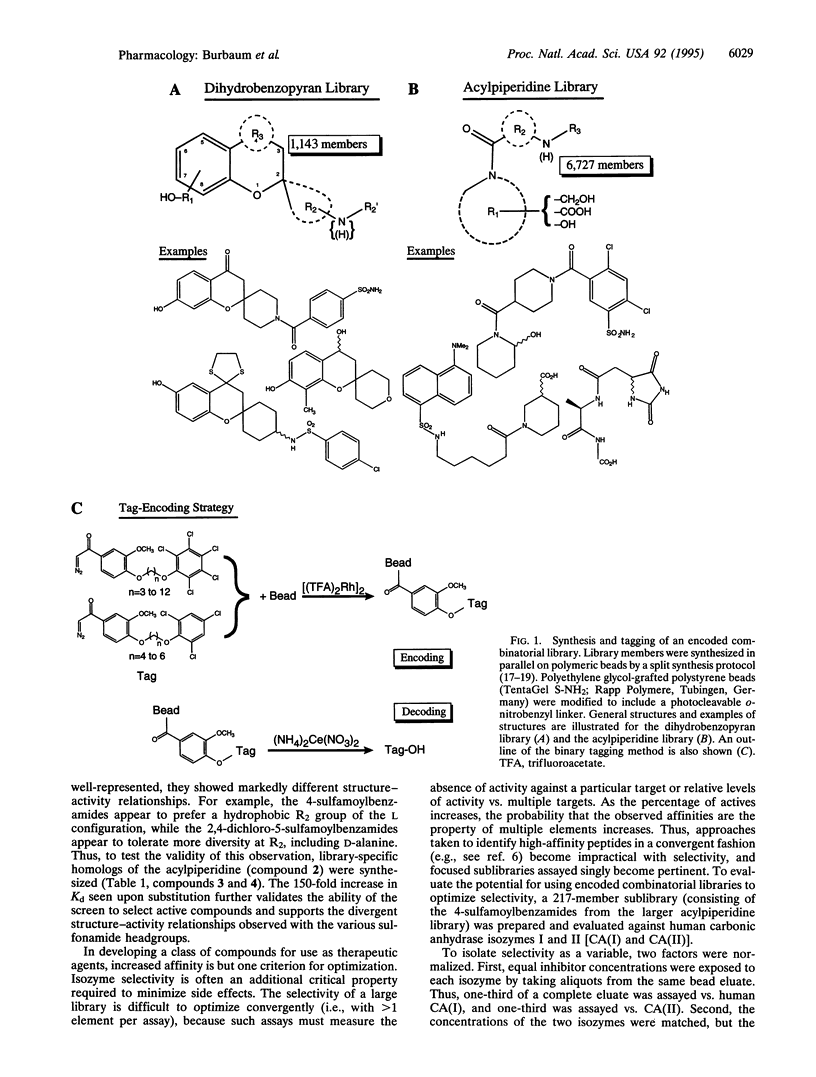
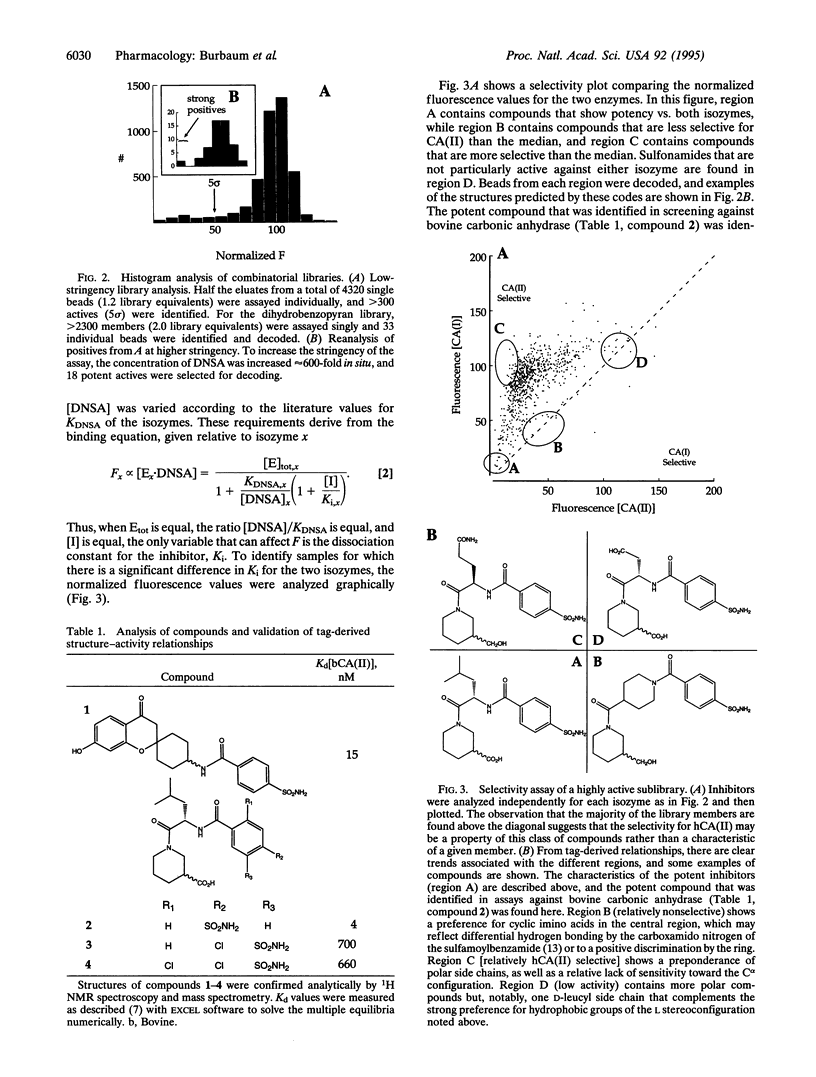
Abstract
Very large combinatorial libraries of small molecules on solid supports can now be synthesized and each library element can be identified after synthesis by using chemical tags. These tag-encoded libraries are potentially useful in drug discovery, and, to test this utility directly, we have targeted carbonic anhydrase (carbonate dehydratase; carbonate hydro-lyase, EC 4.2.1.1) as a model. Two libraries consisting of a total of 7870 members were synthesized, and structure-activity relationships based on the structures predicted by the tags were derived. Subsequently, an active representative of each library was resynthesized (2-[N-(4-sulfamoylbenzoyl)-4'-aminocyclohexanespiro]-4-oxo-7 -hydroxy- 2,3-dihydrobenzopyran and [N-(4-sulfamoylbenzoyl)-L-leucyl]piperidine-3-carboxylic acid) and these compounds were shown to have nanomolar dissociation constants (15 and 4 nM, respectively). In addition, a focused sublibrary of 217 sulfamoylbenzamides was synthesized and revealed a clear, testable structure-activity relationship describing isozyme-selective carbonic anhydrase inhibitors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eriksson A. E., Kylsten P. M., Jones T. A., Liljas A. Crystallographic studies of inhibitor binding sites in human carbonic anhydrase II: a pentacoordinated binding of the SCN- ion to the zinc at high pH. Proteins. 1988;4(4):283–293. doi: 10.1002/prot.340040407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furka A., Sebestyén F., Asgedom M., Dibó G. General method for rapid synthesis of multicomponent peptide mixtures. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1991 Jun;37(6):487–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1991.tb00765.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman G. D., Halczenko W., Smith R. L., Sugŕue M. F., Mallorga P. J., Michelson S. R., Randall W. C., Schwam H., Sondey J. M. 4-substituted thiophene- and furan-2-sulfonamides as topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 1992 Oct 16;35(21):3822–3831. doi: 10.1021/jm00099a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Pinilla C., Blondelle S. E., Appel J. R., Dooley C. T., Cuervo J. H. Generation and use of synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries for basic research and drug discovery. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):84–86. doi: 10.1038/354084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain A., Whitesides G. M., Alexander R. S., Christianson D. W. Identification of two hydrophobic patches in the active-site cavity of human carbonic anhydrase II by solution-phase and solid-state studies and their use in the development of tight-binding inhibitors. J Med Chem. 1994 Jun 24;37(13):2100–2105. doi: 10.1021/jm00039a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner M. W., Marincola E., Teisberg E. O. The role of biomedical research in health care reform. Science. 1994 Oct 7;266(5182):49–51. doi: 10.1126/science.7939643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K. S., Salmon S. E., Hersh E. M., Hruby V. J., Kazmierski W. M., Knapp R. J. A new type of synthetic peptide library for identifying ligand-binding activity. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):82–84. doi: 10.1038/354082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo Y. S., Nolan J. C., Maren T. H., Welstead W. J., Jr, Gripshover D. F., Shamblee D. A. Synthesis and physicochemical properties of sulfamate derivatives as topical antiglaucoma agents. J Med Chem. 1992 Dec 25;35(26):4790–4794. doi: 10.1021/jm00104a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NYMAN P., LINDSKOG S. AMINO ACID COMPOSITION OF VARIOUS FORMS OF BOVINE AND HUMAN ERYTHROCYTE CARBONIC ANHYDRASE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 6;85:141–151. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needels M. C., Jones D. G., Tate E. H., Heinkel G. L., Kochersperger L. M., Dower W. J., Barrett R. W., Gallop M. A. Generation and screening of an oligonucleotide-encoded synthetic peptide library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10700–10704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlmeyer M. H., Swanson R. N., Dillard L. W., Reader J. C., Asouline G., Kobayashi R., Wigler M., Still W. C. Complex synthetic chemical libraries indexed with molecular tags. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):10922–10926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.10922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponticello G. S., Freedman M. B., Habecker C. N., Lyle P. A., Schwam H., Varga S. L., Christy M. E., Randall W. C., Baldwin J. J. Thienothiopyran-2-sulfonamides: a novel class of water-soluble carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 1987 Apr;30(4):591–597. doi: 10.1021/jm00387a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. J., Kania R. S., Zuckermann R. N., Huebner V. D., Jewell D. A., Banville S., Ng S., Wang L., Rosenberg S., Marlowe C. K. Peptoids: a modular approach to drug discovery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9367–9371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. M., Alexander R. S., Christianson D. W., McKeever B. M., Ponticello G. S., Springer J. P., Randall W. C., Baldwin J. J., Habecker C. N. Positions of His-64 and a bound water in human carbonic anhydrase II upon binding three structurally related inhibitors. Protein Sci. 1994 Jan;3(1):118–125. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560030115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W., King R. W., Burgen A. S. Kinetics of complex formation between human carbonic anhydrases and aromatic sulfonamides. Biochemistry. 1970 Jun 23;9(13):2638–2645. doi: 10.1021/bi00815a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



