Abstract
Certain Staphylococcus aureus strains of phage group 2 produced a protein distinct from the alpha and delta toxins which was capable of causing generalized exfoliation in neonatal mice and presumably is responsible for the scalded-skin syndrome in humans. This protein, named “exfoliatin,” was purified and found to have a molecular weight of approximately 24,000. Exfoliatin was acid-labile, rather heat-stabile, and antigenic.
Full text
PDF
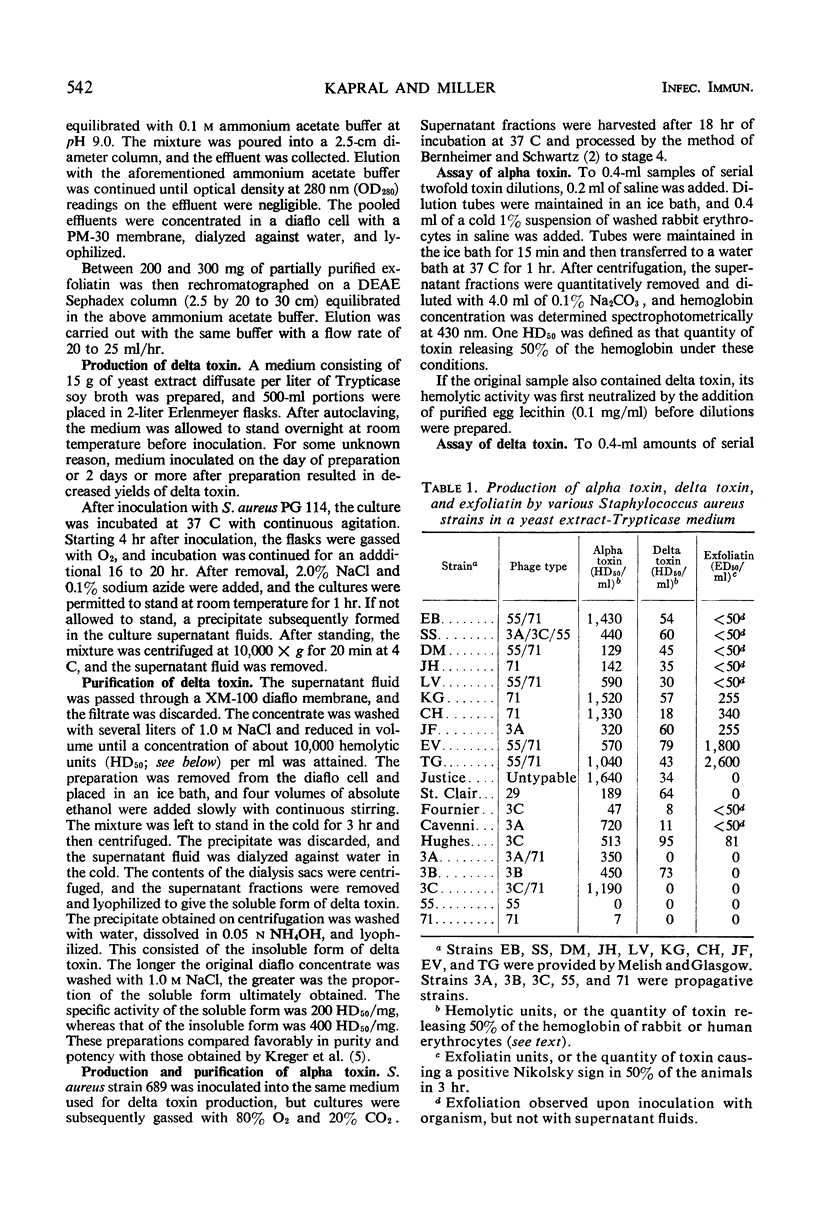
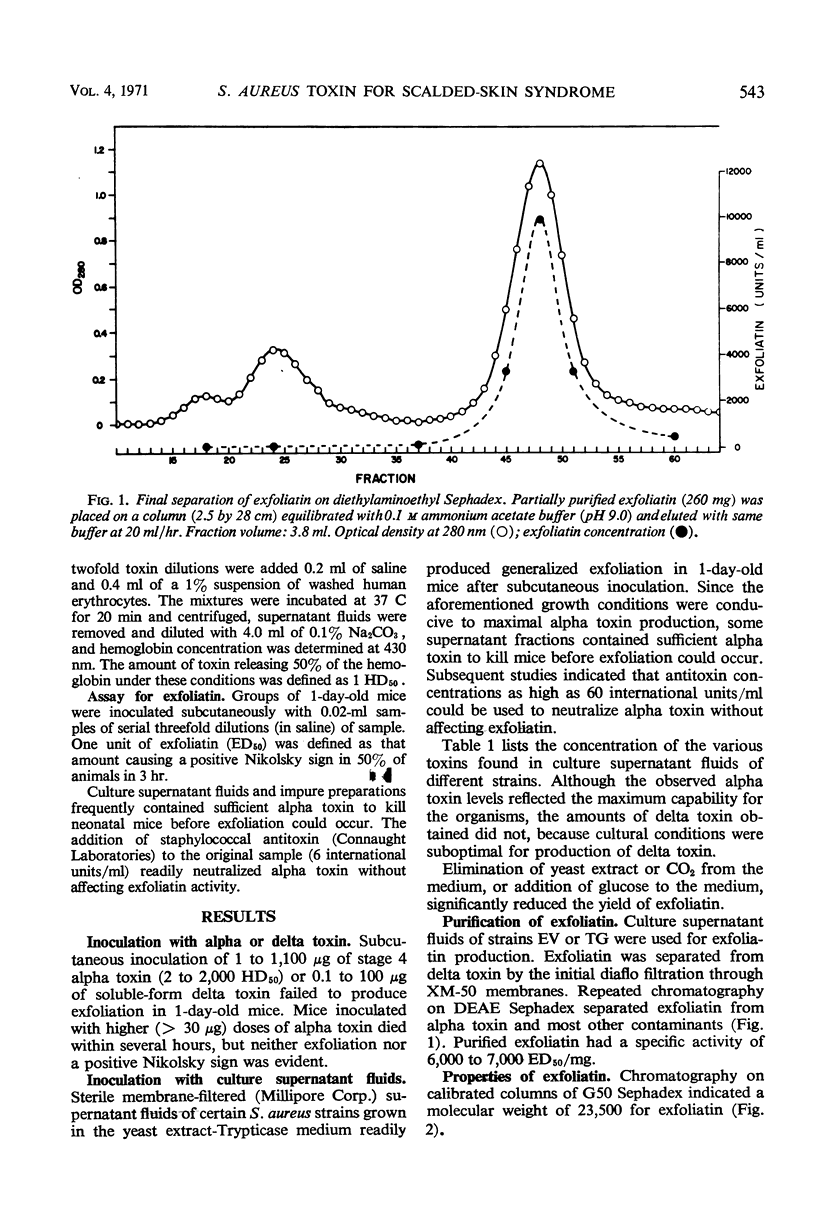

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. Isolation and composition of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:455–468. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNNET W. N., SCHALLIBAUM E. M. Scarlet-fever-like illness due to staphylococcal infection. Lancet. 1960 Dec 3;2(7162):1227–1229. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)92418-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S., Kim K. S., Zaboretzky F., Bernheimer A. W. Purification and properties of staphylococcal delta hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1971 Mar;3(3):449–465. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.3.449-465.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowney E. D., Baublis J. V., Kreye G. M., Harrell E. R., McKenzie A. R. The scalded skin syndrome in small children. Arch Dermatol. 1967 Apr;95(4):359–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melish M. E., Glasgow L. A. The staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1970 May 14;282(20):1114–1119. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197005142822002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



