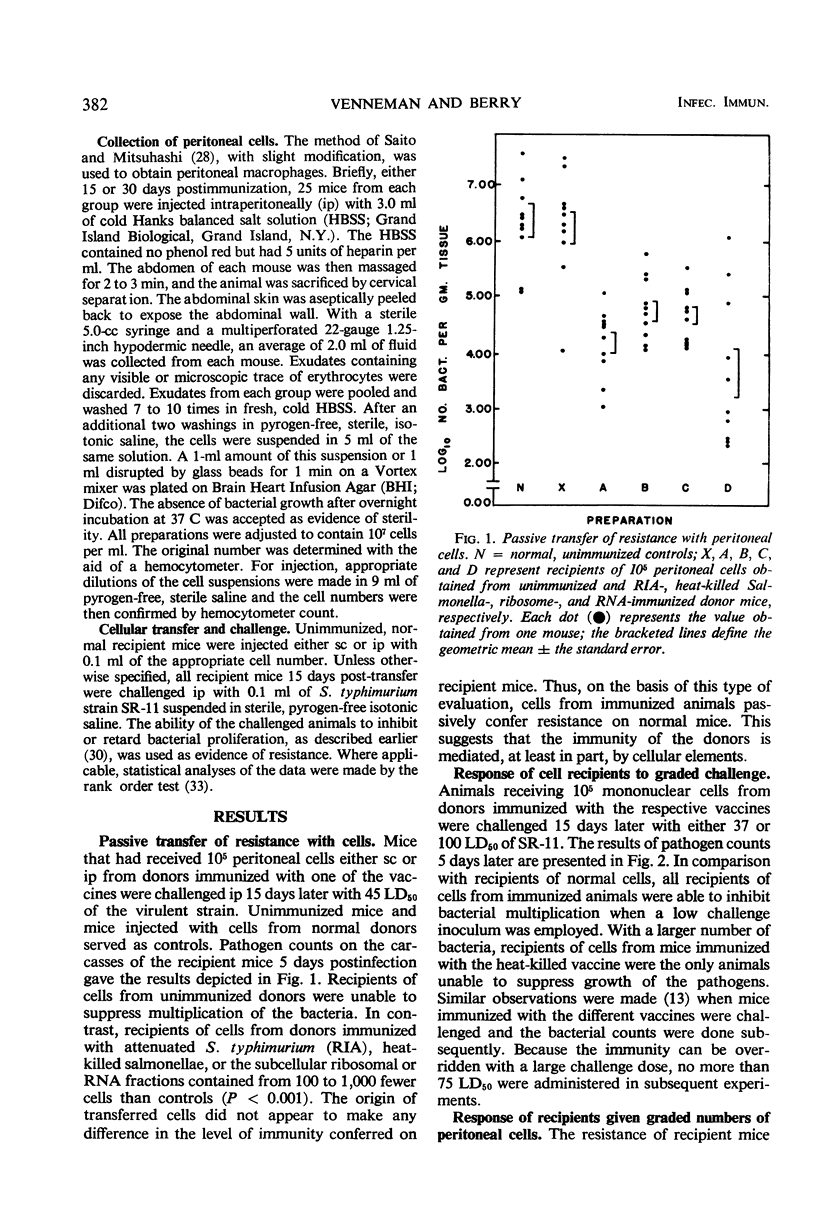
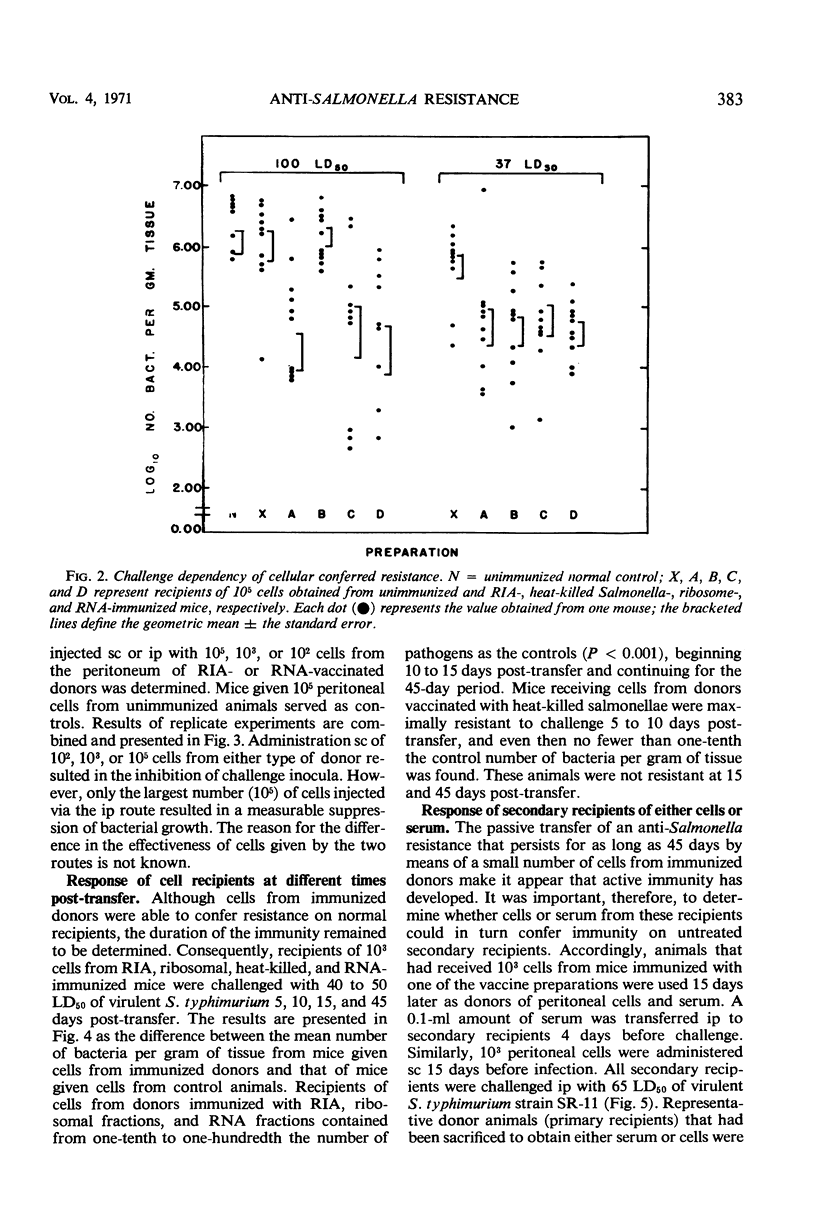
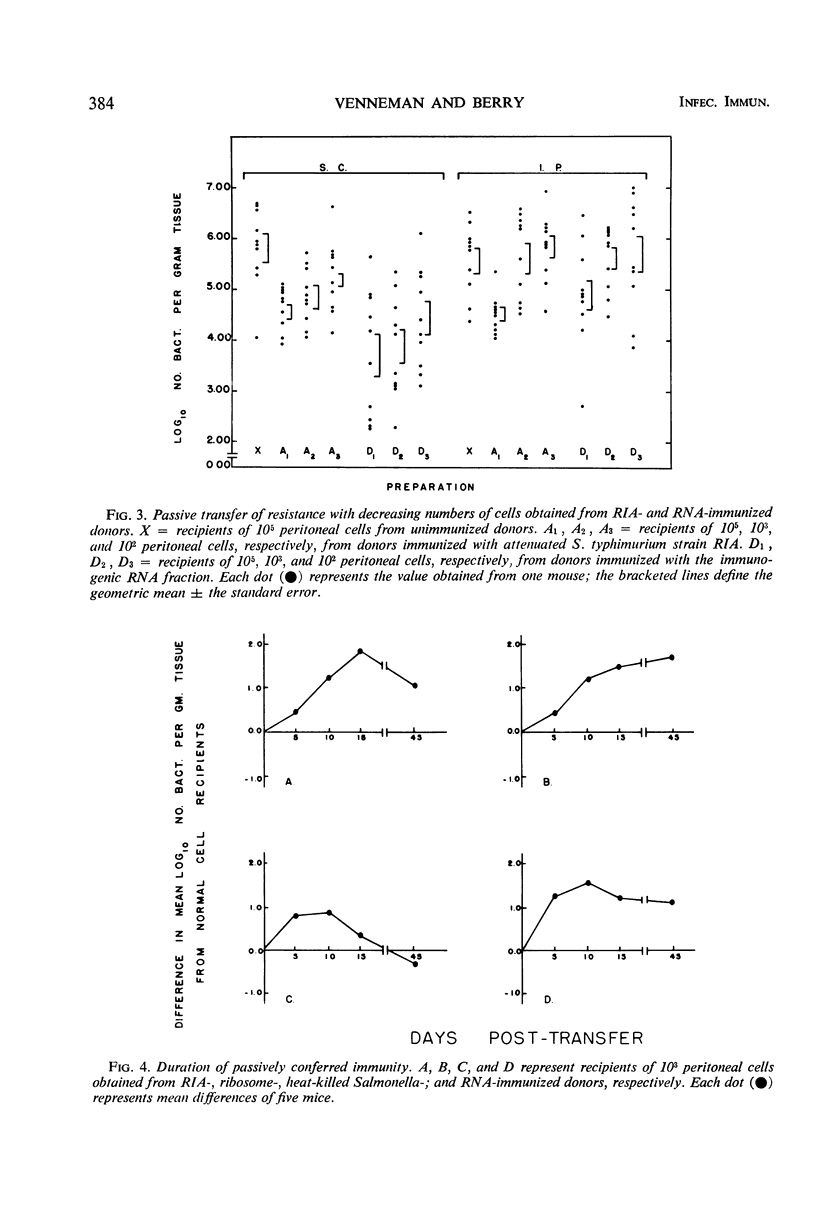
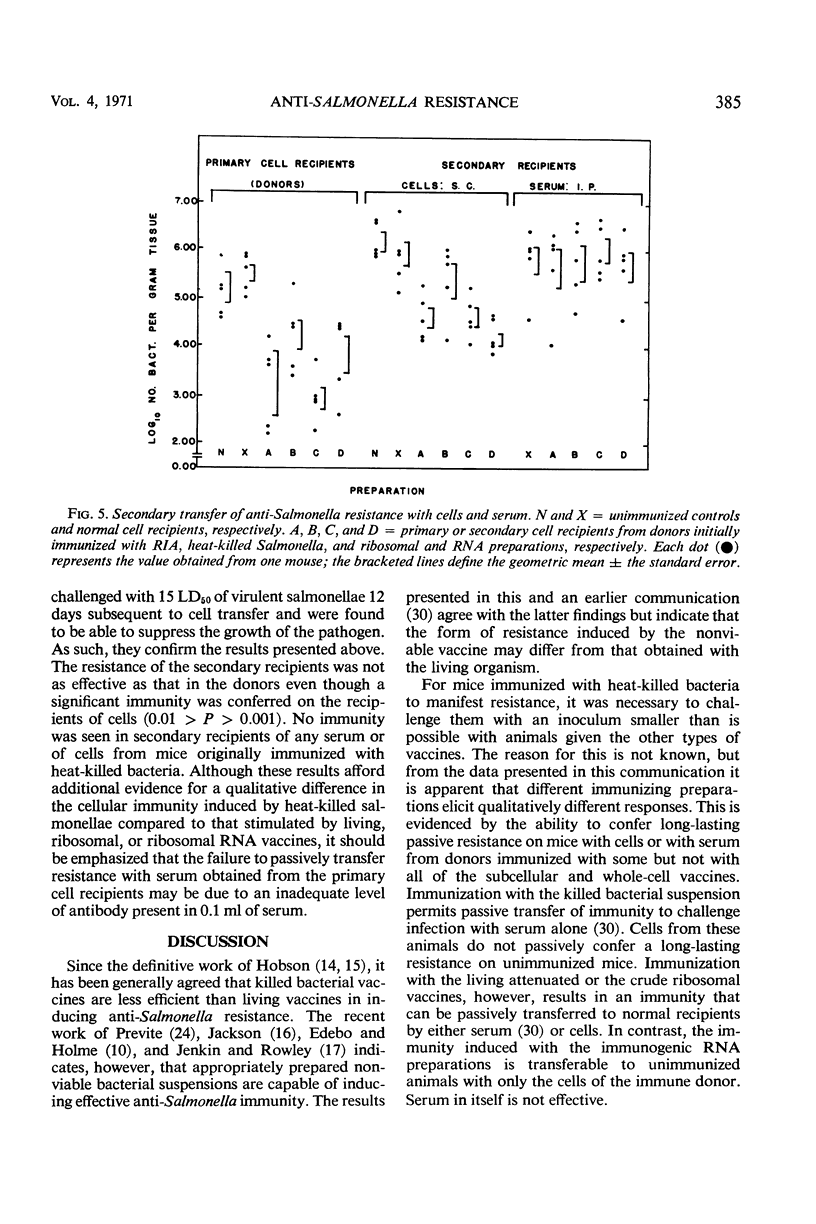
Peritoneal cells obtained from mice immunized 15 or 30 days previously with (i) 0.1 LD50 of attenuated Salmonella typhimurium (RIA), (ii) 20 μg (dry weight) of heat-killed Salmonella (SR-11), (iii) 20 μg (dry weight) of immunogenic ribosomal subfractions, or (iv) 20 μg of ribonucleic acid (RNA) subfractions were passively transferred to normal unimmunized mice. The ability of the recipient animals to inhibit or retard the multiplication of virulent challenge S. typhimurium 5 days post-infection was determined by pathogen counts on the carcasses. Peritoneal cells from donors immunized with the RIA, ribosomal, or RNA preparations (i) conferred maximal resistance to challenge 10 to 15 days after cell transfer and demonstrable resistance throughout the 45-day assay period, (ii) conferred resistance to infection when 105, 103, or 102 peritoneal cells were injected subcutaneously but not with fewer than 105 cells administered intraperitoneally, and (iii) rendered recipients capable of acting as donors of peritoneal cells that conferred demonstrable resistance on normal recipients. Recipients of peritoneal cells obtained from donors immunized with heat-killed bacteria were unable to (i) significantly inhibit bacterial proliferation at 10 days post-transfer, (ii) resist infection by a challenge inoculum greater than 50 LD50, and (iii) secondarily confer resistance on normal animals through the passive transfer of cells or serum.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badakhsh F. F., Herzberg M. Deoxycholate-treated, nontoxic, whole-cell vaccine protective against experimental salmonellosis of mice. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):738–744. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.738-744.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C., Dray S. Conversion of non-immune rabbit spleen cells by ribonucleic acid of lymphoid cells from an immunized rabbit to produce IgG antibody of foreign light chain allotype. J Immunol. 1970 Sep;105(3):541–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Mackaness G. B., Collins F. M. Mechanisms of acquired resistance in mouse typhoid. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):585–600. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cluff L. E. Effects of endotoxins on susceptibility to infections. J Infect Dis. 1970 Sep;122(3):205–215. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.3.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Effect of specific immune mouse serum on the growth of Salmonella enteritidis in nonvaccinated mice challenged by various routes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):667–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.667-675.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V. Infection-immunity in experimental salmonellosis. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):601–619. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Milne M. Heat-labile antigens of Salmonella enteritidis. II. Mouse-protection studies. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):549–557. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.549-557.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel S., Youmans G. P. Specificity of acquired resistance produced by immunization with mycobacterial cells and mycobacterial fractions. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):114–120. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.114-120.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel S., Youmans G. P. Specificity of the anamnestic response produced by Listeria monocytogenes or Mycobacterium tuberculosis to challenge with Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):127–133. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.127-133.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDEBO L., HOLME T. PREPARATION OF BIOLOGICALLY ACTIVE FRACTIONS OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. 3. EXTRACTION OF IMMUNOGENIC COMPONENTS. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;63:228–234. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.63.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHMAN M. Antibody formation in vitro. J Exp Med. 1961 Dec 1;114:837–856. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.6.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREI P. C., BENACERRAF B., THORBECKE G. J. PHAGOCYTOSIS OF THE ANTIGEN, A CRUCIAL STEP IN THE INDUCTION OF THE PRIMARY RESPONSE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jan;53:20–23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finger H., Beneke G., Fresenius H. Cellular kinetics of 19S and 7S hemolysin production in mice under the influence of bacterial endotoxins. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1970;35(5):324–337. doi: 10.1159/000162243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBSON D. Resistance to reinfection in experimental mouse typhoid. J Hyg (Lond) 1957 Sep;55(3):334–343. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400037244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBSON D. The behaviour of a mutant strain of Salmonella typhimurium in experimental mouse typhoid. J Hyg (Lond) 1957 Sep;55(3):322–333. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400037232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKIN C. R., ROWLEY D. PARTIAL PURIFICATION OF THE "PROTECTIVE" ANTIGEN OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM AND ITS DISTRIBUTION AMONGST VARIOUS STRAINS OF BACTERIA. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1965 Feb;43:65–78. doi: 10.1038/icb.1965.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. L. Immunogenicity of deoxycholate-disrupted endotoxins. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):13–15. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.13-15.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami M., Osawa N., Mitsuhashi S. Experimental salmonellosis. VII. Comparison of the immunizing effect of live vaccine and materials extracted from Salmonella enteritidis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1585–1589. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1585-1589.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny K., Herzberg M. Antibody response and protection induced by immunization with smooth and rough strains in experimental salmonellosis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):406–417. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.406-417.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny K., Herzberg M. Early antibody response in mice to either infection or immunization with Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):773–778. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.773-778.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurashige S., Osawa N., Kawakami M., Mitsuhashi S. Experimental salmonellosis. X. Cellular immunity and its antibody in mouse mononuclear phagocytes. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):902–906. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.902-906.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V. Cellular immunity. Prog Allergy. 1967;11:89–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa N., Kawakami M., Kurashige S., Mitsuhashi S. Experimental salmonellosis. 8. Postinfective immunity and its significance for conferring cellular immunity. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1534–1540. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1534-1540.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Previte J. J. Immunogenicity of irradiated Salmonella typhimurium cells and endotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2165–2170. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2165-2170.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLEY D., TURNER K. J., JENKIN C. R. THE BASIS FOR IMMUNITY TO MOUSE TYPHOID. 3. CELL-BOUND ANTIBODY. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1964 Apr;42:237–248. doi: 10.1038/icb.1964.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramming K. P., Pilch Y. H. Transfer of tumor-specific immunity with RNA: demonstration by immune cytolysis of tumor cells in vitro. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Sep;45(3):543–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO K., NAKANO M., AKIYAMA T., USHIBA D. Passive transfer of immunity to typhoid by macrophages. J Bacteriol. 1962 Sep;84:500–507. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.3.500-507.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito K., Mitsuhashi S. Experimental Salmonellosis VI. In Vitro Transfer of Cellular Immunity of Mouse Mononuclear Phagocytes. J Bacteriol. 1965 Sep;90(3):629–634. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.3.629-634.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato I., Mitsuhashi S. Experimental salmonellosis. VII. In vitro transfer of cellular immunity by ribosomal fraction of mouse mononuclear phagocytes. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1194–1199. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1194-1199.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Berry L. J. Serum-mediated resistance induced with immunogenic preparations of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):374–380. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.374-380.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Bigley N. J., Berry L. J. Immunogenicity of Ribonucleic Acid Preparations Obtained from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):574–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.574-582.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Bigley N. J. Isolation and partial characterization of an immunogenic moiety obtained from Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):140–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.140-148.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS A. S., YOUMANS G. P. IMMUNOGENIC ACTIVITY OF A RIBOSOMAL FRACTION OBTAINED FROM MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1291–1298. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1291-1298.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Effect of trypsin and ribonuclease on the immunogenic activity of ribosomes and ribonucleic acid isolated from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2146–2154. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2146-2154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Preparation of highly immunogenic ribosomal fractions of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by use of sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2139–2145. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2139-2145.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


