Abstract
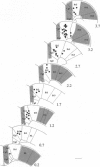
The functional influence of the frontal cortex (FC) on the noradrenergic nucleus locus coeruleus (LC) was studied in the rat under ketamine anesthesia. The FC was inactivated by local infusion of lidocaine or ice-cold Ringer's solution while recording neuronal activity simultaneously in FC and LC. Lidocaine produced a transient increase in activity in FC, accompanied by a decrease in LC unit and multiunit activity. This was followed by a total inactivation of FC and a sustained increase in firing rate of LC neurons. Subsequent experiments revealed antidromic responses in the FC when stimulation was applied to the LC region. The antidromic responses in FC were found in a population of neurons (about 8%) restricted to the dorsomedial area, FR2. The results indicate that there is a strong inhibitory influence of FC on the tonic activity of LC neurons. The antidromic responses in FC to stimulation of the LC region suggest that this influence is locally mediated, perhaps through interneurons within the nucleus or neighboring the LC.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnsten A. F., Goldman-Rakic P. S. Selective prefrontal cortical projections to the region of the locus coeruleus and raphe nuclei in the rhesus monkey. Brain Res. 1984 Jul 23;306(1-2):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90351-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aston-Jones G., Bloom F. E. Norepinephrine-containing locus coeruleus neurons in behaving rats exhibit pronounced responses to non-noxious environmental stimuli. J Neurosci. 1981 Aug;1(8):887–900. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-08-00887.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aston-Jones G., Ennis M., Pieribone V. A., Nickell W. T., Shipley M. T. The brain nucleus locus coeruleus: restricted afferent control of a broad efferent network. Science. 1986 Nov 7;234(4777):734–737. doi: 10.1126/science.3775363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aston-Jones G., Rajkowski J., Kubiak P., Alexinsky T. Locus coeruleus neurons in monkey are selectively activated by attended cues in a vigilance task. J Neurosci. 1994 Jul;14(7):4467–4480. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-07-04467.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedarbaum J. M., Aghajanian G. K. Activation of locus coeruleus neurons by peripheral stimuli: modulation by a collateral inhibitory mechanism. Life Sci. 1978 Oct 2;23(13):1383–1392. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90398-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl D., Winson J. Action of norepinephrine in the dentate gyrus. I. Stimulation of locus coeruleus. Exp Brain Res. 1985;59(3):491–496. doi: 10.1007/BF00261339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalsass M., Kiser S., Mèndershausen M., German D. C. Medial prefrontal cortical projections to the region of the dorsal periventricular catecholamine system. Neuroscience. 1981;6(4):657–665. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90149-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue J. P., Wise S. P. The motor cortex of the rat: cytoarchitecture and microstimulation mapping. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Nov 20;212(1):76–88. doi: 10.1002/cne.902120106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis M., Aston-Jones G. A potent excitatory input to the nucleus locus coeruleus from the ventrolateral medulla. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Nov 21;71(3):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90637-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote S. L., Bloom F. E., Aston-Jones G. Nucleus locus ceruleus: new evidence of anatomical and physiological specificity. Physiol Rev. 1983 Jul;63(3):844–914. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1983.63.3.844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funahashi S., Bruce C. J., Goldman-Rakic P. S. Mnemonic coding of visual space in the monkey's dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Feb;61(2):331–349. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.61.2.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs C. M., Prescott L. B., Powell D. A. A comparison of multiple-unit activity in the medial prefrontal and agranular insular cortices during Pavlovian heart rate conditioning in rabbits. Exp Brain Res. 1992;89(3):599–610. doi: 10.1007/BF00229885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. E. Noradrenergic locus coeruleus neurons: their distant connections and their relationship to neighboring (including cholinergic and GABAergic) neurons of the central gray and reticular formation. Prog Brain Res. 1991;88:15–30. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)63797-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb B. Functions of the frontal cortex of the rat: a comparative review. Brain Res. 1984 Nov;320(1):65–98. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(84)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luppi P. H., Aston-Jones G., Akaoka H., Chouvet G., Jouvet M. Afferent projections to the rat locus coeruleus demonstrated by retrograde and anterograde tracing with cholera-toxin B subunit and Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin. Neuroscience. 1995 Mar;65(1):119–160. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)00481-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. H. Autoradiographic estimation of the extent of reversible inactivation produced by microinjection of lidocaine and muscimol in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Jun 24;127(2):160–164. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90784-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirch J. H., Corbus M. J., Rigdon G. C. Single-unit and slow potential responses from rat frontal cortex during associative conditioning. Exp Neurol. 1983 Oct;82(1):118–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(83)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogawski M. A., Aghajanian G. K. Modulation of lateral geniculate neurone excitability by noradrenaline microiontophoresis or locus coeruleus stimulation. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):731–734. doi: 10.1038/287731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rucker H. K., Corbus M. J., Pirch J. H. Discriminative conditioning-related slow potential and single-unit responses in the frontal cortex of urethane-anesthetized rats. Brain Res. 1986 Jun 25;376(2):368–372. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90201-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sara S. J., Segal M. Plasticity of sensory responses of locus coeruleus neurons in the behaving rat: implications for cognition. Prog Brain Res. 1991;88:571–585. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)63835-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sara S. J., Vankov A., Hervé A. Locus coeruleus-evoked responses in behaving rats: a clue to the role of noradrenaline in memory. Brain Res Bull. 1994;35(5-6):457–465. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(94)90159-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sesack S. R., Deutch A. Y., Roth R. H., Bunney B. S. Topographical organization of the efferent projections of the medial prefrontal cortex in the rat: an anterograde tract-tracing study with Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Dec 8;290(2):213–242. doi: 10.1002/cne.902900205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton P. K., Sarvey J. M. Depletion of norepinephrine, but not serotonin, reduces long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus of rat hippocampal slices. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2169–2176. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02169.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Yamasaki M. Blocking of cortical inhibitory synapses by intravenous lidocaine. Nature. 1966 Jan 8;209(5019):207–208. doi: 10.1038/209207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterhouse B. D., Sessler F. M., Cheng J. T., Woodward D. J., Azizi S. A., Moises H. C. New evidence for a gating action of norepinephrine in central neuronal circuits of mammalian brain. Brain Res Bull. 1988 Sep;21(3):425–432. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(88)90154-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterhouse B. D., Woodward D. J. Interaction of norepinephrine with cerebrocortical activity evoked by stimulation of somatosensory afferent pathways in the rat. Exp Neurol. 1980 Jan;67(1):11–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(80)90159-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Ozawa N. Increased firing of locus coeruleus neurons associated with preparatory set in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Nov 20;106(1-2):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90211-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]